All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Creative Biolabs provides a variety of FOLR1 CAR-T products and high-quality services to aid in CAR-T development. Please browse the following list to find a suitable product.
Folate receptor 1 (FOLR1) is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-binding protein. In the normal tissue, FOLR1 is expressed on the top of the polarized epithelial cell surface only, and not exposed to the bloodstream. Importantly, the overexpression of FOLR1 is associated with a variety of epithelial malignancies, such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, renal cancer, and lung cancer. These characteristics make it an attractive target for cancer therapy.
Associated Disease
Detection of CAR expression level in CAR-T cells is very essential for CART development. At present, we offer comprehensive approaches to test the expression of CAR molecules, either via the detection of specific targets, or via the detection of other CAR construct domains, such as tag, linker, and stimulation domains. These tests can be selected according to the customer's specific project needs.
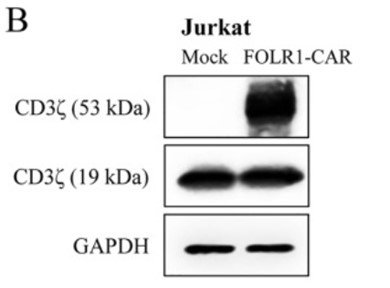
Fig.1 Expression test of FOLR1-CAR on Jurkat cells surface.1
Maintaining robust cell proliferation ability is a prerequisite for CART development projects. For monitoring the proliferation capacity of CAR T cells, Creative Biolabs offers various highly effective in vitro CAR T cell proliferation tests, providing customers with a reliable reference for experimental results, and providing support for the smooth progress of the next stage.
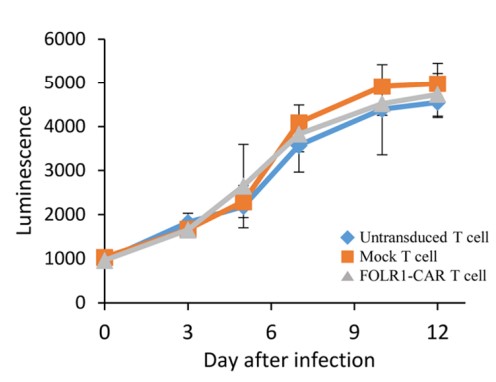
Fig.2 Proliferation test of FOLR1-CAR T cells.1
The production of cytokines during the incubation of CART cells and tumor cells indicates the strength of the response to a certain extent. To provide better cytokine detection services, we have developed comprehensive approaches to assist customers' CART projects, such as intracellular cytokine staining by FACS, ELISA, multi-cytokine detection, etc.
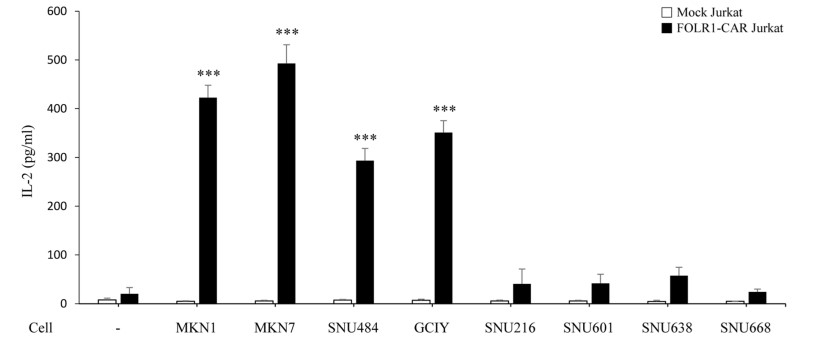
Fig.3 Cytokine release test of FOLR CAR-Jurkat cell co-cultured with different gastric cancer cell lines at 10:1 E: T ratio.1
In vitro cytotoxicity assays are commonly used to evaluate the anti-tumor activity of CAR-T cells. We offer a variety of methods to evaluate anti-FOLR1 CAR-T cell toxicity in vitro, including LDH release, MTT release, and real-time cell analysis assay to facilitate customers' CART projects.
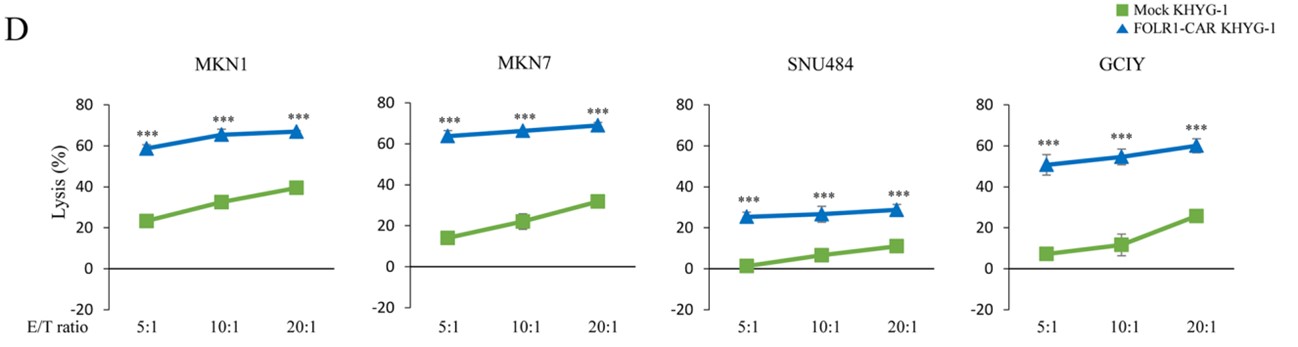
Fig.4 The in vitro killing efficacy of FOLR1-CAR KHYG-1 cells against FOLR1-positive gastric cancer cell lines at indicated E:T ratio.1
For in vivo efficacy evaluation of CAR-T cells, Creative Biolabs has launched several optimized animal models, such as the commonly used CDX and PDX models. At the same time, we have also developed a series of in vivo experiments to aid in CART development.
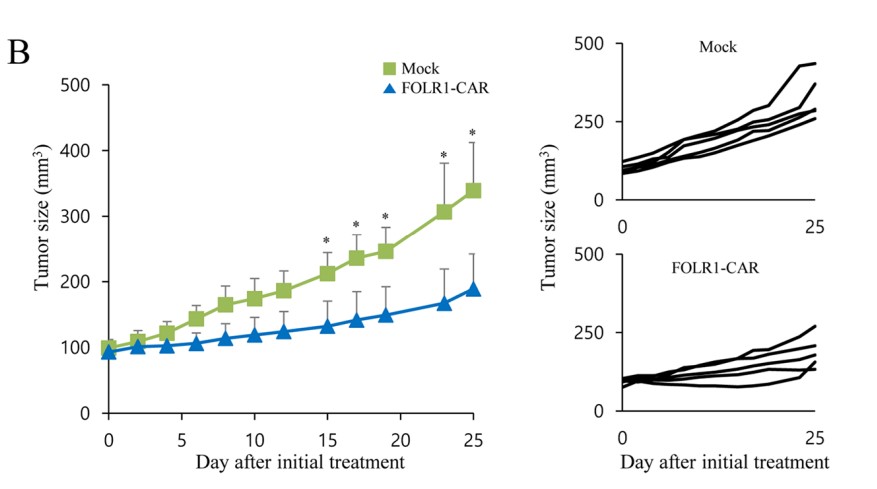
Fig.5 In vivo antitumor effect of FOLR1-CAR KHYG cells in FOLR1-positive MKN1 CDX mice.1
Reference
 Loading...
Loading...
| CAT | Product Name | Target Species | Antibody Clone | Antibody Host | Receptor Construction | Vector Type | Targeting Cell Type | CAR Vector Type | Inquiry & Datasheet |
| CAR-ZP8342 | Anti-FOLR1 (FR1-21) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | FR1-21 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP8343 | Anti-FOLR1 (FR1-21) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | FR1-21 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP8344 | Anti-FOLR1 (FR1-13) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | FR1-13 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP8345 | Anti-FOLR1 (FR1-13) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | FR1-13 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP8346 | Anti-FOLR1 (FR1-9) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | FR1-9 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP8347 | Anti-FOLR1 (FR1-9) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | FR1-9 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP8348 | Anti-FOLR1 (353.2-1) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 353.2-1 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP8349 | Anti-FOLR1 (353.2-1) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 353.2-1 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP8350 | Anti-FOLR1 (353.9-20) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 353.9-20 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP8351 | Anti-FOLR1 (353.9-20) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 353.9-20 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP8352 | Anti-FOLR1 (9F3) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 9F3 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP8353 | Anti-FOLR1 (9F3) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 9F3 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP8354 | Anti-FOLR1 (19D4) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 19D4 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP8355 | Anti-FOLR1 (19D4) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 19D4 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP8356 | Anti-FOLR1 (24F12) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 24F12 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP8357 | Anti-FOLR1 (24F12) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 24F12 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP8480 | A uniCAR [Anti-FITC CAR (4M5.3-4-1BB/CD3ζ)], with a Small molecule-based CAR Adaptor [FolR1], a Switchable CAR System | folate receptor (FR)-overexpressing tumor | Lentiviral vector | ||||||
| CAR-ZP8481 | A uniCAR [Anti-FITC CAR (4-1BB/CD3ζ)], with a Small molecule-based CAR Adaptor [FolR1], a Switchable CAR System | folate receptor (FR)-overexpressing tumor | Lentiviral vector | ||||||
| XS-0722-LX164 | Anti-FOLR1 (X7X164) h(CD28-41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pSBCAR1 | human | X7X164 | Humanized | scFv-CD28-41BB-CD3ζ | Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon | T cell | ||
| XS-0722-LX165 | Anti-FOLR1 (X7X165) h(CD28-41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pSBCAR1 | human | X7X165 | Humanized | scFv-CD28-41BB-CD3ζ | Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon | T cell | ||
| XS-0722-LX166 | Anti-FOLR1 (X7X166) h(CD28-41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pSBCAR1 | human | X7X166 | Humanized | scFv-CD28-41BB-CD3ζ | Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon | T cell | ||
| XS-0722-LX167 | Anti-FOLR1 (X7X167) h(CD28-41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pSBCAR1 | human | X7X167 | Humanized | scFv-CD28-41BB-CD3ζ | Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon | T cell |
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION