All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive range of CD20 CAR-T products and services to support the development of CD20-targeted CAR-T therapy. Please feel free to contact us for more information on our CAR-T products and how they can benefit your research.
CD20 (Cluster of Differentiation 20) is a transmembrane protein that is primarily expressed on the surface of B cells. CD20 can regulate B cell activation and differentiation, as well as the immune response against foreign substances. CD20 is also important for maintaining the balance between B-cell activation and tolerance, ensuring that the immune system responds appropriately to foreign antigens while avoiding autoimmune reactions. In cancer, CD20 expression is particularly relevant in B-cell malignancies such as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). The presence of CD20 on the surface of these cancerous B cells has therapeutic implications. the use of CD20-targeted therapies has significantly improved the treatment outcomes for individuals with CD20-positive B cell cancers, providing a more targeted and effective approach to fighting the disease.
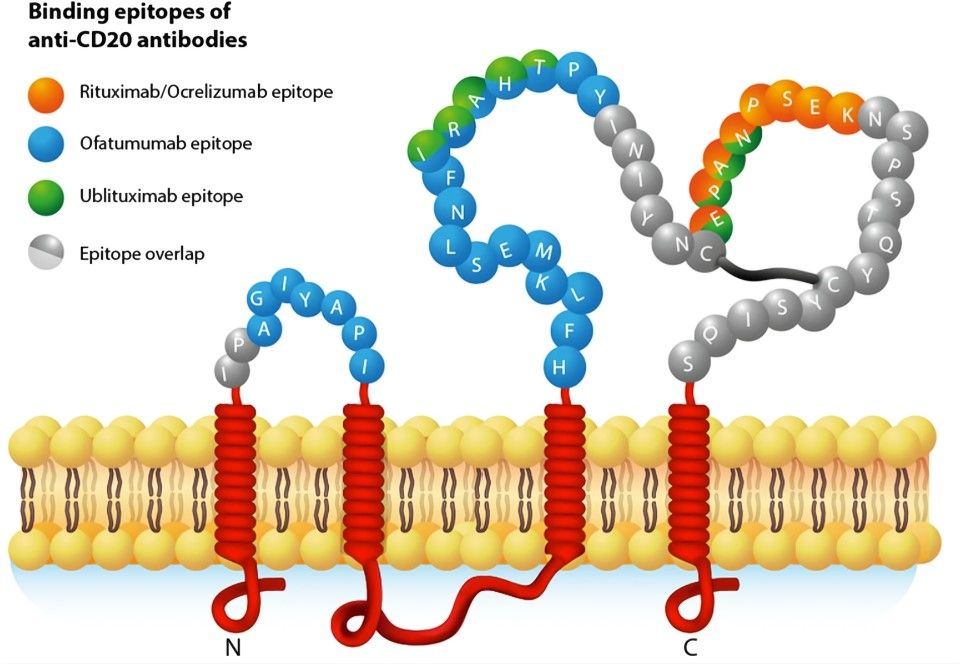
Fig.1 CD20 molecule and binding epitopes of anti-CD20 antibodies.1
Associated Disease
Creative Biolabs offers various CAR-T expression tests to ensure that the CAR construct is successfully expressed in the modified immune cells and to quantify its level of expression. As shown in Fig.2, the CD20 CAR expression was assessed by flow cytometry (Fig.2A) and western blot (Fig.2B). Combining multiple assays can provide a comprehensive assessment of CAR expression at both the protein and gene expression levels.
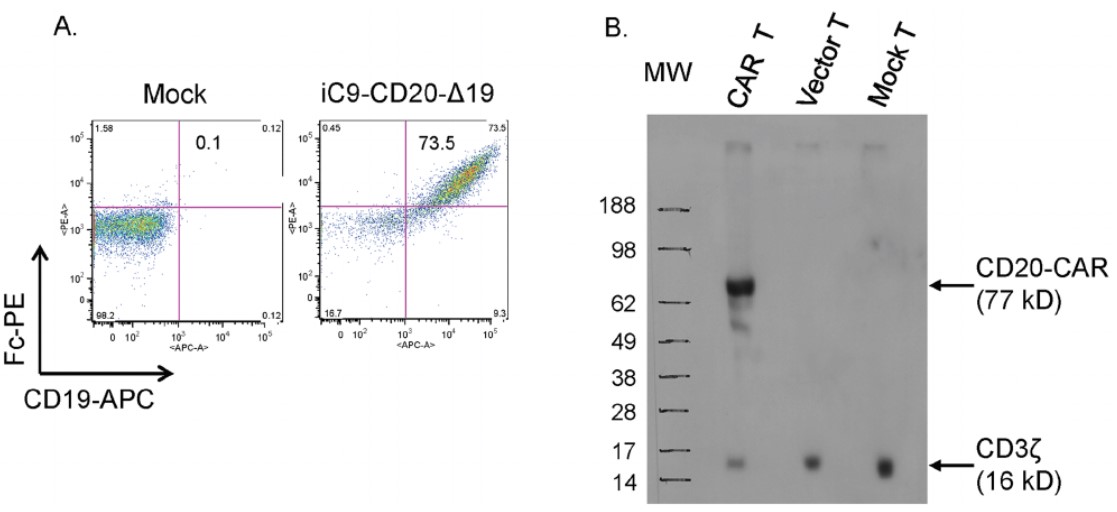
Fig.2 Level of CD20-CAR expression was evaluated by flow cytometric analysis (A) and western blot analysis (B).2
The CAR-T proliferation test provides valuable information about the expansion and activity of CAR-T cells. We provide several common types of proliferation tests, including cell counting, flow cytometry and thymidine incorporation assay.
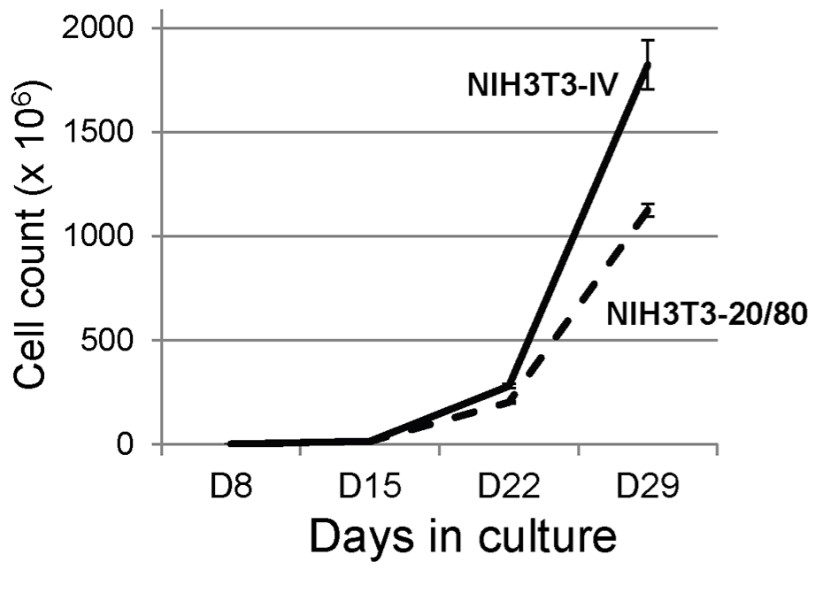
Fig.3 Expansion of CD20-CAR expression using NIH3T3-based artificial APCs.2
In vitro cytokine release tests play a critical role in characterizing and monitoring the activity of CAR-T cells. Our cytokine release tests allow for assessing the release of various cytokines, such as IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-2, and IL-6.
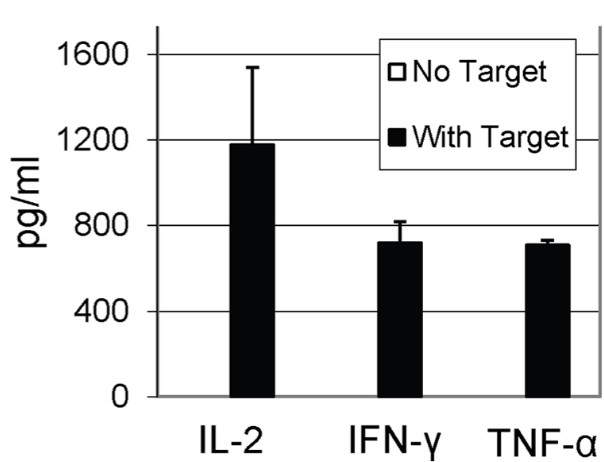
Fig.4 Cytokine production of anti-CD20 CAR-T cells co-cultured with Ramos cells.2
The cytotoxicity of CAR-T cells can be assessed by measuring target cell viability or death using different methods. These include flow cytometry with staining for apoptotic or dead cells, cell counting, or measuring the release of specific cytotoxicity markers such as lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) from damaged cells.
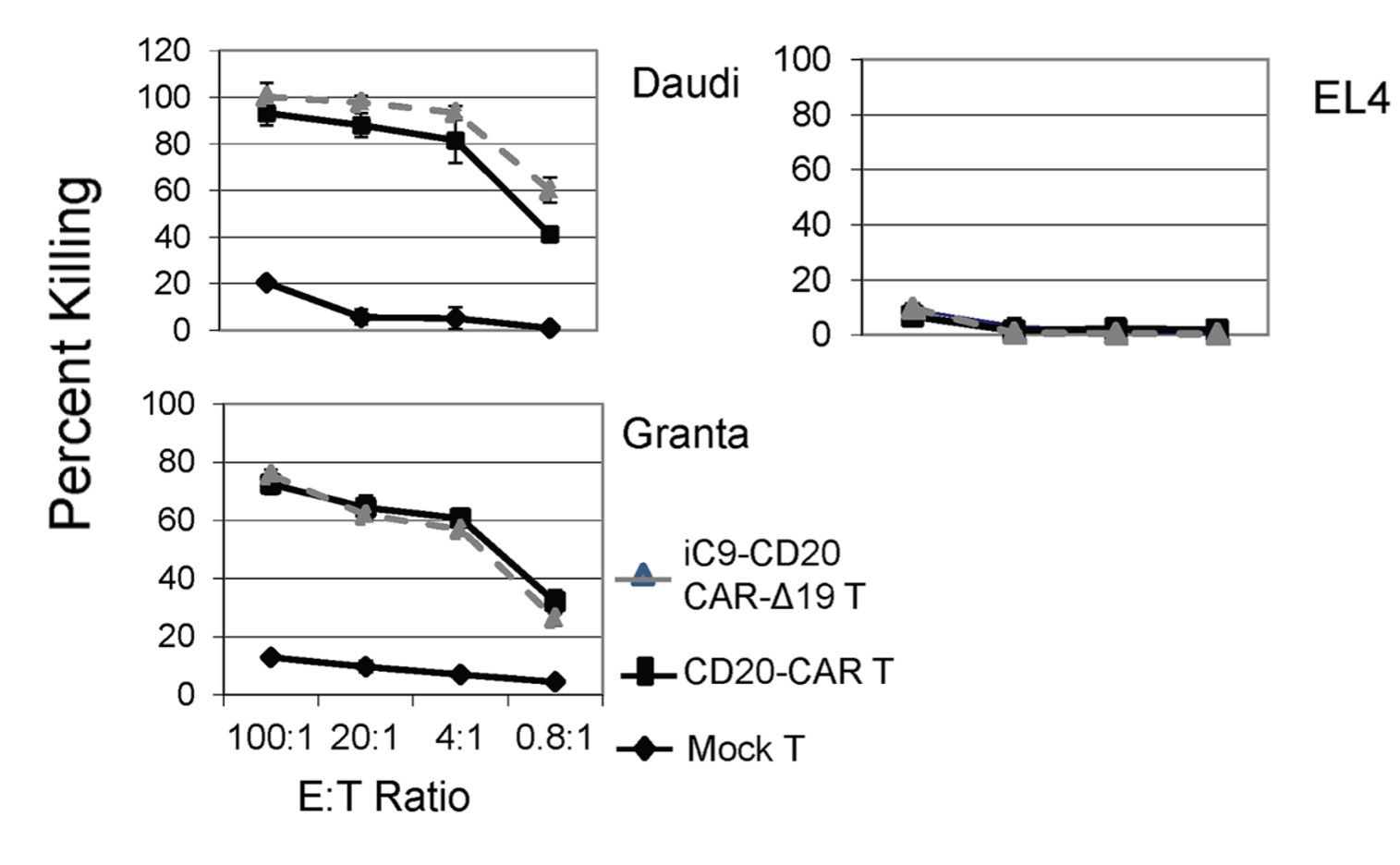
Fig.5 The specific killing activities of anti-CD20 CAR-T cells against EL4, Daudi, and Granta cells.2
Creative Biolabs has the ability to generate tumor-bearing animal models to assess the anti-tumor efficacy of CD20 CAR-T cells. We measure various parameters including tumor size, tumor volume, tumor weight, and overall survival of the animals. Our expertise in mouse models and CAR-T therapies allows us to adapt and refine our methods to ensure that our clients receive the most accurate and relevant data possible.
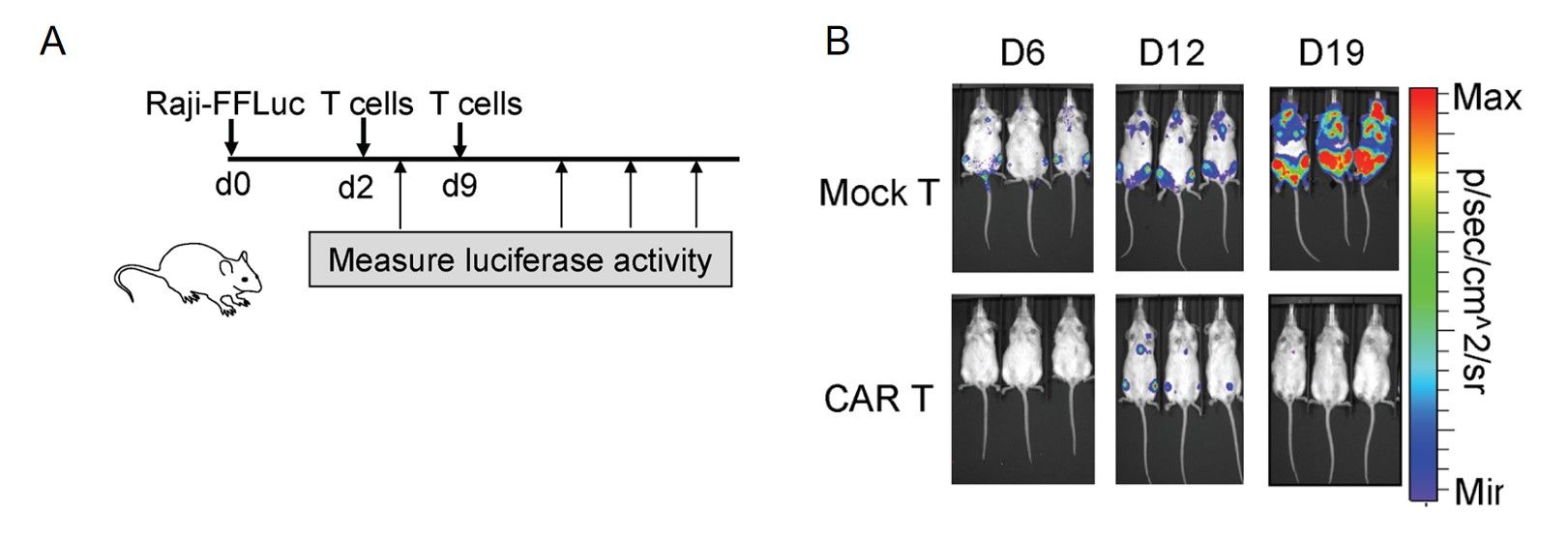
Fig.6 Anti-tumor activity of anti-CD20 CAR-T cells in a Raji tumor xenogeneic NOD/SICD model.2 (A) Schematic of a Raji tumor xenogeneic NOD/SICD model. (B) Tumor growth was monitored by BLI.
References
 Loading...
Loading...
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION