T cells can take part in a variety of immune responses in cancer. Among them, cytotoxic CD8+ T cells (CTLs) are a major population of immune cells that control and clear tumor cells. However, due to persistent antigen exposure and the immunosuppressive TME, the function of T cells becomes compromised, termed T cell dysfunction. Immune inhibition renders T cells dysfunctional in the tumor microenvironment (TME). T cell anergy, exhaustion, and senescence are all considered different types of T cell dysfunction.
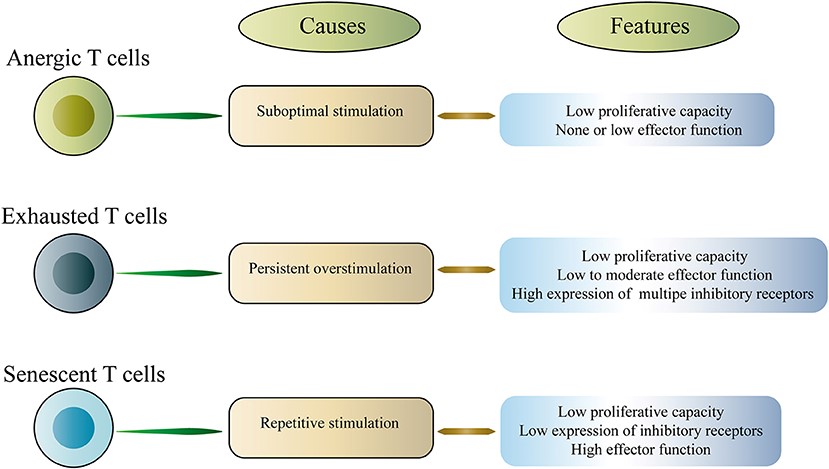 Fig.1 Classification of dysfunctional T cells.1,3
Fig.1 Classification of dysfunctional T cells.1,3
In the TME, cancer cells achieve immunosuppression through the recruitment of immunosuppressive cells (regulatory T cells (Treg) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells) and the expression of ligands for coinhibitory checkpoint molecules such as programmed death-1 (PD-1). Treg cells are considered immunosuppressive cells of the TME. High Treg cell infiltration in the TME is involved in unfavorable prognosis in patients with various types of cancer. Mechanisms of suppression by Treg include cell contact-dependent mechanism and independent mechanism. Contact-dependent mechanisms include interactions between cognate receptors and ligands such as CTLA-4:CD80/CD86, LAG-3:MHC II, and Nrp-1:MHC II. Interactions of these can result in impairing the maturation of dendritic cells (DCs) and inhibiting activation, proliferation, cytokine production, and survival pathways of effector T cells through interactions with antigen-presenting cells. In addition, Tregs also employ contact independent mechanisms of suppression mediated through the secretion of inhibitory cytokines and local competition for growth factors. Therefore, depletion of Treg cells or the control of Treg cell functions could be promising immunotherapies.
The immunosuppressive TME has implications for T cell function in terms of differentiation and exhaustion. The presence of T cells in TME correlates with favorable treatment and prognosis. With the rapid development of immunotherapy, enhancing T cell function is a promising strategy in antitumor immunotherapy and reverse immunosuppressive TME. A sufficient infiltration into the TME and successful activation of effector T lymphocytes against tumor cells have been identified as predictors for responses to T cell-based immunotherapies.
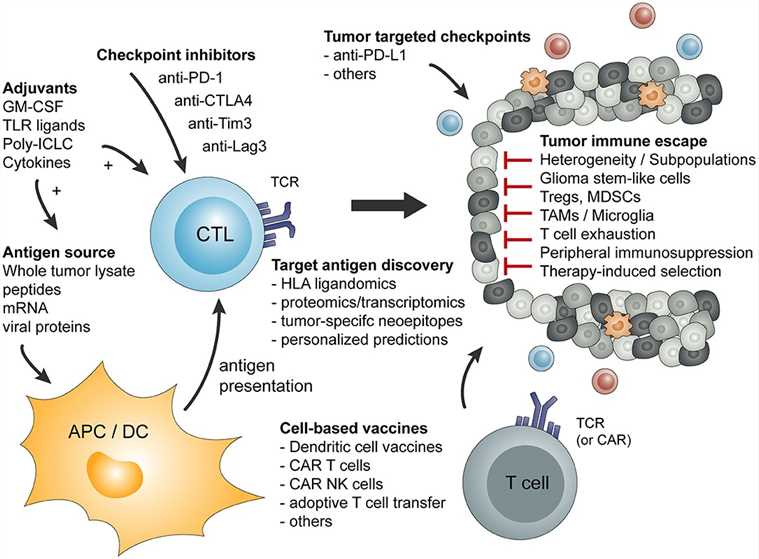 Fig.2 Overview of basic principles of tumor-specific immune activation and the involved cell type.2,3
Fig.2 Overview of basic principles of tumor-specific immune activation and the involved cell type.2,3
Creative Biolabs provides a series of one-stop targeting T cell services, including but not limited to:
Creative Biolabs has developed a range of services by targeting T cells to reshape TME. Our scientists are always ready to help you accelerate your cutting-edge immune-modulating therapies. Please feel free to contact us to learn how we can be involved in your project.
References
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION