All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Creative Biolabs provides a wide selection of CD44V6 molecular-related items, such as CAR vector items, CAR cell items, CAR viral particles, CAR animal cells, etc. These offerings aim to support the progress of CD44V6-targeted CAR-T therapy. Please refer to the list below to find the product that you need.
As a glycoprotein found on the surface of cells, CD44 plays a role in the growth, differentiation, and spread of tumors. CD44v6 is a specific variant of CD44 that is mainly expressed at high levels in solid cancers. It has been involved in the development of tumors, the invasion of tumor cells, and the spread of cancer. CD44v6 also includes exon 11 and is highly expressed in various types of malignancies, including squamous cell carcinomas in the head, neck, lung, skin, cervix, and esophagus, as well as breast, gastrointestinal, hepatocellular, and colorectal cancers, and certain subtypes of acute myeloid leukemias (AML). The effectiveness of using a CD44v6 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) has been investigated in clinical trials for the treatment of AML, multiple myeloma, and solid cancers.
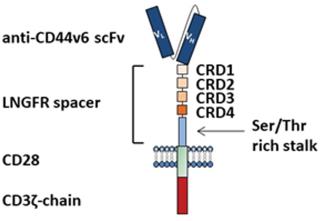 Fig.1 Schematic structure of the CD44v6-LNGFR CAR.1
Fig.1 Schematic structure of the CD44v6-LNGFR CAR.1
Creative Biolabs offers a complete series of protein products to detect the expression of anti-CD44v6 CART cells. These protein and cell products have been widely used for the expression test of anti-CD44v6 CAR-T cells.
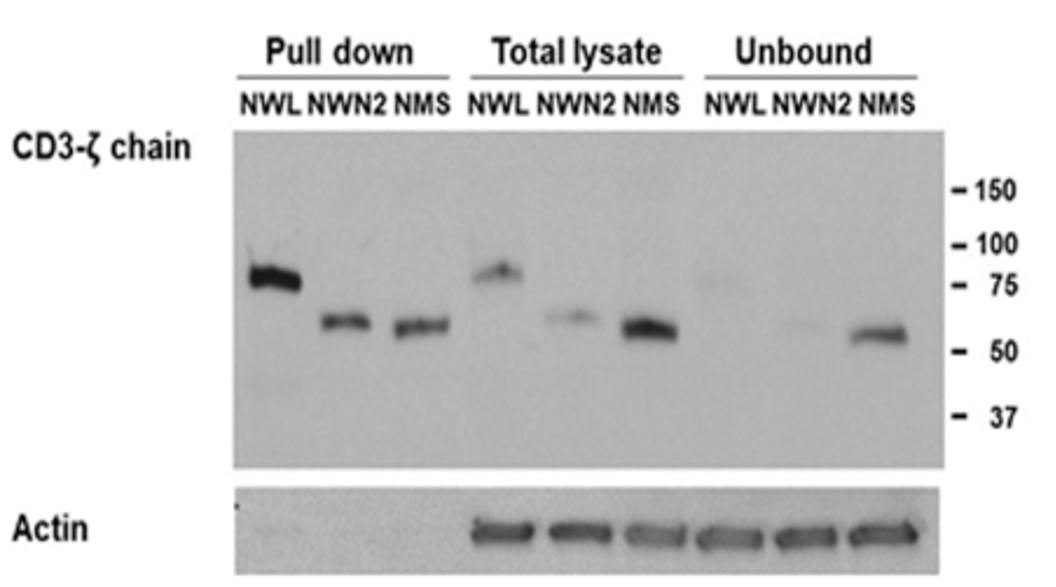 Fig.2 Biochemical analysis of the CD44v6 CAR expression.1
Fig.2 Biochemical analysis of the CD44v6 CAR expression.1
CD44V6 CAR-T Cytokine Release Test
The production of intracellular cytokines (such as TNF-α and IFN-γ) can be assessed using flow cytometry on CAR T cells that have been cultured with various types of target cells.
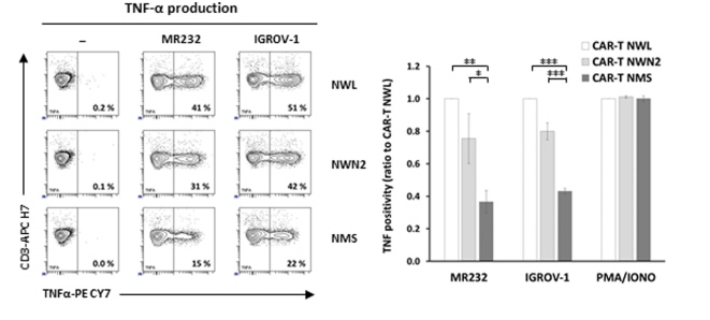 Fig.3 Analysis of intracellular cytokine production of CD44v6 CAR T cells by flow cytometry.1
Fig.3 Analysis of intracellular cytokine production of CD44v6 CAR T cells by flow cytometry.1
CD44V6 CAR-T In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
CD44v6 CAR-T exhibits only mild damage to human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and slight non-tumor cytotoxicity towards T lymphocytes. Creative Biolabs provides exclusive cytotoxicity testing services specifically designed for CD44v6 CAR-T cells. CD44v6-positive tumor cell lines can be used for this purpose.
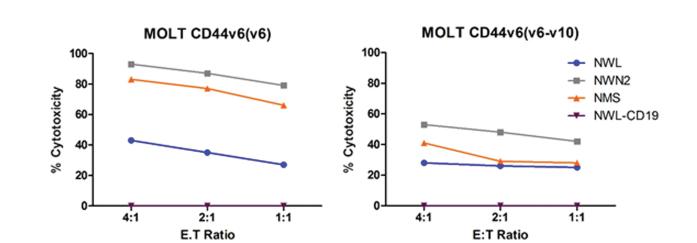 Fig.4 Cytotoxic activity of the differentiated CD44v6 CAR T cells. 1
Fig.4 Cytotoxic activity of the differentiated CD44v6 CAR T cells. 1
CD44V6 CAR-T Cell Proliferation Test
We assure our customers that Creative Biolabs provides top-notch service for customized CAR-T cell proliferation assays.
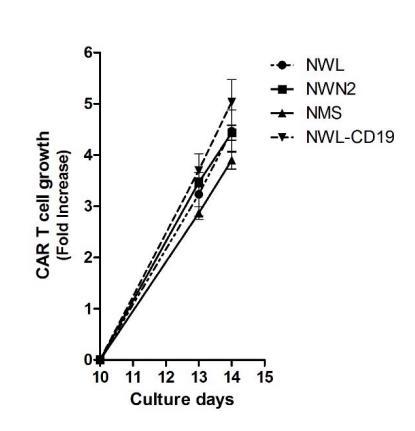 Fig.5 Impact of spacer region of CD44v6 CART on T cells proliferation and activation.1
Fig.5 Impact of spacer region of CD44v6 CART on T cells proliferation and activation.1
CD44V6 CAR-T Cell Therapy Animal Models
Creative Biolabs has developed a diverse selection of efficient models for in vivo evaluation, including immune-oncology animal models, syngeneic models, humanized mice models, patient-derived xenografted (PDX) models, patient-derived organoid models, and cell line-derived xenografted (CDX) models for CD44v6 CAR-T therapy.
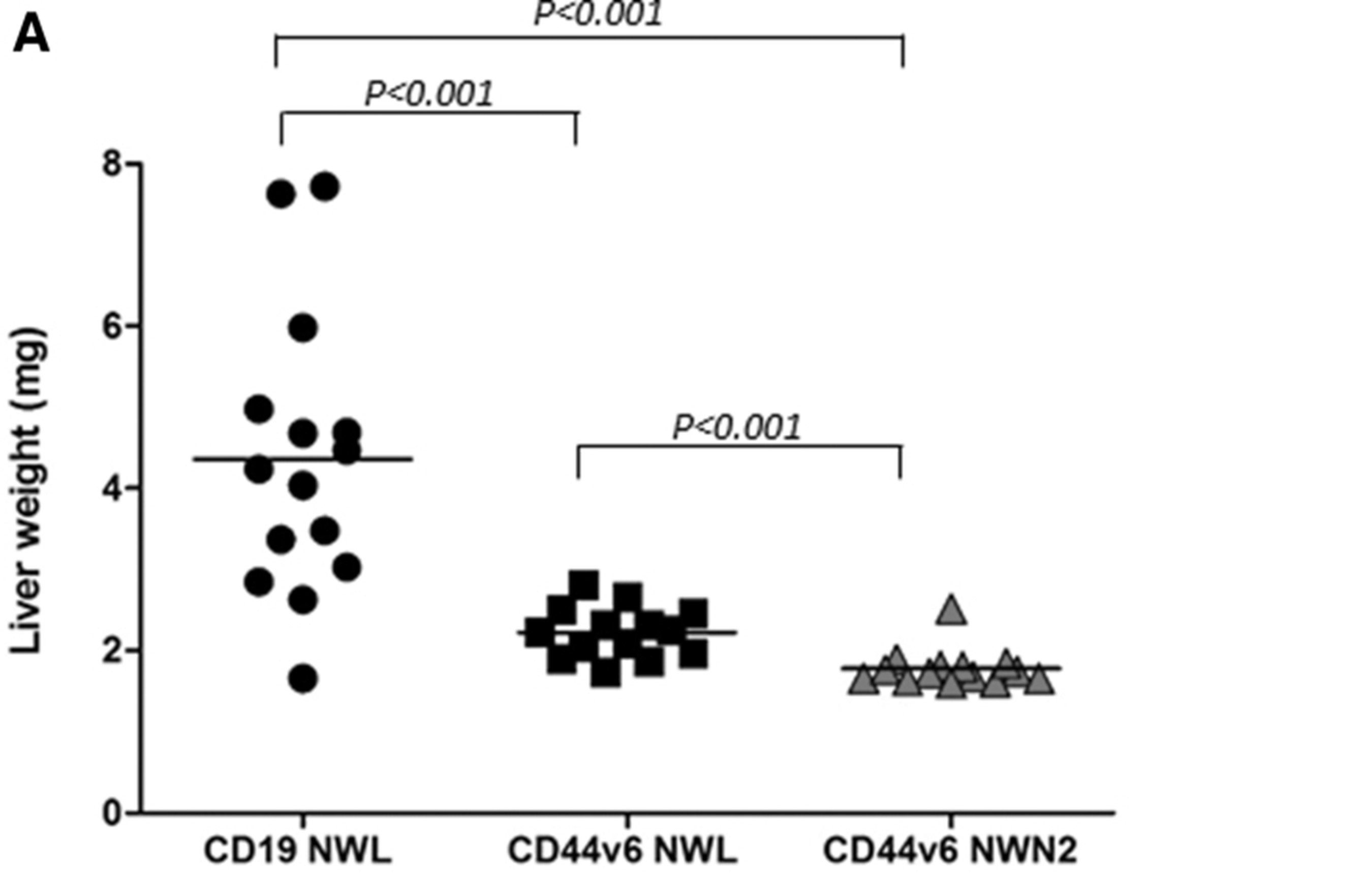 Fig.6 In vivo antitumor activity of CD44v6 CART analyzed in THP-1 high-burden disease model.1
Fig.6 In vivo antitumor activity of CD44v6 CART analyzed in THP-1 high-burden disease model.1
We have a variety of testing methods at our disposal, such as in vivo imaging, flow cytometry, histologic and pathologic analysis, and clinical observation, enabling us to assess the therapeutic effectiveness of CD44v6 CAR-T cell therapy.
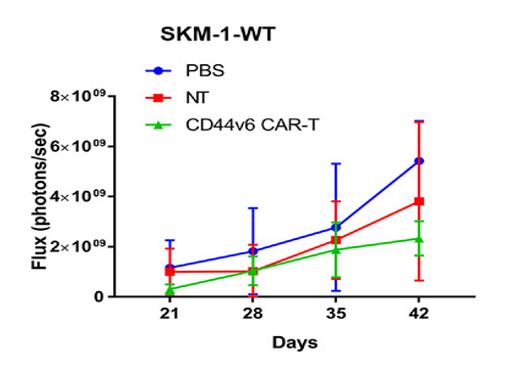 Fig.7 Analysis of potent anti-tumor efficacy of CD44v6 CAR-T cells in vivo.2
Fig.7 Analysis of potent anti-tumor efficacy of CD44v6 CAR-T cells in vivo.2
Toxicity Evaluation of CD44V6 CAR-T
Creative Biolabs offers CAR-T cell toxicity evaluation service, leveraging our profound expertise in preclinical in vivo research, project management, and our ability to employ suitable models, design comprehensive research protocols, and conduct reliable high-quality in vivo studies.
Please feel free to get in touch with us for more information on CD44V6 CAR-related services and products.
References
 Loading...
Loading...
| CAT | Product Name | Target Species | Antibody Clone | Antibody Host | Receptor Construction | Vector Type | Targeting Cell Type | CAR Vector Type | Inquiry & Datasheet |
| CAR-LC346 | Anti-CD44v6 h(CD28-CD3ζ, LNGFR) Marked CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | Human | scFv-LNGFR-CD28-CD3ζ | Retroviral | T cell | |||
| CAR-0720ZP13 | Anti-CD44v6 (CAR-0720ZP134) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CAR-0720ZP13 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0720ZP14 | Anti-CD44v6 (CAR-0720ZP144) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CAR-0720ZP14 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0720ZP15 | Anti-CD44v6 (CAR-0720ZP158) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CAR-0720ZP15 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0720ZP16 | Anti-CD44v6 (CAR-0720ZP168) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CAR-0720ZP16 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0720ZP25 | Anti-CD44v6 (CAR-0720ZP25) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CAR-0720ZP25 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0720ZP26 | Anti-CD44v6 (CAR-0720ZP26) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CAR-0720ZP26 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0720ZP27 | Anti-CD44v6 (CAR-0720ZP27) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CAR-0720ZP27 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0720ZP28 | Anti-CD44v6 (CAR-0720ZP28) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CAR-0720ZP28 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0720ZP29 | Anti-CD44v6 (CAR-0720ZP29) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CAR-0720ZP29 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-0622-ZP3305 | Anti-CD44v6 h(VHH1-VHH2-CD28-CD3ζ) Biepitopic CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | VHH1-VHH2-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||||
| XS-0622-ZP3477 | Anti-CD44v6 h(VHH1-VHH2-4-1BB-CD3ζ) Biepitopic CAR, pCDCAR1 | VHH1-VHH2-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | |||||
| XS-0822-YF185 | Anti-Human CD44v6 (XW-185) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-185 | Humanized | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF1105 | Anti-Human CD44v6 (XW-185) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-185 | Humanized | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF2025 | Anti-Human CD44v6 (XW-185) h(CD28-41BB-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-185 | Humanized | scFv-CD28-41BB-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-1122-YF185 | Anti-CD44v6 KIR CAR (scFv-KIR2DS2-DAP12, XW-185), pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-185 | Humanized | scFv-KIR2DS2 TM&ICD-2A-DAP12 | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF1105 | Anti-CD44v6 TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRα, XW-185) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-185 | Humanized | scFv-TCRα | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2025 | Anti-CD44v6 TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-185) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-185 | Humanized | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2945 | Anti-CD44v6 TCR-ABR (scFv-CD3γ, XW-185) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-185 | Humanized | scFv-CD3γ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF3865 | Anti-CD44v6 TCR-ABR (scFv-CD3δ, XW-185) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-185 | Humanized | scFv-CD3δ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell |
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION