Diabetes is a major disease that endangers human health in the 21st century. The main manifestations of diabetic patients are polydipsia, polyuria and high blood sugar levels, which will increase the risk of organ and tissue lesions in the body, cause various complications and seriously threaten human physical and mental health. The pathogenesis of diabetes is generally insufficient insulin secretion or insulin utilization disorder. The main treatment methods for diabetes include insulin injection and oral hypoglycemic drugs. The control of blood sugar levels relies on medication, which can also alleviate symptoms and improve prognosis. Previous clinical treatment methods could not cure diabetes completely and were prone to increasing the risk of complications. With the rise of cell therapy, scientists are also seeking cell therapies that can treat diabetes. This article mainly introduces the application of cell therapy in diabetes and the latest research progress.
Diabetes is generally caused by insufficient insulin secretion or insulin utilization disorders. According to different pathogenesis, it is mainly divided into two types: Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM): The main cause of the disease is pancreatic islet destruction, usually occurring in children and young people. It is caused by the body's immune system attacking insulin-producing cells, resulting in insulin deficiency. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM): The cause of the disease is damage to pancreatic beta cells. The degree of damage to pancreatic beta cells and their repair capacity are the key to the therapeutic effect of T2DM. The main clinical treatment methods for diabetes include insulin injection and oral hypoglycemic drugs. These drugs are used to control blood sugar levels, alleviate symptoms and improve prognosis. For a long time, traditional treatment methods have not been able to cure diabetes completely and are prone to increasing the risk of complications. With the accelerated development of the global cell therapy track, a new era has been ushered in for the treatment of diabetes.
Based on the pathogenesis of diabetes, the ideal treatment for diabetes is to improve peripheral insulin resistance while promoting the regeneration of pancreatic β cells. Compensating for and restoring the function of insulin-secreting pancreatic β cells is the most promising approach. The essence of cell therapy can be summarized as stem cell therapy, which restores the insulin secretion capacity of pancreatic β cells through the supplementation of exogenous cells or the repair of endogenous cells. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) from various adult tissues are a type of pluripotent stem cells with strong proliferation and differentiation potential, which can serve as a potential source of pancreatic β cells and have received significant attention in the treatment of diabetes. MSCs are matrix-derived non-hematopoietic progenitor cells, derived from various tissues of adults and newborns (such as bone marrow, placenta, etc.). Based on the frequency of colony formation, multi-directional differentiation ability, expansion characteristics, immunophenotype and paracrine function of mesenchymal stem cells obtained from different sources, their different clinical applications are determined.
At present, there are two main pathways for stem cell therapy of diabetes: One is the islet cell transplantation alternative plan: inducing MSCs to differentiate directionally into insulin-secreting cells (IPCs), and transplanting them into the patient's body to promote pancreatic regeneration, replace damaged cells to perform functions, and also alleviate insulin resistance. The second is cell repair. MSCs can also migrate to damaged islet cells and secrete various cytokines and growth factors to participate in the repair of islet cells, thereby promoting the regeneration of islet β cells. MSCs can also promote the transdifferentiation of pancreatic α cells into β cells(Fig1).
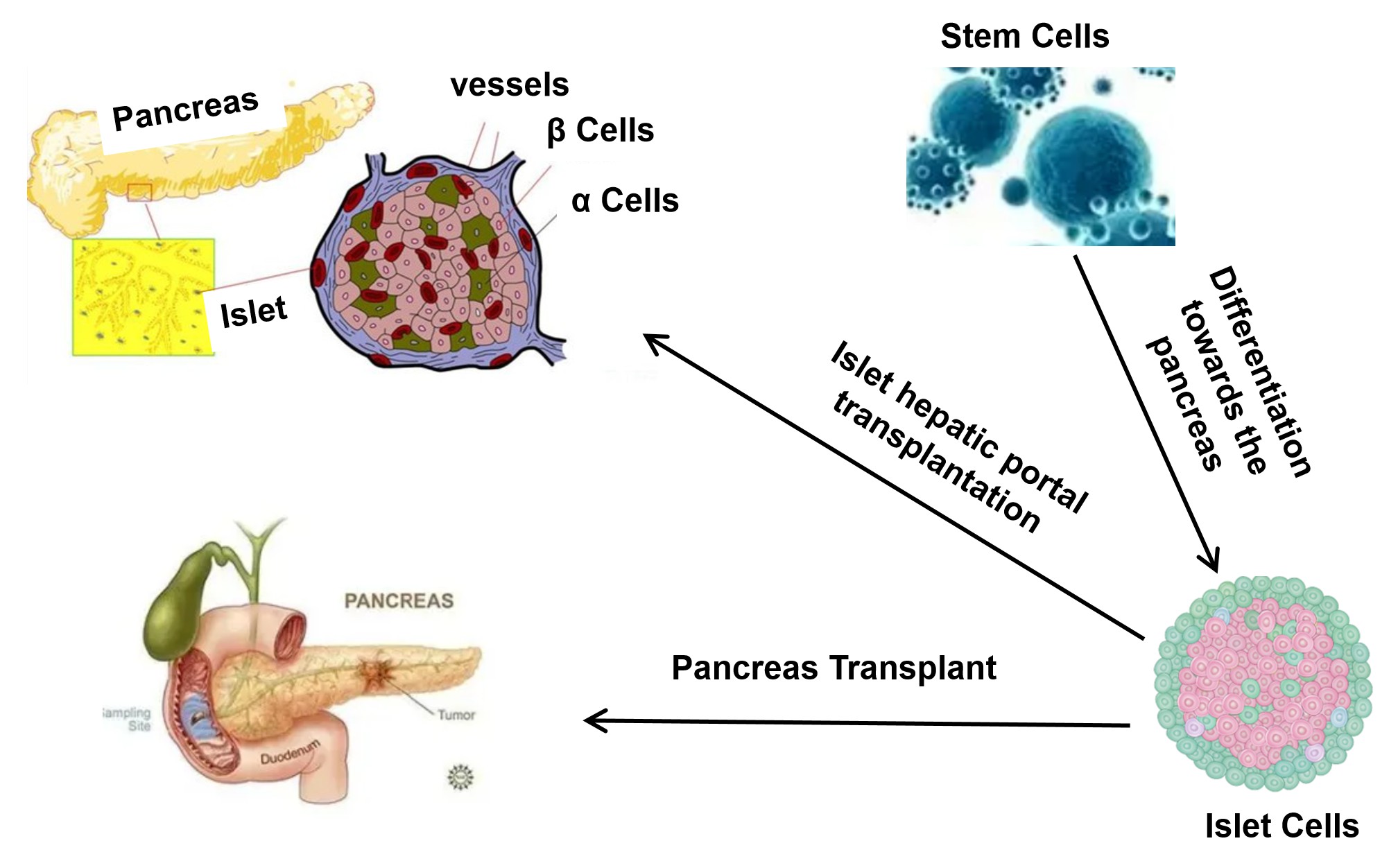 Fig.1 Diagram of Cell Therapy for Diabetes.
Fig.1 Diagram of Cell Therapy for Diabetes.
In recent years, a large number of clinical studies have been conducted on stem cell transplantation for the treatment of T1DM. As early as 2012, a hospital in Nanjing, China, published experimental results showing that autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation could regulate immune active cells and improve the function of β cells. A hospital in Shanghai also reported that autologous hematopoietic stem cells enabled 15 out of 28 patients with T1DM (53.6%) to completely stop using exogenous insulin by improving the function of pancreatic β cells. In 2017, it was reported that stem cell educational therapy was used to treat children with T1DM. After treatment, teenagers from various countries were completely free from insulin therapy. A clinical study published in 2021 on a single intravenous injection of allogeneic umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of T1DM showed that for newly diagnosed T1DM patients, a single intravenous injection of allogeneic umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells is safe and may better preserve pancreatic β cells within the first year after diagnosis compared with standard treatment alone. In 2022, Iran published a Phase I/II randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial on mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for the treatment of newly diagnosed patients with T1DM. The results show that early mesenchymal stem cell transplantation can significantly improve the levels of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and C-peptide in patients, and convert pro-inflammatory cytokines into anti-inflammatory cytokines. In addition, combining exercise with mesenchymal stem cell transplantation can improve blood sugar levels and immune-related indicators. In 2024, the journal Cell published the world's first clinical study reporting the transplantation of islet cells prepared from chemically reprogramming-induced pluripotent stem cells for the treatment of T1DM.
On June 28, 2023, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Lantidra, the first cell therapy drug in the United States, for the treatment of T1DM in adults. It is the world's first cell therapy for diabetes. Allogeneic islet cells made from donor pancreatic cells are used to treat adult patients with T1DM who cannot achieve the target glycated hemoglobin through diabetes management. Some patients with T1DM encounter serious difficulties during treatment. That is, hypoglycemic reactions are always inevitable when using insulin drugs to lower blood sugar, and some patients may also experience asymptomatic hypoglycemia. Lantidra offers new treatment options for such patients. Lantidra is an allogeneic islet cell therapy drug made from pancreatic cells donated by the deceased. The allogeneic pancreatic beta cells infused for the patient secrete insulin. Lantidra is intravenously infused into the hepatic portal vein. Generally, only one dose is required, but some patients may need an additional dose. The allogeneic pancreatic β cells in Lantidra can secrete and produce sufficient insulin on their own, so patients with T1DM do not need to use other insulin drugs to control their blood sugar levels. Patients receiving this treatment must take immunosuppressive drugs to prevent their immune system from damaging the donor cells that secrete insulin.
The current research hotspot is stem cell-derived islet cell therapy. The more mature technology is islet cell transplantation. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy is more suitable for T2DM. Antibody drugs revolutionized treatment methods in the last century. At this juncture, precise cellular immunotherapy will bring about new breakthroughs.
References
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION