Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are a group of myeloid-derived natural immune cells with inhibitory functions and contribute to an immunologically permissive microenvironment for cancer cells. Immature MDSCs can differentiate into multiple mature myeloid cells such as mature granulocytes, macrophages, or dendritic cells. TME not only affects the function of MDSCs but also changes the pattern of MDSCs differentiation. Activated MDSCs are also related to aspects of tumor progression. The presence of MDSCs in the TME might decrease the efficacy of immunotherapies and are responsible for the poor prognosis of chemotherapy. MDSCs can cause tumor immune tolerance by inhibiting both natural immunity and T cell adaptive immunity. Therefore, targeting MDSCs is a promising approach to reshape TME and improve immunotherapies.
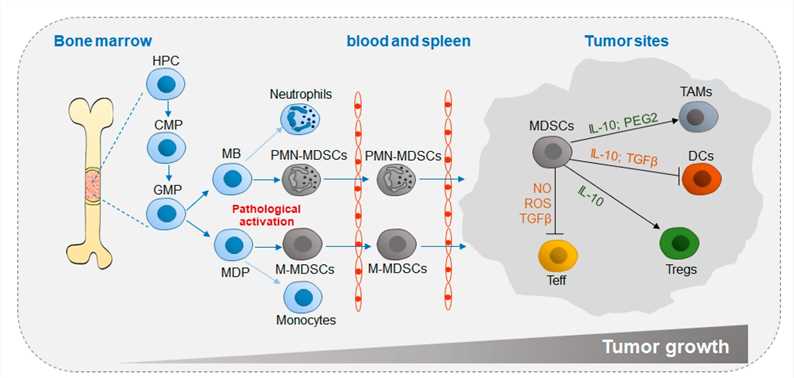 Fig.1 Differentiation and accumulation of MDSCs in the TME.1,3
Fig.1 Differentiation and accumulation of MDSCs in the TME.1,3
MDSCs can suppress both innate and adaptive immune responses. T-cell activation is suppressed by MDSC-mediated deprivation of L-arginine and cysteine from the TME, production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and peroxynitrite, downregulation of L-selectin, and the induction of T regulatory (Treg) cells through MDSCs IL-10 and TGF-β production. MDSCs may make up a substantial fraction of the tumor-infiltrating macrophage pool, therefore, MDSCs may be the precursors of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). And both populations appear to play fundamental roles in shaping the immunosuppressive environment in solid tumors. MDSCs also suppress natural killer (NK) cell cytotoxicity via the production of ROS/ nitric oxide (NO) and suppress IFN-γ production and inhibit M1 macrophages. Moreover, MDSCs inhibit antitumor responses through the interaction of immune checkpoint molecules.
MDSCs promote tumor progression also through non-immune activities. MDSCs actively participate in tumor metastasis by inducing EMT, increasing the invasiveness and stemness of tumor cells, and stimulating angiogenesis, including the secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9.
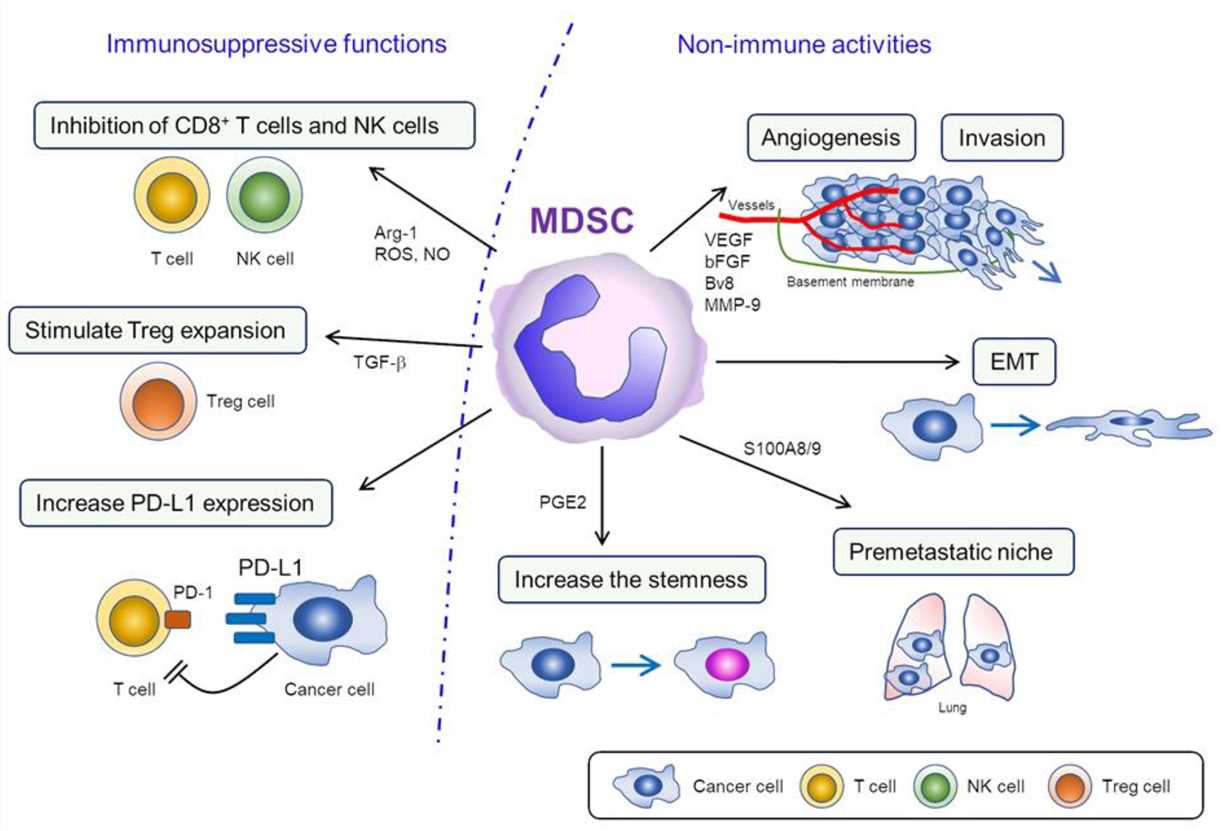 Fig.2 Functions of MDSCs in the TME.2,3
Fig.2 Functions of MDSCs in the TME.2,3
MDSCs play crucial roles in shaping immunosuppressive TME and their accumulation is a major obstacle for tumor immunotherapy. Therefore, MDSCs have been explored as an important immunotherapeutic target to enhance anticancer responses.
MDSCs are actively recruited to primary and metastatic tumor sites by chemokines produced by the tumor with little specificity. Targeting chemokine receptors on MDSCs could be applied to prevent the migration and accumulation of MDSCs in the TME. For example, treatments targeting cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2)/PGE2 signaling and CSF-1R/CSF-1 might prevent MDSCs recruitment to the tumor site to retard tumor growth and improve T-cell activity.
Regulation of the maturation and differentiation of MDSCs will be potential strategies to reshape the immunosuppressive TME. Multiple agents such as RUNX1, all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), IL-12, CCL5, drive MDSCs differentiation into mature myeloid cells. MDSCs could also be depleted with HSP90 (heat shock protein 90) inhibitors.
Blockade of MDSCs immunosuppressive mechanisms represents the major therapeutic approach to re-establishing T-cells activity and immunotherapy success. For example, MDSCs upregulated the expression of immune suppressive factors such as ROS, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and arginase1 (ARG1) to reduce T cells antitumor activity. Thus, those factors above become important therapeutic targets.
Creative Biolabs is dedicated to assisting our clients to develop reshaping TME strategies. We are confident in providing services with the best quality to assist in accomplishing your programs' goals. For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us or directly sent us an inquiry.
References
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION