All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Creative Biolabs offers various KLK3 CAR-T products for research purposes, including CAR vectors, CAR viral particles, and CAR-T cell lines. These cell lines are ready to use in in vitro studies and can be further modified for specific research needs.
The Kallikrein-related peptidase 3 gene (KLK3) is located on chromosome 19 and encodes the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) protein. KLK2 activates KLK3 by cleaving it from its precursor form, resulting in the release of the mature active enzyme. KLK3 functions as a serine protease and is involved in the breakdown of seminal fluid proteins, thereby liquefying semen and facilitating sperm mobility. KLK3 is primarily associated with prostate cancer. In prostate cancer, the expression of KLK3 is often upregulated, leading to increased levels of KLK3 in the blood. Therefore, it is commonly used as a biomarker for prostate cancer diagnosis and monitoring.
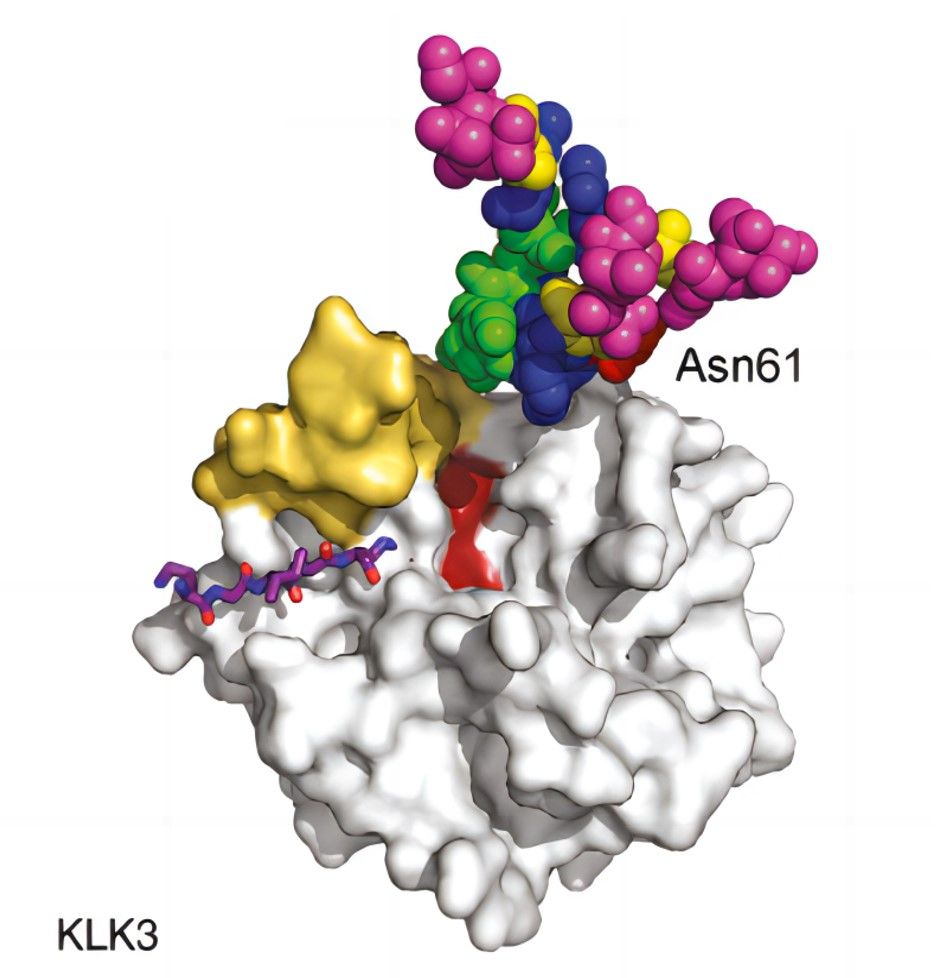
Fig.1 Schematic of KLK3.1
Associated Disease
Our team of experts is dedicated to delivering high-quality KLK3 CAR products and services that meet the specific needs of each client. Some services we offer include:
Creative Biolabs performs anti-KLK3 CAR expression tests to determine the level of expression of CAR constructs. These tests help researchers and scientists assess the efficiency of CAR expression and monitor and optimize the manufacturing process.
CAR-T cell proliferation is a critical step in the development of CAR-T cell therapy. In the context of in vitro proliferation, CAR-T cells are typically cultured and expanded in a controlled environment, such as in specialized culture media containing cytokines and growth factors. By measuring the increase in cell numbers with time, we assess the ability of CAR-T cells to proliferate and potentially generate an effective immune response against target cells or tumors.
One important aspect in evaluating the efficacy and safety of CAR-T cell therapy is assessing the cytokine release profile of CAR-T cells. Our cytokine release assays are typically performed by analyzing cytokines in the cell culture supernatant using several methods such as ELISA, cytometric bead array (CBA), or multiplex cytokine assays.
In vitro cytotoxicity assays provide valuable information about the killing efficiency of CAR-T cells, helping to select the most effective CAR constructs, optimize treatment conditions, and predict patient response to CAR-T therapy. We utilize various techniques to assess CAR-T cytotoxicity, including flow cytometry-based assays, LDH release assay, and cell viability assays.
At Creative Biolabs, our service includes the evaluation of the anti-tumor efficacy of CAR-T therapies in animal models. Our facility is well-equipped to handle mouse models and we strictly adhere to ethical guidelines to ensure the welfare of the animals. Our assays involve injecting tumor cells into animal models and subsequently administering CAR-T cells to assess their ability to eradicate the tumor. In addition, further analysis can be performed on tumor tissues, such as histology and immunohistochemistry, to understand the mechanism of action of CAR-T cells and their impact on the tumor microenvironment.
Reference
 Loading...
Loading...
| CAT | Product Name | Target Species | Antibody Clone | Antibody Host | Receptor Construction | Vector Type | Targeting Cell Type | CAR Vector Type | Inquiry & Datasheet |
| CAR-0120ZP1639 | Anti-KLK3 (FS-QS9) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | FS-QS9 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1640 | Anti-KLK3 (FS-QS9) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | FS-QS9 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1641 | Anti-KLK3 (CBACN-463) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Rabbit | CBACN-463 | Rabbit | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1642 | Anti-KLK3 (CBACN-463) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Rabbit | CBACN-463 | Rabbit | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1643 | Anti-KLK3 (8G8F5) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | 8G8F5 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1644 | Anti-KLK3 (8G8F5) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | 8G8F5 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1645 | Anti-KLK3 (5D5A5) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | 5D5A5 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1646 | Anti-KLK3 (5D5A5) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | 5D5A5 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1649 | Anti-KLK3 (C9-B) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | C9-B | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1650 | Anti-KLK3 (C9-B) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | C9-B | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1651 | Anti-KLK3 (N8-B) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | N8-B | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1683 | Anti-KLK3 (PS1) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | PS1 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1684 | Anti-KLK3 (PS1) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | PS1 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1685 | Anti-KLK3 (P1D10AT) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | P1D10AT | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1686 | Anti-KLK3 (P1D10AT) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | P1D10AT | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1687 | Anti-KLK3 (TD11B3-4) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | TD11B3-4 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1688 | Anti-KLK3 (TD11B3-4) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | TD11B3-4 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1689 | Anti-KLK3 (PSAK3-1) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | PSAK3-1 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1749 | Anti-KLK3 (214) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | 214 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP1750 | Anti-KLK3 (214) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | 214 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell |
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION