Creative Biolabs is a contract research organization (CRO) developed by a team of scientists with considerable experience in cell therapy research and development. We are committed to offering the top products and services to clients in the academic and industrial sectors across the world, supporting in the quest of breakthrough scientific discoveries to efficiently advance preclinical and clinical research.
CD30 is a receptor molecule located on the surface of the cell membrane and is known as a cluster of differentiation 30. It is also known as tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 8 (TNFRSF8) and is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNF) family. CD30 protein is a cell surface molecule that is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. Its molecular size is about 120 kDa and consists of 391 amino acids. The outer layer of CD30 contains four c2-type calcium binding sites and a "death domain" structure. These include the TNF receptor associated factor (TRAF) interaction cassette, the intracellular tyrosine kinase structural domain, and the SH2 structural domain. The main role of CD30 is to participate in apoptosis, proliferation, and differentiation, especially in the biology of lymphocytes. CD30 has a specific expression pattern, which is generally little expressed in normal cells and highly expressed in certain malignant tissues. In particular, CD30 expression is generally high in lymphoma types such as Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL) and t-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (T-NHL).
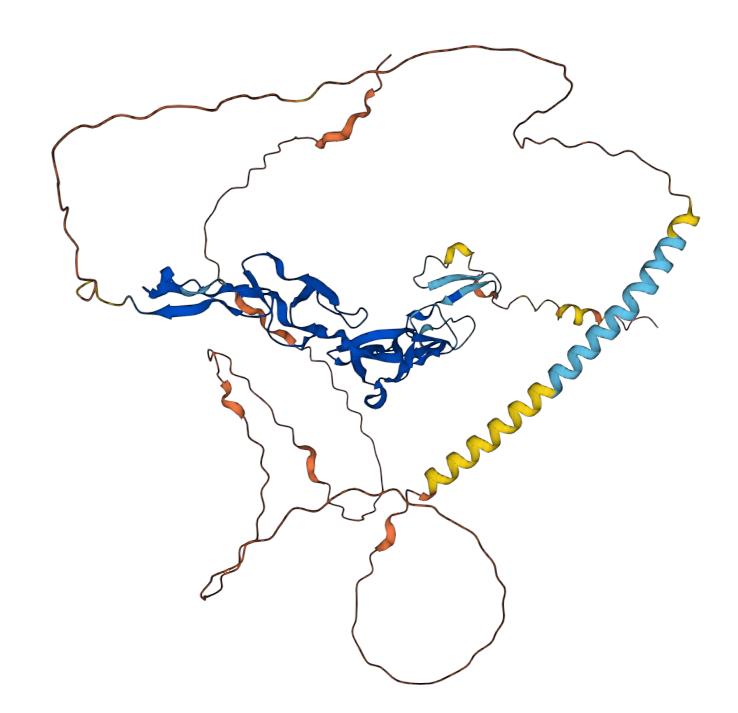 Fig.1 Structure of CD30
Fig.1 Structure of CD30
The CD30 signaling pathway is a series of signaling events regulated by the activation of the CD30 molecule, a member of the tumor necrosis factor family. CD30 signaling pathway is involved in a variety of normal cellular physiological activities, including macrophage activation, T lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation, B lymphocyte survival, and inflammatory cell-mediated inflammatory responses. CD30 is expressed on the surface of T and B lymphocytes, with CD153 (CD30L) as its ligand. When CD153 binds to CD30, it forms a CD30/CD153 complex that initiates downstream signaling pathways.
CD30 triggers signaling cascade responses by inducing TRAF family proteins to bind to CD30, including TRAF1, TRAF2, and TRAF3. Some experimental data suggest that CD30 can ubiquitinate TRAF1 and TRAF2, which further activates the downstream inhibitor kappa B (IκB) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB ) pathways.
CD30 is an important marker found in HL and T-NHL. in anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) patients, certain genetic mutations lead to excessive activation of the CD30 signaling pathway, which affects the proliferation and differentiation of T cells and ultimately leads to tumorigenesis. CD30 expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma is closely related to the grade and prognosis of this tumor. Koda's sarcoma is a rare lymphoma in which CD30 is highly expressed and is closely associated with the growth, proliferation and infiltration of this tumor. CD30 was found to be highly expressed in HL, and patients with CD30-positive Hodgkin's lymphoma have a relatively poor prognosis. Therefore, the study of CD30 CAR-T cell therapy targeting CD30 has become a hot research topic in HL.
CD30 also plays an important role in many inflammatory diseases, such as asthma, hepatitis, and autoimmune diseases. Activation of the CD30 signaling pathway may lead to activation of inflammatory cells and the release of large amounts of inflammatory mediators, exacerbating the development and progression of the disease.
Currently, there is only one FDA-approved CAR T-cell therapy targeting CD30, Adcetris CAR T-cell therapy (also known as SEA-CD30), which was developed by Seattle Genetics and Legendary Biology. It is a CAR-T cell therapy targeting CD30-positive HL and ALCL. The therapy uses CAR-T cells carrying monoclonal antibodies to CD30 that recognize and attack CD30-expressing cells, triggering tumor cell death.
Table 1. Approved CD30 -Targeted CAR Cell Therapy
| Trade name | Indication | Adaptive population | Approved area |
| Adcetris |
1. CD30 positive recurrent or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. 2. CD30 positive recurrent or refractory T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
The treatment is intended for patients who have already received other treatments that have failed or are not tolerable. Specific treatment plans need to be tailored to the patient's situation. | The treatment, developed by Seattle Genetics and Astellas Pharma, is currently only approved by the FDA in the United States and has not been approved for marketing elsewhere |
Ongoing clinical trials of CAR-T cell therapies targeting CD30 are primarily in early-stage trials, including Phases I, I/II, and II. These trials are focused on assessing the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of the therapies. Targeting CD30-positive diseases, mainly including HL and ALCL, these diseases often have readily identifiable CD30 expression and therefore CD30 is selected as a target for CAR-T cells. Different CD30 CAR-T therapies have been developed using slightly different immune vectors and treatment regimens, but they all aim to activate the patient's own immune system to attack CD30-positive tumor cells.
Table 2. Ongoing CD30-Targeted CAR Cell Therapy Clinical Trials
| NCT Number | Title | Status | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Phases |
| NCT05320081 | Camrelizumab Combined With CD30 CAR-T in the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory CD30+ Lymphoma | Recruiting | Lymphoma|Relapse/Recurrence | Huazhong University of Science and Technology|The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University | Phase 2 |
| NCT05352828 | Autologous CD30.CAR-T in Combination With Nivolumab in cHL Patients After Failure of Frontline Therapy | Recruiting | Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma|Hodgkin Disease Refractory|Hodgkin Disease Recurrent | Tessa Therapeutics|Bristol-Myers Squibb | Phase 1 |
| NCT04526834 | Phase 1 Study of Autologous CD30.CAR-T in Relapsed or Refractory CD30 Positive Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma | Active, not recruiting | Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma|Peripheral T Cell Lymphoma|Extranodal NK/T-cell Lymphoma|Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma|Primary Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma (PMBCL) | Tessa Therapeutics | Phase 1 |
| NCT05208853 | An Exploratory Clinical Study Evaluating the Safety and Efficacy of Anti CD30 CAR-T Cells in Patients With CD30+ Relapsed/Refractory Lymphoma | Not yet recruiting | Hodgkin Lymphoma|NK/T Cell Lymphoma|Peripheral T Cell Lymphoma, Unspecified|Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma|Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma|Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma|Mediastinal B-Cell Diffuse Large Cell Lymphoma|Gray Zone Lymphoma | Zhejiang University|Shanghai First Song Therapeutics Co., Ltd | Early Phase 1 |
| NCT04288726 | Allogeneic CD30.CAR-EBVSTs in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory CD30-Positive Lymphomas | Recruiting | Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type|Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma | Baylor College of Medicine|The Methodist Hospital Research Institute | Phase 1 |
| NCT04268706 | Phase 2 Study Evaluating Autologous CD30.CAR-T Cells in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma (CHARIOT) | Active, not recruiting | Hodgkin Lymphoma, Adult|Hodgkin Disease Recurrent|Hodgkin Disease Refractory|Hodgkin Disease, Pediatric | Tessa Therapeutics | Phase 2 |
| NCT02917083 | CD30 CAR-T Cells, Relapsed CD30 Expressing Lymphoma (RELY-30) | Recruiting | Hodgkin's Lymphoma|Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma | Baylor College of Medicine|The Methodist Hospital Research Institute | Phase 1 |
| NCT04952584 | Allogeneic CD30 Chimeric Antigen Receptor Epstein-Barr Virus-Specific T Lymphocytes in Relapsed or Refractory CD30-Positive Lymphomas | Not yet recruiting | Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type|Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma | Baylor College of Medicine|The Methodist Hospital Research Institute | Phase 1 |
| NCT04134325 | Study of PD-1 Inhibitors After CD30.CAR T Cell Therapy in Relapsed/Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma | Recruiting | Relapsed Hodgkin Lymphoma|Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma | UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center|American Society of Clinical Oncology | Early Phase 1 |
| NCT04653649 | CAR T-cells Against CD30 (HSP-CAR30) for Relapsed/ Refractory Hodgkin and T-cell Lymphoma. | Recruiting | Hodgkin Lymphoma, Adult|T Cell Lymphoma | Fundació Institut de Recerca de l'Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau|Josep Carreras Leukaemia Research Institute|Instituto de Salud Carlos III | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT02259556 | CD30-directed Chimeric Antigen Receptor T (CART30) Therapy in Relapsed and Refractory CD30 Positive Lymphomas | Recruiting | Hodgkin's Lymphoma|Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma | Chinese PLA General Hospital | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT05634785 | CD30 CAR for CD30+ NSGCT | Recruiting | Germ Cell Tumor|Nonseminomatous Germ Cell Tumor | UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center|University Cancer Research Fund at Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center | Phase 2 |
| NCT04083495 | CD30 CAR for Relapsed/Refractory CD30+ T Cell Lymphoma | Recruiting | Peripheral T Cell Lymphoma | UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center | Phase 2 |
| NCT02690545 | Study of CD30 CAR for Relapsed/Refractory CD30+ HL and CD30+ NHL | Recruiting | Lymphoma|Lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin|Immune System Diseases|Immunoproliferative Disorders|Lymphatic Diseases|Lymphoproliferative Disorders|Neoplasms|Neoplasms by Histologic Type | UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT03383965 | CD30 Targeted CAR-T in Treating CD30-Expressing Lymphomas | Recruiting | Hodgkin Lymphoma|Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma | Immune Cell, Inc.|Weifang People's Hospital | Phase 1 |
| NCT01192464 | EBV CTLs Expressing CD30 Chimeric Receptors For CD 30+ Lymphoma | Active, not recruiting | Hodgkin's Lymphoma|Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma | Baylor College of Medicine|Center for Cell and Gene Therapy, Baylor College of Medicine|The Methodist Hospital Research Institute | Phase 1 |
| NCT02663297 | Administration of T Lymphocytes for Prevention of Relapse of Lymphomas | Active, not recruiting | Hodgkin Disease|Lymphoma|Lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin|Immune System Diseases|Immunoproliferative Disorders|Lymphatic Diseases|Lymphoproliferative Disorders|Neoplasms|Neoplasms by Histologic Type | UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center|National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) | Phase 1 |
| NCT03602157 | Study of CAR-T Cells Expressing CD30 and CCR4 for r/r CD30+ HL and CTCL | Recruiting | Lymphoma|Immune System Diseases|Immunoproliferative Disorders|Lymphatic Diseases|Lymphoproliferative Disorders|Neoplasms|Cutaneous Lymphoma|Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma|Mycosis Fungoides|Sezary Syndrome|Lymphomatoid Papulosis|Cutaneous T Cell Lymphoma|Gray Zone Lymphoma | UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center|University Cancer Research Fund at Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center|Stand Up To Cancer | Phase 1 |
References
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION