Cell and gene therapy (CGT) is reshaping the modern medical pattern. According to the latest statistics, there are more than 2,800 clinical trials of CGT in the world, in which cell therapy has made a breakthrough in the field of tumors and degenerative diseases1. This article will discuss the key technological innovation, industrialization challenges and future development direction in the field of cell therapy.
Allogeneic universal cell therapy (such as UCAR-T) has achieved a major leap forward through gene editing technology mediated by CRISPR-Cas9. By knocking out HLA-I/II loci, host rejection can be greatly reduced, which makes the cells reduce the risk of being attacked by the immune system after entering the patient's body, to play a more stable therapeutic role. At the same time, the key operation of TCR gene deletion effectively reduces the risk of graft versus host disease (GVHD). This is of great significance to patients receiving allogeneic transplantation and reduces the probability of serious complications after transplantation.
According to the latest clinical data, UCAR-T targeting CD19 performs well in relapsed/refractory B-cell malignant tumors. With an objective response rate (ORR) of 67%, over two-thirds of patients see significant improvements after treatment—their tumors shrink, or associated symptoms become less severe. What's more, the median progression-free survival (mPFS) hits 8.3 months, meaning that on average, patients' disease doesn't progress for 8.3 months post-treatment, buying them valuable time to fight the illness.
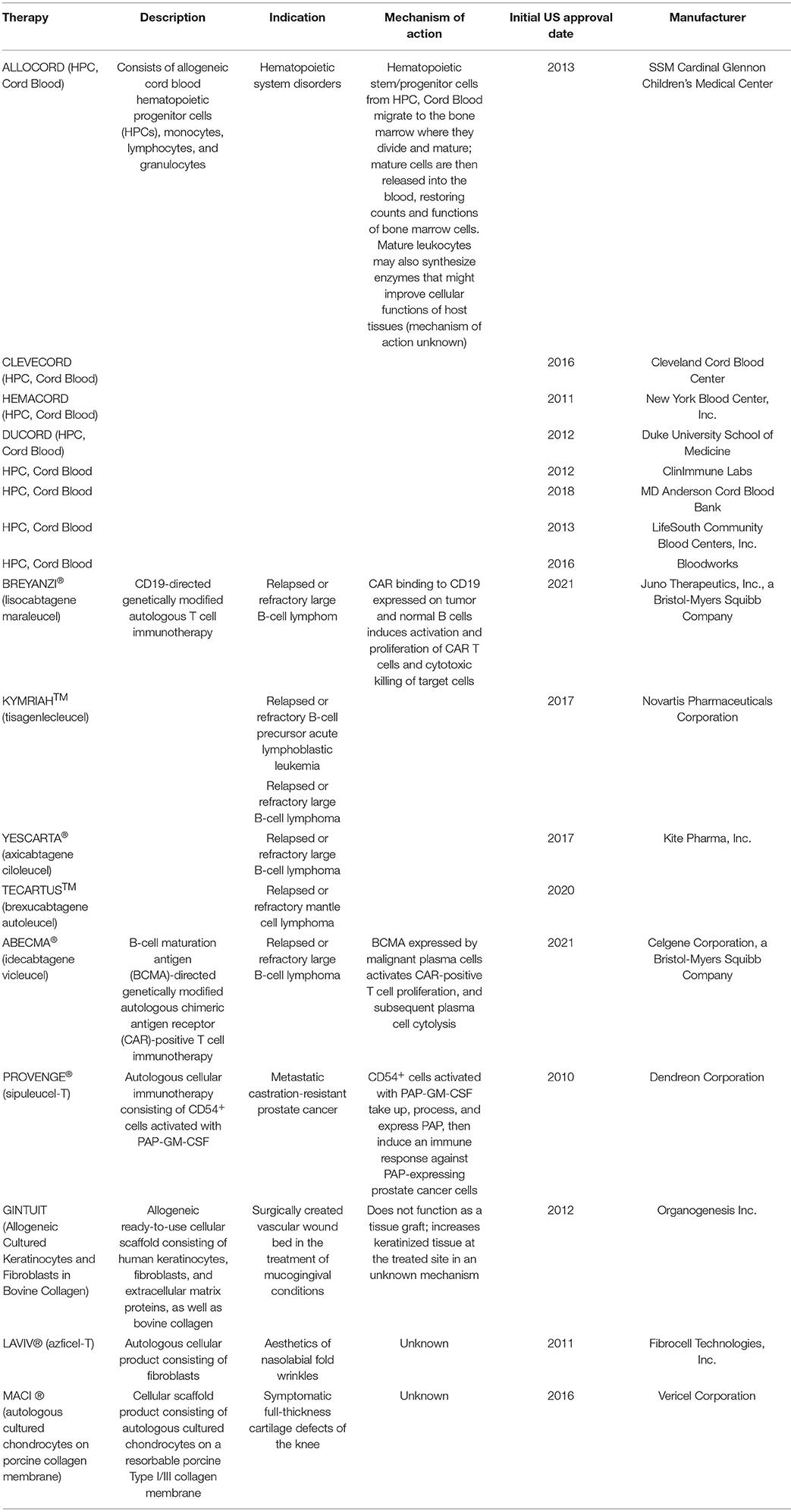 Fig.1 FDA-approved cell therapy products1.
Fig.1 FDA-approved cell therapy products1.
Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy has great potential, but it also faces many key challenges. Cell heterogeneity is one of them. The development of single cell sequencing technology reveals the transcriptome differences of MSC from different donors. This means that even the same type of mesenchymal stem cells has different gene expression due to different donors, which may affect the stability and consistency of therapeutic effect. In terms of large-scale production, the traditional production mode is difficult to meet the growing clinical needs. However, the emergence of 3D bioreactor system has brought a turning point, which can increase the cell yield by 15 times. By simulating the microenvironment in vivo, 3D bioreactor provides more suitable growth space for cells, promotes cell proliferation and differentiation, greatly improves the production efficiency of stem cells, and lays a foundation for the wide application of stem cell therapy.
The latest research shows that distributed manufacturing mode has obvious advantages. It can shorten the product transportation time to 8 hours, which is very important for some cell therapy products with high timeliness requirements. For example, some immune cell therapies need to be processed and transfused in a short time after collecting patients' cells, and shortening the transportation time can ensure the activity and therapeutic effect of cells to the greatest extent. At the same time, this model reduces the risk of cold chain failure by 73%. Cell therapy products require strict environmental conditions such as temperature during transportation, and the failure of cold chain may lead to cell death or inactivation. The distributed manufacturing mode effectively reduces this risk by reducing transportation distance and time.
Real-time monitoring technology based on the Internet of Things provides a strong guarantee for the logistics and transportation of cell therapy products. This state-of-the-art technology limits temperature swings to within 0.5℃, keeping cells in an optimally suited thermal environment throughout every stage of transportation. Such precise temperature regulation is critical for maintaining cellular activity and functionality—even the smallest deviation outside this range could cause irreversible damage, compromising the cells' quality and their effectiveness in subsequent use. In addition, the geographical location tracking accuracy reaches 10 meters , which enables logistics personnel and medical institutions to grasp the location information of products in real time and prepare for receiving and using them in time.
Remarkable breakthroughs have been made in the field of in vivo reprogramming technology. Through mRNA-LNP delivery of reprogramming factor (Oct4/Sox2/Klf4/c-Myc), scientists have successfully achieved in-situ myocardial cell regeneration. This technology brings new hope to patients with heart disease. In the past, the treatment methods for myocardial injury were relatively limited, but in vivo reprogramming technology is expected to directly promote myocardial cell regeneration, repair damaged heart tissue and improve heart function in patients.
Machine learning model has shown great application potential in the field of cell therapy. It can predict the response rate of CAR-T treatment (AUC=0.89), and help doctors to judge the possible response of patients to CAR-T treatment in advance. For patients with low response rate, the treatment plan can be adjusted in advance to improve the treatment effect. At the same time, the model can also predict the risk of cytokine release syndrome (CRS). CRS is a serious complication that may occur in CAR-T treatment. By predicting the risk in advance, doctors can take preventive and coping measures to reduce the treatment risk of patients.
Organ-like disease model plays an increasingly important role in cell therapy research. Tumor organs can predict drug sensitivity with an accuracy rate of 92%2. This means that medical practice is undergoing a revolutionary change: when oncologists choose treatment plans for cancer patients, they can first use tumor-like organ models for drug testing. These tests can guide doctors to select the most effective drugs accurately and abandon the "trial and error" prescription mode. Its effect is remarkable: the treatment effect is better, the pain of patients is alleviated, and the economic burden is also alleviated.
This effect is not limited to the field of tumor. The neural organ model can simulate the progress of Alzheimer's disease and provide valuable tools for researchers. They can not only reveal the root cause of the disease, but also accelerate the research and development of innovative therapies-opening up a new way for the treatment of this devastating disease.
The emergence of new high-fidelity Cas9 variants has greatly improved the security of gene editing. The off-target rate is reduced to 0.01%, which greatly reduces the accidental modification of non-target gene regions in the process of gene editing, and reduces the potential risks caused by off-target effect, such as causing other diseases3. At the same time, the editing efficiency is more than 90%, which ensures that the effectiveness of gene editing is not affected while the safety is improved, making the gene editing treatment safer and more reliable.
Germany's "gene therapy fund" adopts the method of five-year installment payment, which reduces the pressure on patients to pay high treatment costs at one time and enables more patients to have the opportunity to receive cell therapy. The NHS's curative effect-based payment scheme in Britain links the payment amount with the treatment effect, encouraging medical institutions and pharmaceutical companies to continuously improve the quality of treatment and ensure that patients can really benefit from treatment.
It is estimated that by 2030, the cure rate of gene editing in vivo is expected to increase to 95%. With the continuous optimization and improvement of gene editing technology, scientists can repair pathogenic genes more accurately and fundamentally cure more hereditary diseases and incurable diseases. The emergence of automated factories will reduce the production cost by 80%. Automated production can reduce human errors caused by manual operation and improve production efficiency. In addition, the combination of mass production and cutting-edge automation technology will greatly reduce the cost of cell therapy products-so that more patients can get such treatment.
In clinical application, cell therapy is expected to cover 50% of malignant tumors, provide more treatment options for tumor patients and improve their survival rate and quality of life. At the same time, it can treat 50 kinds of monogenic diseases, improve the condition of patients with monogenic diseases by repairing or replacing abnormal genes, and even achieve complete cure.
References
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION