Europe and the United States are in the forefront of the world in terms of payment policies for cell and gene therapy. The Cell and Gene Therapy (CGT) Access Model introduced by the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) in the United States is groundbreaking. This voluntary framework aims to solve the problem of obtaining cell and gene therapy for the beneficiaries of Medicaid, improve their health outcomes and reduce the cost burden of state Medicaid programs. In this model, CMS negotiates outcome-based agreements (OBAs) with pharmaceutical manufacturers on behalf of participating states. Taking gene therapy for sickle cell disease as an example, CMS and manufacturers will jointly agree on key terms, including price, rebate, curative effect index and patient access policy. Participating States can get supplementary rebates according to the treatment results, and at the same time, they need to implement standardized gene therapy access policies. By linking reimbursement with the actual treatment effect of patients, this policy ensures that payment reflects the real effectiveness of treatment, which not only promotes the accessibility of treatment, but also encourages manufacturers to provide high-quality and high-value products1. European countries are also actively exploring payment strategies suitable for their national conditions. Some countries adopt risk sharing agreement, that is, the payment amount is adjusted according to whether the treatment reaches the preset clinical endpoint. If the treatment fails to achieve the expected effect, the pharmaceutical company will have to bear part of the cost. This method balances the risks of payers and pharmaceutical manufacturers, and promotes the reasonable pricing and wide application of cell and gene therapy products2. At the same time, some European countries have integrated various resources, established joint procurement mechanisms, strengthened bargaining chips with pharmaceutical manufacturers, reduced product prices and improved the efficiency of medical resources3.
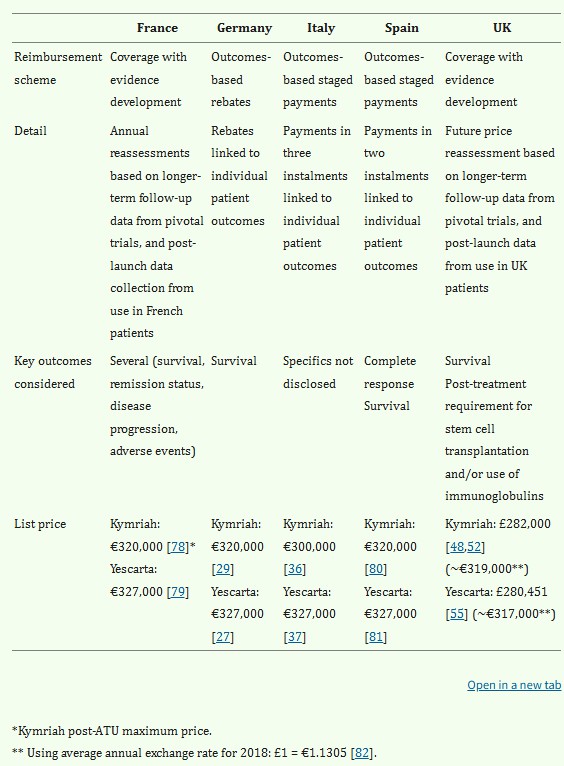 Fig.1 Summary of CAR-T pricing, reimbursement schemes and key outcomes in France, Germany, Italy, Spain & UK2.
Fig.1 Summary of CAR-T pricing, reimbursement schemes and key outcomes in France, Germany, Italy, Spain & UK2.
Tab.1 Comparison of innovative payment mechanisms used for gene therapies across the countries in scope3.
| Country | Innovative payment schemes employed |
| France | CED scheme on national level based on cohort data (from long-term follow-up of pivotal trials and real-world use) |
| Germany | CED scheme on national level based on cohort data (from long-term follow-up of pivotal trials)Rebates (on regional/insurer level) based on IPD |
| Italy | Payments in installments based on IPD |
| Spain | Payments in installments based on IPD |
| England | CED scheme on national level based on long-term cohort data (from follow-up of pivotal trials and real-world use) |
| USA | Rebates (on regional/insurer level) based on IPDLong-term rebate and payment schemes offered by manufacturers; confirmative data on implementation lacking |
The Asian market also shows innovative vitality in the field of cell and gene therapy payment. Through medical insurance negotiations, Japan has included some cell and gene therapy products in the scope of medical insurance reimbursement, and continuously optimized the reimbursement process. For cell therapy of some rare diseases, the government negotiates with enterprises to reasonably determine the reimbursement ratio on the premise of ensuring the product quality and curative effect, which greatly reduces the economic burden of patients and improves the accessibility of treatment. For example, in the gene therapy of some hereditary retinal diseases, the proportion of patients' out-of-pocket expenses has decreased significantly, and more patients have been treated.
South Korea pays attention to building a diversified payment system. In addition to medical insurance coverage, commercial insurance is actively encouraged to participate in the payment of cell and gene therapy. Through policy guidance, commercial insurance companies have developed targeted insurance products, which are complementary to medical insurance. In addition, South Korea has also set up a patient assistance fund, which is jointly funded by the government, enterprises and society, to provide additional support for low-income patients or patients who still have a heavy burden after medical insurance reimbursement, so as to ensure that patients with different economic conditions have the opportunity to benefit from advanced cell and gene therapy technologies.
Large-scale production technology is the key to reduce the cost of cell and gene therapy. Advanced bioreactor systems are widely used, such as disposable stirred bioreactor, which can expand the scale of cell culture and reduce the risk of cross-contamination. Taking the production of CAR-T cells as an example, a large number of active immune cells can be cultivated in a shorter time by using an efficient bioreactor, which improves the production efficiency and dilutes the unit production cost. In addition, the continuous production process is gradually emerging. Compared with the traditional batch production, it can realize the seamless connection of production processes, reduce the idle time of equipment and the loss of intermediate links, and further reduce costs.
The process optimization scheme is devoted to improving the preparation process of cell and gene therapy products. In the process of cell collection and processing, using automatic equipment instead of manual operation not only improves the accuracy and consistency of operation, but also shortens the operation time and reduces the product quality difference and loss caused by human factors. In the process of gene editing, we should optimize the design and delivery method of gene vector, improve the efficiency of gene editing, reduce the risk of off-target effect and reduce the cost of repeated operation caused by editing failure. For example, by optimizing the carrier of lipid nanoparticles (LNP), the therapeutic gene can be delivered to the target cells more efficiently, and the economy of the whole process can be improved.
Long-term efficacy data collection is very important to prove the value of cell and gene therapy. Through large-scale and long-term clinical follow-up research, the health status of patients receiving treatment is continuously tracked. Taking gene therapy for some hereditary diseases as an example, long-term data show that after several years of treatment, patients' symptoms continue to improve, their physical functions are significantly improved, and even the diseases are cured clinically. These data strongly prove that cell and gene therapy can not only alleviate the disease in a short time, but also have a lasting therapeutic effect, which provides a strong value support for its high cost investment4.
Health economics evaluation analyzes cells and gene therapy from cost-effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and other dimensions. The research shows that, although the initial one-time investment of cell and gene therapy is high, in the long run, because it can fundamentally treat diseases and reduce patients' subsequent medical intervention needs, such as hospitalization times and drug use, the overall social medical cost can be reduced. In some tumor cell therapy cases, although the treatment cost is high, compared with the comprehensive cost of traditional multiple radiotherapy and chemotherapy and long-term palliative treatment, cell therapy has a better cost-benefit ratio, and at the same time significantly improves the quality of life of patients, showing good health economic value.
In terms of insurance product design, insurance companies work closely with medical service providers and pharmaceutical manufacturers to develop insurance products specifically for cell and gene therapy. These products design differentiated insurance clauses according to different treatment types, diseases and patients' risk status. For common cell therapy projects, set reasonable insurance coverage and premium to ensure that patients receive adequate economic security when receiving treatment, while maintaining the sustainability of insurance products. For high-risk and high-cost gene therapy, co-insurance and deductible are adopted to balance the responsibilities of insurance companies and patients and improve the feasibility and attractiveness of insurance products5.
Optimizing the reimbursement process aims to improve the convenience and efficiency of reimbursement for cell and gene therapy expenses. Establish a unified reimbursement information platform, integrate patients' medical records, treatment plans, expense details and other data, and realize information sharing and rapid transmission. Medical institutions, medical insurance departments and insurance companies can be connected in real time through this platform, which simplifies the process of reimbursement application, review and payment. For example, after patients receive treatment, medical institutions can directly submit reimbursement applications on the platform, and medical insurance and insurance companies use the platform data to quickly review, reducing manual review links and time delays, so that patients can get reimbursement in time and alleviate economic pressure.
Personalized therapy pricing is a unique challenge for cell therapy services. Because cell therapy is often customized according to the individual situation of each patient, every link from cell collection, processing to transfusion is highly specific, which leads to great cost difference. In order to solve this problem, the pricing method based on cost plus combined with curative effect evaluation is adopted. On the basis of calculating the production cost, the final price is determined by considering the improvement degree of patients' condition and the extension of life expectancy. For personalized cell therapy with significant therapeutic effect and great improvement of patients' quality of life, the pricing should be appropriately increased; Otherwise, it should be adjusted accordingly to reflect the true value of treatment.
Establishing a perfect curative effect monitoring system is an important guarantee to ensure the quality and value of cell therapy. Advanced medical detection technologies, such as gene sequencing, imaging examination and biomarker detection, are used to comprehensively and dynamically monitor the physical condition of patients after treatment. After CAR-T cell therapy, the activity and quantity of CAR-T cells in patients and the level of tumor markers were regularly detected to evaluate the therapeutic effect. Timely discover the possible problems in the treatment process, such as adverse reactions such as cytokine release syndrome, adjust the treatment plan to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the treatment, and provide scientific basis for the subsequent payment decision. Only the treatment that meets the good curative effect standard will be paid in full, encouraging medical service providers to continuously optimize the treatment process.
References
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION