All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Creative Biolabs is your one-stop solution for comprehensive anti-GPRC5D CAR-T therapy development support. Our product line includes a variety of anti-GPRC5D CAR-T vectors, cells, and reagents designed to facilitate your research. Please browse the following list to find the products you need.
The orphan G protein-coupled receptor (GPRC5D) is a gene with widespread expression in the human body. The GPRC5D protein is a cytokine receptor and plays an important role in the nervous system and immune system. GPRC5D expresses abnormalities in various cancers, including breast cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, etc., and is thus considered a potential tumor marker. Additionally, GPRC5D is also associated with some autoimmune diseases. Currently, antibody drugs and small molecule inhibitors targeting GPRC5D are being developed to treat cancer and autoimmune diseases.
Liver cancer
Melanoma
Pancreatic cancer
Anti-GPRC5D CAR-T Expression Test
Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive range of GPRC5D protein products, such as biotinylated GPRC5D, unconjugated GPRC5D, and fluorescent-labeled GPRC5D. These products efficiently identify the expression of anti-GPRC5D CAR on the surface of T cells. Furthermore, the anti-GPRC5D CAR-T expression test can be customized to meet each client's specific research requirements.
Anti-GPRC5D CAR-T Proliferation Test
Our scientists perform a variety of cell proliferation assays including flow cytometry analysis, CFSE-based proliferation test, MTT assay, and CCK-8 assay. These assays can be used individually or in combination to comprehensively assess the proliferation of CAR-T cells in response to different stimuli or treatments.
 Fig.1 Proliferation of GPRC5D CAR T cells cultured alone, with GPRC5D− or GPRC5D+ cells was tested by flow cytometry analysis.1
Fig.1 Proliferation of GPRC5D CAR T cells cultured alone, with GPRC5D− or GPRC5D+ cells was tested by flow cytometry analysis.1
Anti-GPRC5D CAR-T Cytokine Release Test
The anti-GPRC5D CAR-T cytokine release test is a crucial tool in assessing the efficacy and safety of anti-GPRC5D CAR-T therapy. The levels of released cytokines can be quantified using various techniques, such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) and multiplex bead arrays.
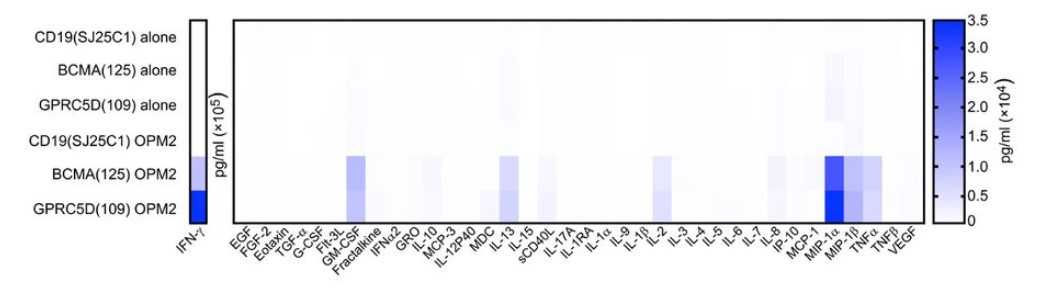 Fig.2 The cytokines produced by GPRC5D CAR-T cells cocultured with OPM2 human MM cells.1
Fig.2 The cytokines produced by GPRC5D CAR-T cells cocultured with OPM2 human MM cells.1
Anti-GPRC5D CAR-T In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
We offer a variety of methods to evaluate the cytotoxic potential of GPRC5D CAR-T cells against target cells. These assays provide valuable insights into the cytotoxic potential and specificity of CAR-T cells, thereby guiding researchers in optimizing their therapeutic strategies.
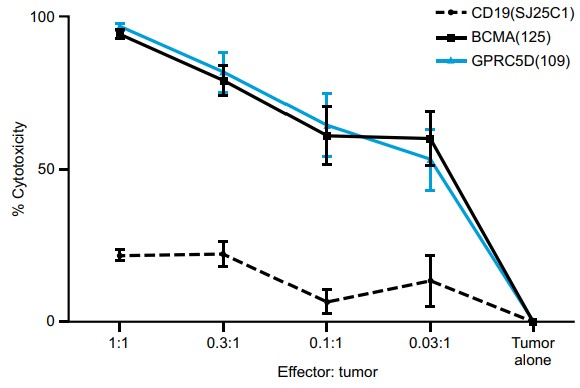 Fig.3 The cytotoxicity of GPRC5D CAR-T cells against OPM2 human MM cells.1
Fig.3 The cytotoxicity of GPRC5D CAR-T cells against OPM2 human MM cells.1
Anti-GPRC5D CAR-T Cell Therapy Animal Models
At our lab, we offer a range of anti-GPRC5D CAR-T cell therapy testing mouse models, including xenograft, humanized, syngeneic, and transgenic models. These animal models play a crucial role in the development and evaluation of CAR-T therapies.
Efficacy Test of Anti-GPRC5D CAR-T
The efficacy tests of GPRC5D CAR-T cells play a vital role in assessing the therapeutic potential and safety of these cells in a living organism. We assess the therapeutic effect of anti-GPRC5D CAR-T cells in animal models.
 Fig.4 The antitumor activity of GPRC5D targeted CAR-T in the OPM2 human myeloma cell xenograft mouse model.1
Fig.4 The antitumor activity of GPRC5D targeted CAR-T in the OPM2 human myeloma cell xenograft mouse model.1
Toxicity Evaluation Anti-GPRC5D CAR-T
To ensure the optimal therapeutic index of anti-GPRC5D CAR T cell therapy, it is crucial to monitor and assess the safety profile of the treatment. Our comprehensive CAR-T evaluation services help clients identify and characterize potential adverse events associated with the therapy, enabling researchers to make informed decisions on the development and translation of CAR-T cell therapies.
 Fig.5 Evaluation of on-target/off-tumor toxicity induced by GPRC5D-targeted CAR T cells. (A) Body mass, (B) body temperature, and (C) BLI of OPM2-ffLuc cells.1
Fig.5 Evaluation of on-target/off-tumor toxicity induced by GPRC5D-targeted CAR T cells. (A) Body mass, (B) body temperature, and (C) BLI of OPM2-ffLuc cells.1
Reference
 Loading...
Loading...
| CAT | Product Name | Target Species | Antibody Clone | Antibody Host | Receptor Construction | Vector Type | Targeting Cell Type | CAR Vector Type | Inquiry & Datasheet |
| CAR-WFY0875 | Anti-GPRC5D (CBFYH-0465) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBFYH-0465 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-WFY0876 | Anti-GPRC5D (CBFYH-0466) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBFYH-0466 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-WFY4128 | Anti-GPRC5D (CBFYH-0465) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBFYH-0465 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-WFY4129 | Anti-GPRC5D (CBFYH-0466) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBFYH-0466 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-LY1357 | Anti-GPRC5D (11D88) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 11D88 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-LY1358 | Anti-GPRC5D (571961) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 571961 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-LY1359 | Anti-GPRC5D (CBLG1-206) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBLG1-206 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-LY1360 | Anti-GPRC5D (CBLG1-207) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBLG1-207 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-LY1361 | Anti-GPRC5D (CBLG1-208) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBLG1-208 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-LY1362 | Anti-GPRC5D (6D9) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 6D9 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-LY1363 | Anti-GPRC5D (CBLG1-3204) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse, Rat | CBLG1-3204 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-LY1364 | Anti-GPRC5D (CBLG1-1652) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBLG1-1652 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-LY1365 | Anti-GPRC5D (CBLG1-1653) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBLG1-1653 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-LY2997 | Anti-GPRC5D(11D88) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 11D88 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-LY2998 | Anti-GPRC5D(571961) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 571961 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-LY2999 | Anti-GPRC5D(CBLG1-206) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBLG1-206 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-LY3000 | Anti-GPRC5D(CBLG1-207) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBLG1-207 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-LY3001 | Anti-GPRC5D(CBLG1-208) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBLG1-208 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-LY3002 | Anti-GPRC5D(6D9) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 6D9 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-LY3003 | Anti-GPRC5D(CBLG1-3204) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse, Rat | CBLG1-3204 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| XS-0823-LX64 | Anti-hGPRC5D (Ab) ICD(CD28-OX40-CD3ζ) CAR-MA, pAd5f35 Vector | Human | Ab | Adenoviral vectors |
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION