North America is active in the field of cell therapy for type 1 diabetes, and has a variety of treatment schemes. In addition to traditional stem cell transplantation, gene editing techniques such as CRISPR-Cas9 are widely used to improve the survival rate and function of transplanted cells. The strict clinical trial system in this area and the strict control of the regulatory authorities on the approval of new therapies have promoted the development of the field in a more standardized and safer direction while ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of treatment. At the same time, there are sufficient research funds in North America, and various research funds and private investments are pouring in, which provides a strong financial guarantee for related research and promotes technical exchanges and cooperation between different research teams. Many research results have entered the stage of clinical transformation, and some early clinical trials have recruited hundreds of patients, covering different ages and stages of disease, which has accumulated valuable clinical data for subsequent large-scale application. For example, in related research, clinical trials using embryonic stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to repair or replace damaged islet β cells in patients have observed a significant improvement trend in insulin secretion function in some patients during long-term follow-up1.
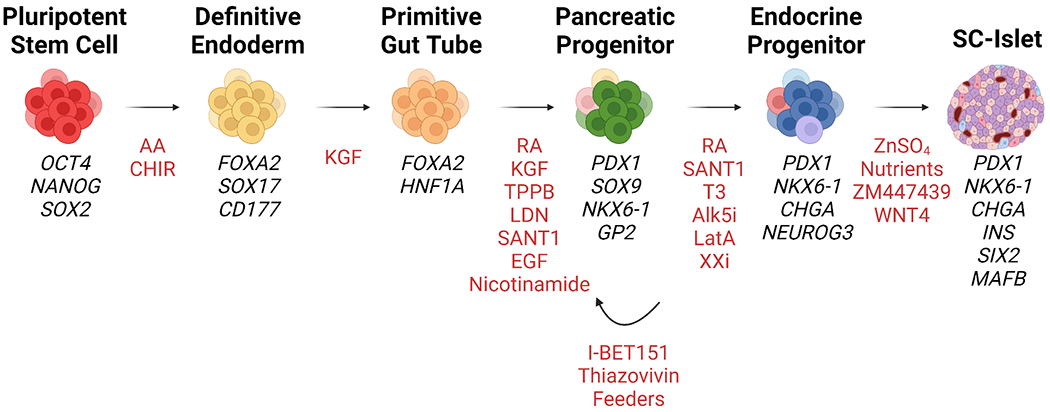 Fig.1 Growth factors and small molecules used during the multistage differentiation of hPSCs to SC-islets1.
Fig.1 Growth factors and small molecules used during the multistage differentiation of hPSCs to SC-islets1.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has unique requirements for the approval of cell therapy for diabetes. Compared with other regions, it pays more attention to the long-term data of the quality, safety and effectiveness of cell therapy products and the results of multi-center trials. There are differences in specific implementation in different countries. Some countries emphasize the traceability of cell sources and ethical compliance in the treatment process. Some countries focus on the innovation and stability evaluation of treatment technology. This regulatory feature urges European research forces to strengthen transnational cooperation, integrate technology and resources through regional framework projects, and carry out multi-center clinical trials to jointly verify the safety and effectiveness of stem cell transplantation in treating diabetes, and accelerate the transformation of research results from laboratory to clinical application. In addition, EMA also gives priority to the review of diabetic cell therapy with great innovation potential by establishing a fast-track mechanism, which encourages research institutions to increase investment in technology research and development. At the same time, the supervision system pays attention to improving patients' participation in clinical trials. Through transparent information disclosure, patients can better understand the risks and benefits of treatment and improve their enthusiasm for participating in clinical trials.
China has made remarkable achievements in the field of diabetic cell therapy. The research team reprogrammed PBMC from patients' blood into autologous iPSC cells, then induced them into endodermal stem cells, and finally reconstructed islet tissue in vitro, successfully curing a type 2 diabetic with severely impaired islet function. The patient has been completely divorced from insulin for 33 months, which has become a major breakthrough in the field of regenerative medicine. Related clinical trials focus on the repair of islet β cells by embryonic stem cells or iPSCs, and some enterprises are also actively deploying autologous regenerative islet transplantation therapy from stem cells. In April, 2025, the self-developed "E-islet 01" was implicitly approved by clinical trials in National Medical Products Administration, becoming the first approved general-purpose allogeneic islet regeneration therapy in China2. In addition, islet cell injection was accepted by IND in July 2024. It adopts the technology of chemical reprogramming induced pluripotent stem cells (CiPS), and its safety has been verified in primate models. It has the characteristics of short treatment cycle, wide indications and controllable cost. Related clinical research on the treatment of type II diabetes mellitus shows that intravenous infusion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells can reduce the demand for exogenous insulin and relieve insulin resistance.
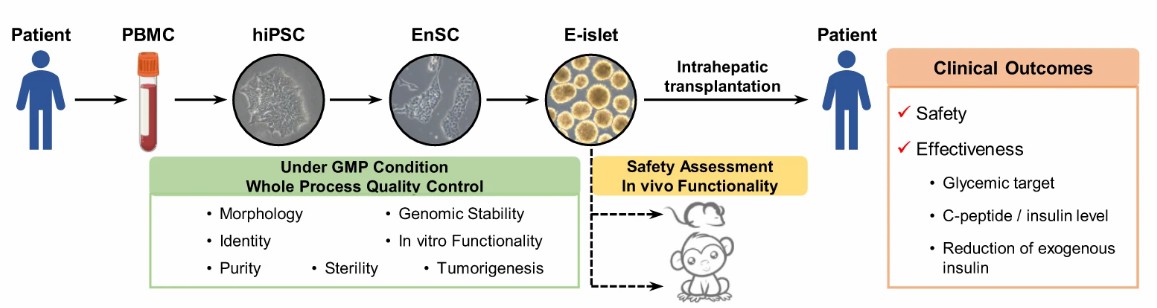 Fig.2 E-islets generation quality control and transplantation safety effectiveness evaluation2.
Fig.2 E-islets generation quality control and transplantation safety effectiveness evaluation2.
Japan is in the leading position in the research of iPS cells in the world, and the clinical trials of iPS cells in the treatment of diabetes have achieved initial results. IPS cells can be obtained from patients' own skin or blood cells, which greatly reduces the risk of immune rejection. The active support of the government, including financial and policy support, has strongly promoted the commercialization of stem cell therapy.
South Korea has invested a lot of resources in the research and development of stem cell technology, and scientific research forces are committed to developing new treatment strategies for diabetic cells, constantly innovating in cell culture and differentiation technology, and improving the efficiency and purity of stem cell differentiation into islet β cells. At the same time, pay attention to the combination of Industry-University-Research and promote the rapid transformation of scientific research results into clinical applications.
In the field of cell therapy for diabetes mellitus, stem cell therapy with research and development subjects has made remarkable progress. In November 2024, it was announced that the phase 1/2 trial was transformed into the phase 3 key trial, and a total of 50 people were recruited. It uses the technology of embryonic stem cells (ESC) to derive islets, which has high differentiation efficiency and purity. The purity of the obtained beta cells is higher than 90%3, and the insulin secretion level can reach 80% of that of natural islets. One batch can prepare 100 million beta cells, meeting the treatment needs of about 50 patients. As of September, 2024, the data of Phase II clinical trials were positive. Eleven of the 12 patients had reduced or stopped using insulin, and four patients were completely free from insulin dependence after more than one year of follow-up. The median glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) of patients decreased to 6.3%, and the time for blood glucose reaching the standard (TIR) increased from 43% to 78%. In order to achieve global distribution, the R&D entity has reached strategic cooperation with other institutions, established special production facilities for producing cell therapy products for treating type 1 diabetes, and is expected to create new jobs to help the commercial production of products and expand in the global market.
At present, cell therapy for diabetes mellitus faces common challenges such as immune rejection, limited cell source and high cost in the world, which creates a broad space for international cooperation. Different regions have their own advantages, and North America has rich experience in technology research and development and clinical trials. Europe's transnational cooperation platform and strict supervision system help to improve the quality of treatment; Asia has made rapid progress in stem cell research and clinical application, and has a huge patient population resources. Through international cooperation, countries can share research data and technical resources, jointly carry out clinical trials and jointly overcome technical problems4. For example, in the optimization of immunosuppression programs, research teams from various countries can exchange experiences and develop safer and more effective methods; In terms of cell source expansion, we will cooperate to explore new ways to obtain stem cells or cell engineering technologies. International cooperation can also promote the rational allocation of resources, reduce the cost of treatment, benefit more diabetic patients, and accelerate the process of diabetic cell therapy from laboratory to clinical application.
References
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION