All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Creative Biolabs offers a wide range of CCR2 CARs to choose from, including CAR vector products, CAR cell products, mRNA, and more.
CCL2/MCP-1 was the first to be identified among the human CC chemokines. Its receptor CCR2 is expressed on the surface of cells such as leukocytes and mesenchymal stem cells, giving them homing abilities in response to inflammatory signals. Due to its various functions, CCR2 has become a key target for the treatment of cancer, inflammation, and other diseases. CCR2 was first identified in monocytes, mainly constitutively expressed in subsets of highly expressing LY6C (LY6Chi), which play a key role in immune defense and tissue healing. A small percentage of NK cells, T cells, basophils, and even endothelial cells have CCR2 expression under inflammatory conditions. In addition, immature B cells, dendritic cells, were also detected to have CCR2 mRNA expression.
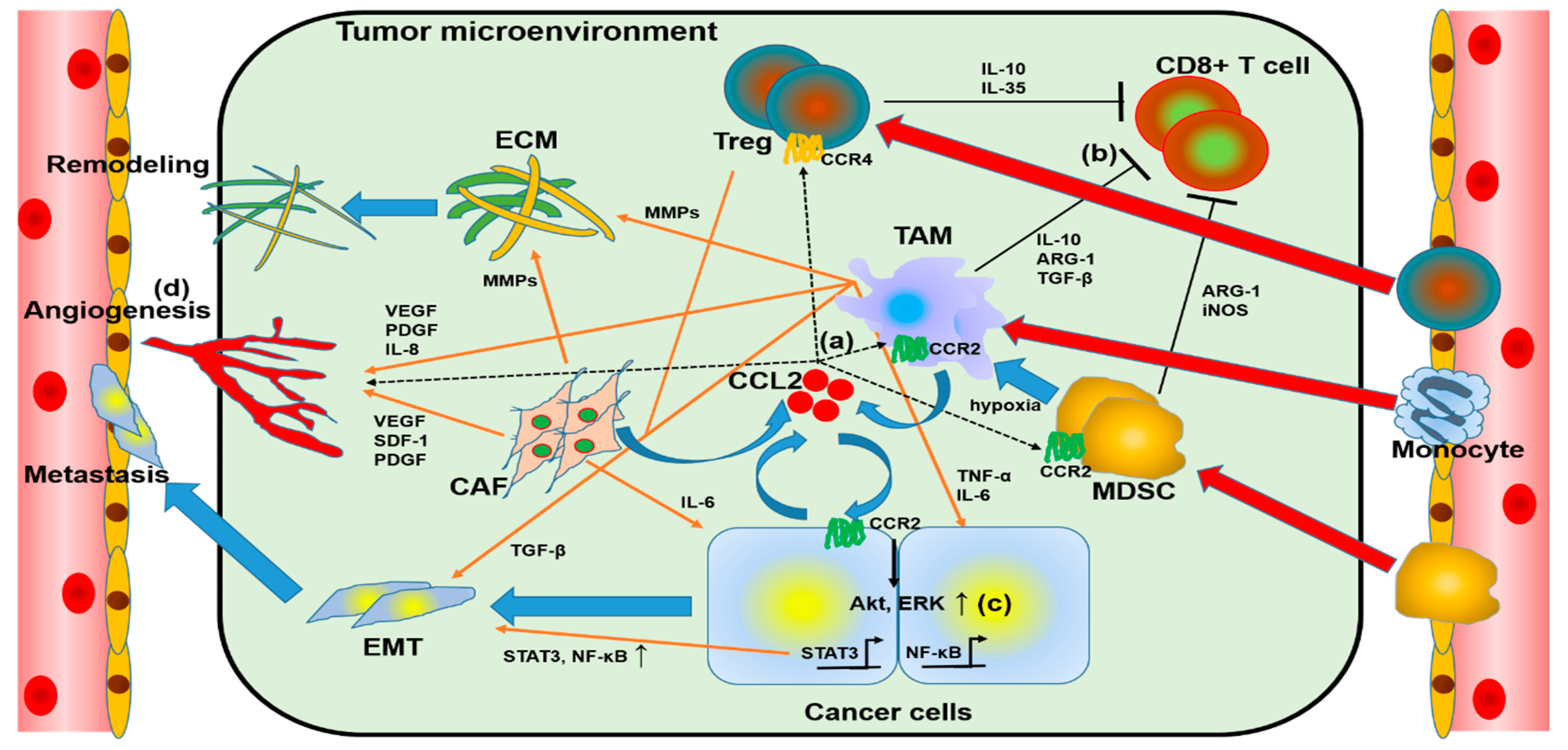 Fig.1 Correlations between CCL2 and the tumor microenvironment (TME).1
Fig.1 Correlations between CCL2 and the tumor microenvironment (TME).1
Skin Cancer
Non-small Cell Lung Carcinoma
GD2-positive Neuroblastoma and Melanoma
Creative Biolabs has built a one-stop service platform for CCR2 CAR (The cDNA of CCR2 can encode two proteins, CCR2a and CCR2b. CCR2b is the predominant form of expression), which can provide researchers with services from scFv sequence screening, CAR molecular design to in vitro killing assay, helping users improve the efficiency and accuracy of CAR-T/NK related research.
![]() Fig.2 Schematic diagram of the construction of CCR2b CAR.2
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of the construction of CCR2b CAR.2
Anti-CCR2 CAR-T Expression Test
Creative Biolabs offers PE-labeled CCR2b, FITC-labeled CCR2b, Protein L, and anti-Fab antibodies, which are effective tools for detecting anti-CCR2b CAR expression on the surface of CAR-T cells. These reagents bind specifically to the scFv region of the CAR molecule and can detect CAR expression sensitively and accurately.
 Fig.3 Flow cytometry analysis to evaluate CCR2b CAR expression.2
Fig.3 Flow cytometry analysis to evaluate CCR2b CAR expression.2
Anti-CCR2 CAR-T Cell Proliferation Test
When the CAR molecule recognizes the antigen, it releases T cell effector responses, including proliferation, cytokine release, metabolic alterations, and cytotoxicity. Creative Biolabs offers in vitro CCR2b CART cell value-added assays. As shown in the figure below, CCR2b modification had no effect on the proliferative activity of CAR T cells by CCK-8 test.
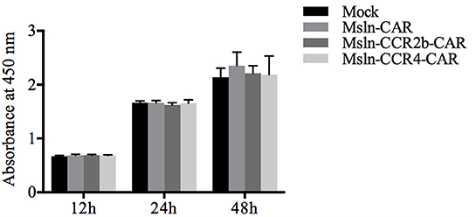 Fig.4 Proliferative capacity of CCR2b CAR T cells.2
Fig.4 Proliferative capacity of CCR2b CAR T cells.2
Anti-CCR2 CAR-T Cytokine Release Test
Cytokines such as interferon IFN-γ and interleukin IL-2 can regulate immune responses and perform different anti-tumor functions. Creative Biolabs provides commonly used cytokine assays, such as ELISA and CBA.
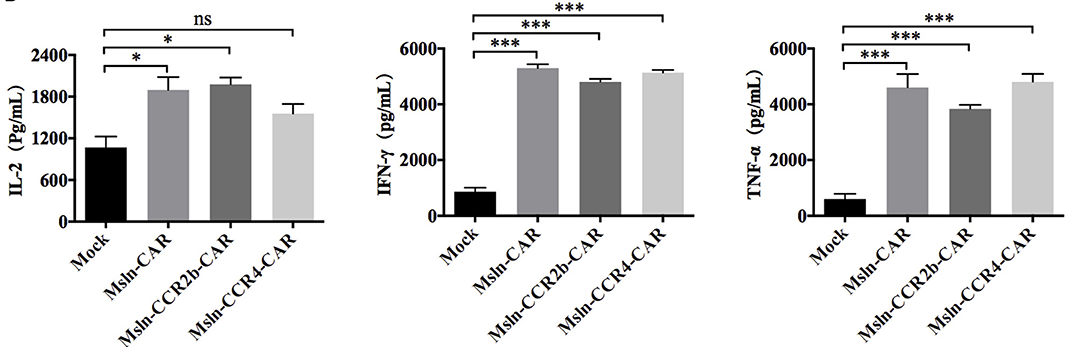 Fig.5 ELISA was used to detect the level of cytokines secreted by CCR2b CAR T cells.2
Fig.5 ELISA was used to detect the level of cytokines secreted by CCR2b CAR T cells.2
Anti-CCR2 CAR-T Cell Therapy Animal Models
After in vitro confirmation of the function of CCR2b CAR T cells, the next step of preclinical in vivo efficacy and safety assessment with appropriate animal models is required. Creative Biolabs offers models such as NSCLC CDX models, which have been used in several published papers to help you assess CCR2b CAR T in vivo. The figure below shows the experimental flow chart of CCR2b CAR T cells studied in vivo using the NSCLC CDX model.
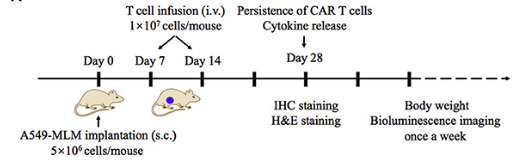 Fig.6 Anti-CCR2 CAR-T in vivo protocol.2
Fig.6 Anti-CCR2 CAR-T in vivo protocol.2
Efficacy Test of Anti-CCR2 CAR-T
In vivo imaging is often used for anti-tumor monitoring of CAR-T cells, so the construction of Luci-GFP target cells to express green fluorescent protein is one of the commonly used methods. As shown in Figure 7, the results of bioluminescence imaging showed that CCR2b CAR T cells had superior anti-tumor function.
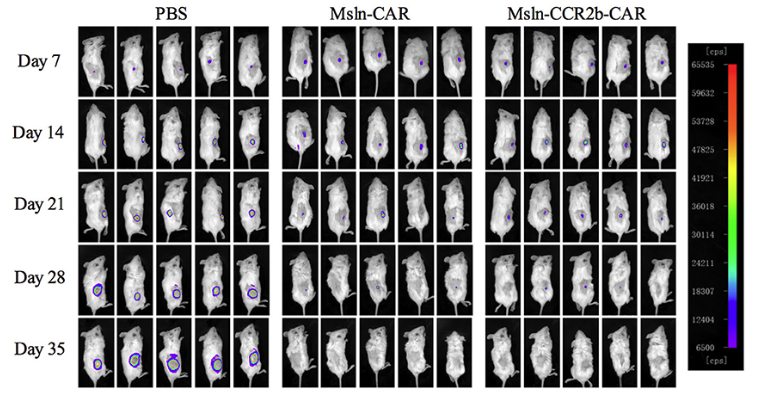 Fig.7 Bioluminescence imaging was used to monitor the efficacy of CCR2 CAR-T in vivo.2
Fig.7 Bioluminescence imaging was used to monitor the efficacy of CCR2 CAR-T in vivo.2
References
 Loading...
Loading...
| CAT | Product Name | Target Species | Antibody Clone | Antibody Host | Receptor Construction | Vector Type | Targeting Cell Type | CAR Vector Type | Inquiry & Datasheet |
| XS-0622-LX274 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X88) h(ICOS-4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | X6X88 | Human | scFv-ICOS-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX275 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X89) h(ICOS-4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | X6X89 | Human | scFv-ICOS-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX276 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X90) h(ICOS-4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | X6X90 | Human | scFv-ICOS-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX277 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X91) h(ICOS-4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | X6X91 | Human | scFv-ICOS-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX483 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X88) h(CD28-OX40-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | X6X88 | Human | scFv-CD28-OX40-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX484 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X89) h(CD28-OX40-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | X6X89 | Human | scFv-CD28-OX40-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX485 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X90) h(CD28-OX40-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | X6X90 | Human | scFv-CD28-OX40-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX486 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X91) h(CD28-OX40-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | X6X91 | Human | scFv-CD28-OX40-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX493 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X98) h(CD28-OX40-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | X6X98 | Human | scFv-CD28-OX40-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX494 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X99) h(CD28-OX40-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | X6X99 | Human | scFv-CD28-OX40-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX495 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X100) h(CD28-OX40-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | X6X100 | Human | scFv-CD28-OX40-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX496 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X101) h(CD28-OX40-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | X6X101 | Human | scFv-CD28-OX40-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX497 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X102) h(CD28-OX40-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | X6X102 | Human | scFv-CD28-OX40-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX692 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X88) h(CD28-41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pSBCAR1 | Human | X6X88 | Human | scFv-CD28-41BB-CD3ζ | Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX693 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X89) h(CD28-41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pSBCAR1 | Human | X6X89 | Human | scFv-CD28-41BB-CD3ζ | Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX694 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X90) h(CD28-41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pSBCAR1 | Human | X6X90 | Human | scFv-CD28-41BB-CD3ζ | Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX1099 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X87) h(CD28-OX40-CD3ζ) CAR, pSBCAR1 | Human | X6X87 | Human | scFv-CD28-OX40-CD3ζ | Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX1100 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X88) h(CD28-OX40-CD3ζ) CAR, pSBCAR1 | Human | X6X88 | Human | scFv-CD28-OX40-CD3ζ | Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX1101 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X89) h(CD28-OX40-CD3ζ) CAR, pSBCAR1 | Human | X6X89 | Human | scFv-CD28-OX40-CD3ζ | Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-LX1102 | Anti-CCR2 (X6X90) h(CD28-OX40-CD3ζ) CAR, pSBCAR1 | Human | X6X90 | Human | scFv-CD28-OX40-CD3ζ | Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon | T cell |
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION