Cell therapy refers to the transplantation or input of normal or bioengineered human cells into the patient's body. The newly input cells can replace damaged cells, mainly stem cell therapy, or immune cell therapy with stronger immune killing function, thereby achieving the purpose of treating diseases. With the rapid development of biotechnology, cell therapy has become increasingly mature. The production of emerging cell therapy products has also received attention. The cell therapy industry has developed rapidly, and cell manufacturing technology has entered the "fast lane".
Cell therapy products mainly refer to categories such as T cells, NK cells, and stem cells that have undergone genetic modification. Taking chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy as an example, the principle is to obtain T cells from the patient's body, modify the CAR protein gene using gene editing technology or lentivirus, and then re-inject them into the patient's body after amplification to generate immune killing of tumor cells. The main production process is as follows(Fig.1):1,2
1. Cell collection and screening: The starting point of cell therapy is the collection of cells. Cell collection can be carried out through methods such as bone marrow puncture, peripheral blood collection, and fat extraction. After collection, the cells need to undergo appropriate processing, such as removing impurities and separating the cells. Subsequently, cell separation techniques such as centrifugation, flow cytometry, magnetic bead separation, and colloid dialysis were adopted to separate the cells.
2. Cell activation: After cell isolation, cell activation is carried out. Cell activation is achieved by generating major specific signals through cell receptors or other co-stimulatory signals. Autologous antigen-presenting cells, such as dendritic cells (DCS), are endogenous activators of T-cell responses. Activation triggers cell division, thereby promoting gene transduction. The efficiency of subsequent gene transduction is affected by the way cells are activated.
3. Cell modification and engineering: The ways of cell modification include lentiviral systems, gene editing technology and electroporation technology. After obtaining stable cells through genetic modification, large-scale in vitro expansion is still required to obtain the therapeutic dose needed. Cells can be expanded through different containers, including T-flasks, plates or culture bags, as well as bioreactors. Amplification using a swing bioreactor is currently the main culture method. In addition, the automated cell production equipment can also produce a large amount of CAR-T. This kind of automated equipment can greatly reduce manual operation compared with the swing bioreactor.
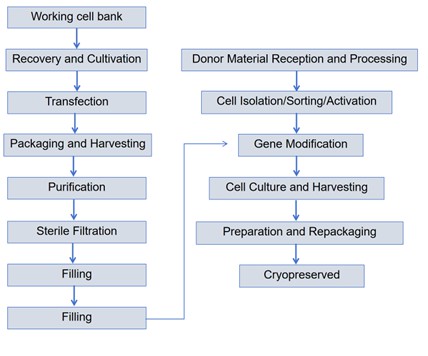 Fig.1Production process of GMP cell therapy products (CAR-T)
Fig.1Production process of GMP cell therapy products (CAR-T)
The core requirements of GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) in cell therapy include that the production of cell therapy products (such as CAR-T and stem cell therapies) must be carried out under strict adherence to GMP conditions to ensure the safety, consistency, and effectiveness of the products. The core requirements of GMP cell therapy are as follows:
The control requirements for production environment and facilities require that key operations (such as cell culture and packaging) be conducted in an A-class (ISO 5) laminar flow environment, with the background environment being B-class (ISO 7). Regular environmental monitoring (particle suspension, microbial limits, surface colony detection) is carried out. A closed production system is established, and automated equipment (such as Cocoon, CliniMACS Prodigy) is used to reduce the risk of human contamination, prevent cross-contamination during the production process, thoroughly clean after single batch production, and avoid cross-contamination of different donor cells or products (such as the individualized characteristics of CAR-T). Raw materials must be compliant and traceable, with full records from donors to the final product (such as the ISBT 128 coding system). The production process must be validated to prove that the production process (such as cell expansion, virus transduction) can stably produce products that meet the standards (such as a viability rate of ≥80%, CAR expression rate of ≥30%). Sterility testing (in accordance with <USP 71> or <EP 2.6.27>), efficacy testing (such as the cell killing activity of CAR-T, the osteogenic/adipogenic differentiation ability of stem cells), and purity testing (flow cytometry analysis of CD3+, CD34+, etc. markers) are conducted for intermediates and final products. Detailed records of production steps, parameters, and deviation handling (such as corrective measures when the culture temperature exceeds the limit) are made. Equipment operation follows standard procedures, and relevant personnel are trained. Supervision must comply with standard regulations. With the popularization of automation (such as fully enclosed production) and digitalization (such as MES systems), the GMP standards will continue to drive the industrialization process of cell therapy.
CDMO (Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization) plays a crucial role in the field of cell therapy, providing full-process support from early development to commercial production for pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology companies and research institutions. The main functions of CDMO in the field of cell therapy are as follows:Provide personalized treatment support, conduct process development, optimize key steps such as cell separation, gene editing (e.g. CRISPR), amplification, cryopreservation, etc. to increase production volume and cell activity. Introduce closed automated systems (such as CliniMACS, Xuri bioreactors), reduce manual operations, and lower the risk of contamination. CDMO can carry out compliant production and quality management and achieve large-scale production and cost reduction and efficiency improvement.
CMC (Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls),it covers aspects such as drug production process research, impurity research, quality research, stability research, and process validation. It is an important part of drug research and development, providing technical and material support for both non-clinical and clinical research trials, and runs through the entire life cycle of drug research and development and production. CMC is the cornerstone of cell therapy moving from the laboratory to clinical and commercialization, conducting tests and evaluations on the chemical properties of cell products such as activity, purity, and stability; optimizing production processes to ensure the quality and consistency of cell products; and establishing strict quality control standards for the entire process monitoring of cell products. CMD (Contract Manufacturing and Development, Contract Manufacturing and Development Organization) plays a role in multiple key aspects before the clinical application of cell therapy, including process development, GMP production, quality control, and regulatory support, directly influencing the safety, efficacy, and commercial feasibility of the product. CMD conducts research on the pharmacology, toxicology, and pharmacokinetics of cell therapy, evaluating its safety and effectiveness. Through animal experiments, it observes the physiological functions, tissue organs of animals, the distribution and metabolism of cells in the body, providing scientific basis for the entry of cell therapy into clinical trials. With technological advancements (such as gene editing, AI-driven process optimization), CMC strategies will continue to evolve to support safer and more efficient cell therapy products on the market. Clinical Research Coordinators (CRC, Clinical Research Coordinator) undertake core responsibilities such as cross-departmental coordination, data quality assurance, and subject safety monitoring in cell therapy clinical trials, serving as a key hub connecting researchers, sponsors, laboratories, and regulatory agencies.
Cell therapy is currently one of the most watched and fastest-growing innovative medical fields. Although the development prospects of the cell therapy industry are very broad and it is an inevitable trend in the future, there are still many challenges in the commercialization process of cell therapy products at present. The process of cell therapy products remains a challenge for the cell therapy industry, involving the preparation of gene vectors, the selection of cell preparation platforms, and the characterization of cell therapy products. The high cost of CAR-T stems from the complex process of individualized preparation (viral vectors, cold chain transportation, etc.). Enterprises can reduce costs and increase efficiency from two aspects: developing general technologies (such as allogeneic CAR-T) and introducing automated production equipment to shorten the preparation cycle. The cell therapy industry is at a crucial turning point from technological breakthroughs to commercial application. CAR-T therapy has gradually moved from "sky-high priced drugs" to accessible treatment through the expansion of indications and universal technological innovations. Stem cell regenerative medicine, with its wide range of application scenarios, has become a potential Nemesis of chronic diseases and aging-related diseases. In the next three years, the industry will present three major trends: First, the integration of technologies will accelerate. The combination of CAR-T with stem cells and gene editing (such as CRISPR) will give rise to safer and more efficient therapies. Second, the payment system is diversified. The synergy of medical insurance, commercial insurance and financial tools is expected to cover more than 50% of the treatment costs. Thirdly, with the intensification of global competition, Chinese enterprises need to strike a balance between independent innovation (such as target discovery) and international cooperation (such as mutual recognition of clinical data).
References
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION