All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Creative Biolabs offers a wide range of high-quality products. To ensure the success of our clients' projects, we maintain a state-of-the-art R&D facility equipped with advanced tools and technologies. This allows us to offer advanced solutions and support to our clients, helping them to accelerate their research and bring innovative therapies to market. Please browse the following list to find the appropriate product for you.
c-Met protein, also known as the hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGFR), is a receptor tyrosine kinase that plays a crucial role in cell growth, proliferation, and survival. Aberrant activation or overexpression of c-Met has been observed in various types of cancers, including lung, breast, liver, and gastric cancer, and correlates with tumor progression, metastasis, and poor prognosis. Therefore, c-Met has emerged as a promising therapeutic target for cancer therapy.
T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia
Anti-c-Met CAR-T Expression Test
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive range of c-Met protein products for the direct measurement of CAR expression levels. In addition, we also offer customized anti-c-Met CAR-T expression tests. Our team of experts is committed to collaborating with clients to design and perform experiments tailored to their specific research needs.
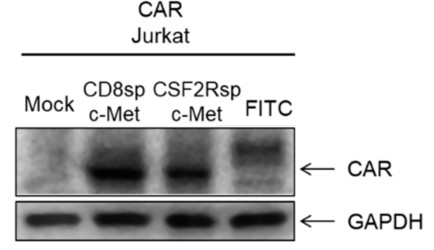 Fig.1 The evaluation of anti-c-Met CAR expression.1
Fig.1 The evaluation of anti-c-Met CAR expression.1
Anti-c-Met CAR-T Proliferation Test
CAR-T cell proliferation assays include detecting the CAR-T cells labeling with a fluorescent dye by flow cytometry, cell counting, as well as the use of proliferation-related markers such as Ki-67 or PCNA. These techniques may have limitations and should be chosen based on the specific requirements of the study, such as sensitivity, throughput, and cost.
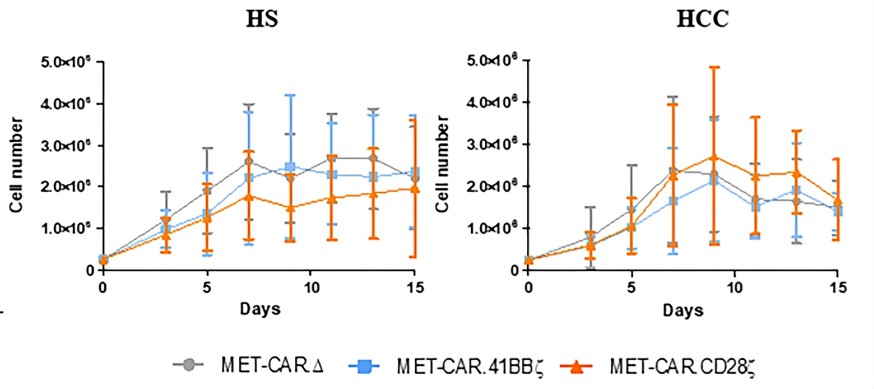 Fig.2 In vitro growth curves of anti-c-Met CAR-T cells.2
Fig.2 In vitro growth curves of anti-c-Met CAR-T cells.2
Anti-c-Met CAR-T Cytokine Release Test
Creative Biolabs provides Anti-c-Met CAR-T cytokine release tests that enable researchers to determine the ability of anti-c-Met CAR-T cells to produce and release cytokines in response to specific stimuli, which plays a vital role in understanding their immune-stimulating potential.
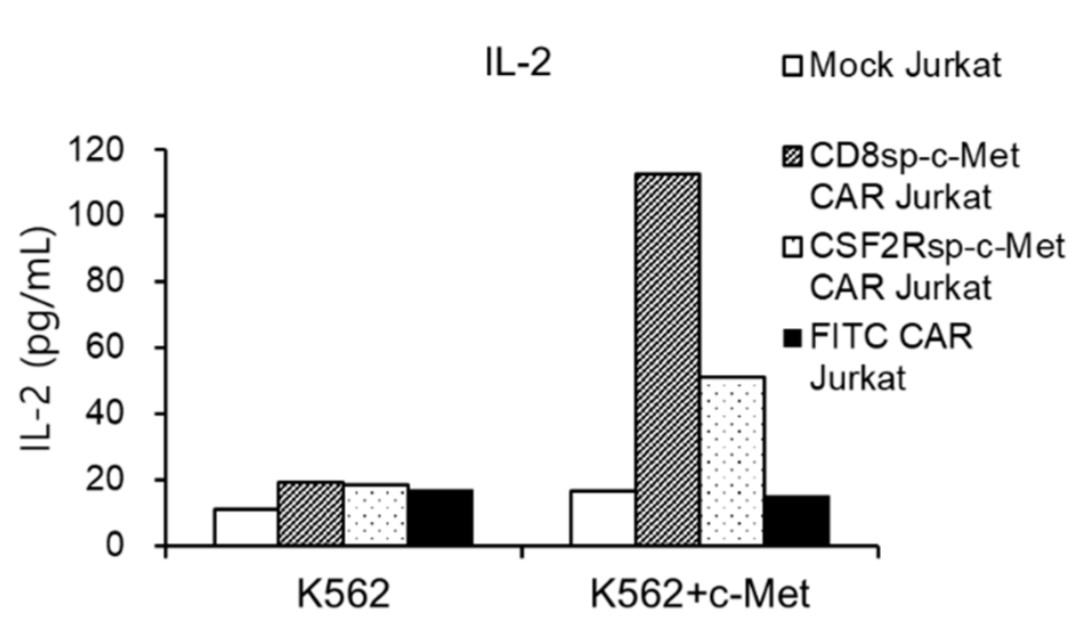 Fig.3 IL-2 release by anti-c-Met CAR-T cells with K562 or c-Met-K562 stimulation.1
Fig.3 IL-2 release by anti-c-Met CAR-T cells with K562 or c-Met-K562 stimulation.1
Anti-c-Met CAR-T In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
Our c-Met CAR-T cytotoxicity assays are important in determining the effectiveness of c-Met CAR-T cell therapies for cancer treatment.
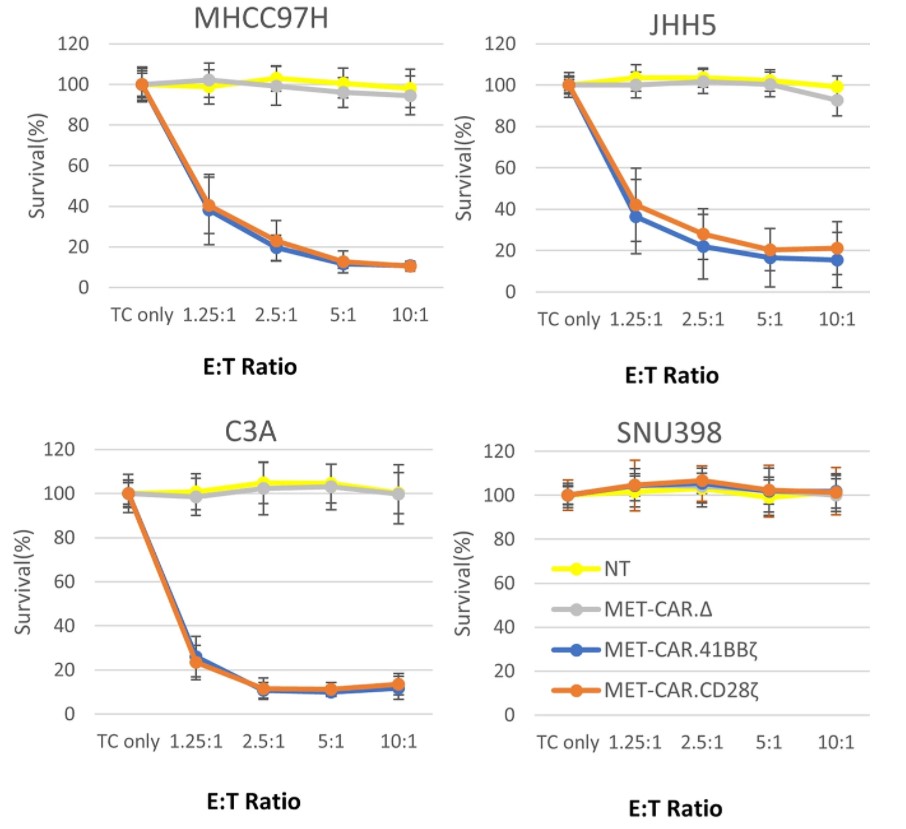 Fig.4 The cell killing activity of anti-c-Met CAR-T against Met-positive tumor cells and SNU398 (Met negative) tumor cells.2
Fig.4 The cell killing activity of anti-c-Met CAR-T against Met-positive tumor cells and SNU398 (Met negative) tumor cells.2
Anti-c-Met CAR-T Cell Therapy Animal Models
To evaluate the antitumor effects of CAR-T cells in vivo, At our lab, we offer a range of mouse tumor models, including xenograft, humanized, syngeneic, and transgenic models. These animal models play a crucial role in the development and evaluation of CAR-T therapies.
Efficacy Test of Anti-c-Met CAR-T
We perform comprehensive in vivo assays to thoroughly evaluate the therapeutic potential and safety of anti-c-Met CAR-T cells.
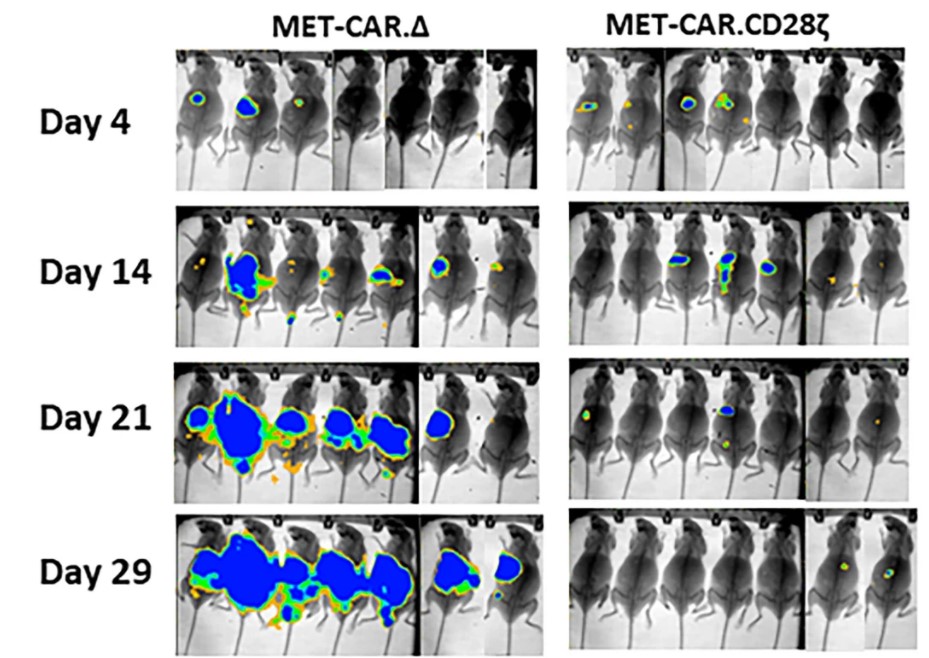 Fig.5 The antitumor activities of the anti-c-Met CAR-T cells. The anti-c-Met CAR-T cells specifically inhibited MHCC97H tumor growth.2
Fig.5 The antitumor activities of the anti-c-Met CAR-T cells. The anti-c-Met CAR-T cells specifically inhibited MHCC97H tumor growth.2
Toxicity Evaluation Anti-c-Met CAR-T
With our expert team and state-of-the-art technologies, we are committed to supporting the development of safe and effective CAR-T cell therapies for the treatment of various cancers and other diseases. We provide CAR-T toxicity study services to ensure the safety of CAR-T therapy.
Persistence of anti-c-Met CAR-T cell
CAR-T persistence is highly correlated with the life expectancy and survival of patients. To monitor the persistence of c-Met CAR-T cells in vivo, we evaluate CAR-T cell numbers over time by various techniques such as flow cytometry and BLI.
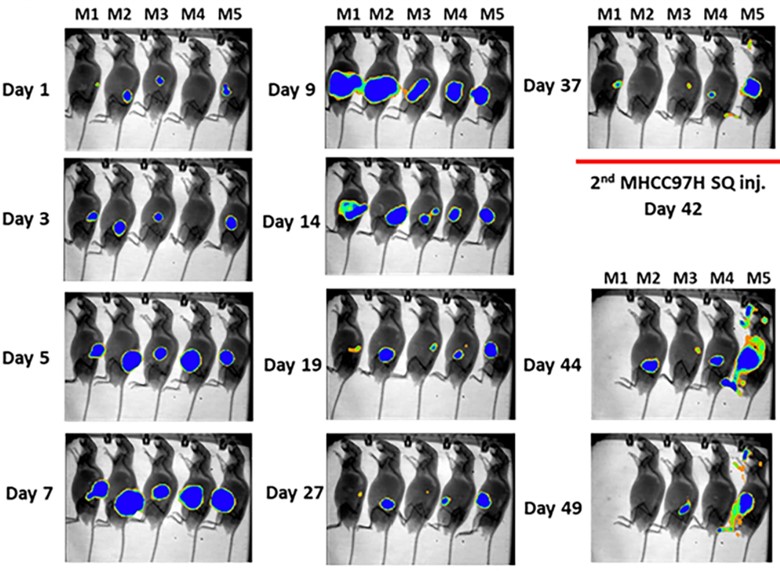 Fig.6 BLI imaging of anti-c-Met CAR-T cell expansion and persistence in vivo over time.2
Fig.6 BLI imaging of anti-c-Met CAR-T cell expansion and persistence in vivo over time.2
References
 Loading...
Loading...
| CAT | Product Name | Target Species | Antibody Clone | Antibody Host | Receptor Construction | Vector Type | Targeting Cell Type | CAR Vector Type | Inquiry & Datasheet |
| XS-0822-YF637 | Anti-Human c-Met (XW-637) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-637 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF638 | Anti-Human c-Met (XW-638) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-638 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF639 | Anti-Human c-Met (XW-639) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-639 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF640 | Anti-Human c-Met (XW-640) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-640 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF641 | Anti-Mouse c-Met (XW-641) m(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Mouse | XW-641 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF1557 | Anti-Human c-Met (XW-637) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-637 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF1558 | Anti-Human c-Met (XW-638) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-638 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF1559 | Anti-Human c-Met (XW-639) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-639 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF1560 | Anti-Human c-Met (XW-640) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-640 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF1561 | Anti-Mouse c-Met (XW-641) m(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Mouse | XW-641 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF2477 | Anti-Human c-Met (XW-637) h(CD28-41BB-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-637 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-41BB-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF2478 | Anti-Human c-Met (XW-638) h(CD28-41BB-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-638 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-41BB-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF2479 | Anti-Human c-Met (XW-639) h(CD28-41BB-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-639 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-41BB-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF2480 | Anti-Human c-Met (XW-640) h(CD28-41BB-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-640 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-41BB-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF8510 | TS-Fluc Anti-Human c-Met scFv (XW-637) CD28-CD3ζ CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-637 | Mouse | 7H-YB-Fluc-EF1a-scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF8511 | TS-Fluc Anti-Human c-Met scFv (XW-638) CD28-CD3ζ CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-638 | Mouse | 7H-YB-Fluc-EF1a-scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF8512 | TS-Fluc Anti-Human c-Met scFv (XW-639) CD28-CD3ζ CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-639 | Mouse | 7H-YB-Fluc-EF1a-scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF8513 | TS-Fluc Anti-Human c-Met scFv (XW-640) CD28-CD3ζ CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-640 | Mouse | 7H-YB-Fluc-EF1a-scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF8514 | TS-Fluc Anti-Mouse c-Met scFv (XW-641) CD28-CD3ζ CAR, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | XW-641 | Mouse | 7H-YB-Fluc-EF1a-scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF8919 | TS-Fluc Anti-Human c-Met scFv (XW-637) 41BB-CD3ζ CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-637 | Mouse | 7H-YB-Fluc-EF1a-scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector |
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION