In cancer immunology research, the development and application of mouse models are crucial. As our understanding of the tumor microenvironment and immune response mechanisms deepens, researchers increasingly rely on customized mouse models to better simulate the complexity and heterogeneity of human cancers.
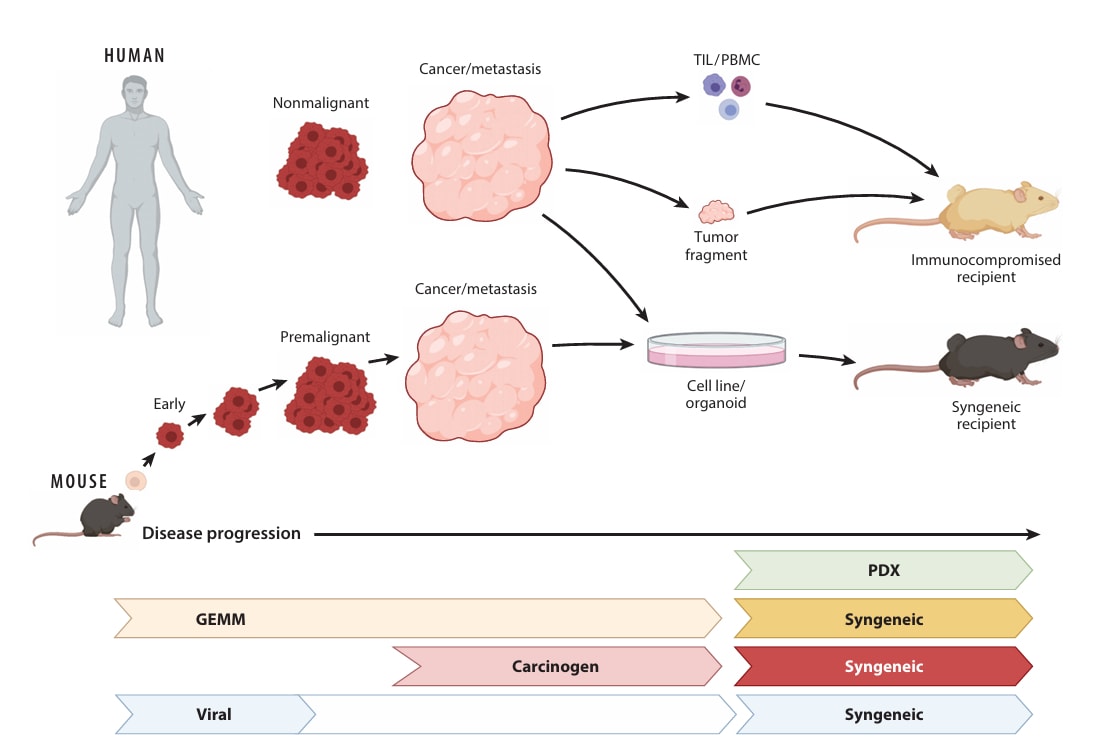 Fig. 1 The strengths of different mouse models in recapitulating various stages of cancer progression in humans.1
Fig. 1 The strengths of different mouse models in recapitulating various stages of cancer progression in humans.1
We will present two main approaches to custom animal model development:
Genetically engineered mouse models (GEMMs) are created using transgenic or knockout technologies aimed at studying TIL function and the interactions between tumors and the immune system. These models allow for precise manipulation of specific gene expressions, helping researchers gain insights into how tumors evade immune surveillance and how immune cells recognize and attack tumor cells.
For example, researchers can create transgenic mice that express specific tumor antigens to observe TIL responses and functions. This model provides real-time observations of the dynamic changes of immune cells within the tumor microenvironment, helping scientists identify key factors that influence immune responses. Additionally, knockout models can be used to study the role of specific genes in tumor initiation and progression, revealing mechanisms of tumor immune evasion.
The advantages of genetically engineered models lie in their high controllability and specificity, enabling researchers to simulate the biological characteristics of human cancers in an in vivo environment. However, these models also have certain limitations; for instance, some models may not fully replicate the complexity of human tumors, particularly regarding the diversity of the tumor microenvironment and the heterogeneity of immune cells.
With the rise of personalized medicine and precision healthcare, on-demand model creation services have emerged. These services offer customized mouse model development that can be designed and produced based on specific client requirements and research objectives. This flexibility allows researchers to quickly adapt to the ever-changing research needs, especially in the development of emerging cancer immunotherapies and personalized treatment plans.
The process of on-demand model creation typically involves close collaboration with clients to determine specific research goals and requirements. We will select appropriate gene editing technologies based on these requirements to create mouse models that fit your experimental needs. This customized service not only enhances research efficiency but also accelerates the development and validation of new therapies.
Creative Biolabs provides powerful tools for cancer immunology research. Through genetically engineered models, researchers can delve into the interactions between tumors and the immune system; while on-demand model creation services offer flexibility and specificity, advancing the field of personalized medicine. As technology continues to progress, future animal models will become more precise, better serving the needs of cancer research and treatment. Get in touch with us to customize your animal model.
Reference
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION