Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells that play a central role in initiating and regulating immune responses. Their ability to capture and process antigens, and subsequently present them to T cells makes them attractive targets for immunomodulation. Dendritic cell dysfunction has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various diseases, including infectious diseases, autoimmune disorders, cancer, and chronic inflammatory conditions. Therefore, Dendritic cell-targeted monoclonal antibodies and dendritic cell vaccines offer an effective treatment for various diseases, such as autoimmune diseases and cancer.
Cancer immunotherapy
Cancer immunotherapy leverages the host's immune system to identify and eliminate cancerous cells. Compared with conventional modalities such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy, which directly target malignant cells, immunotherapy aims to strengthen the immune system's capacity to recognize and clean cancer cells.
Dendritic cell-targeting monoclonal antibodies have been thoroughly investigated in the realm of cancer immunotherapy. They are utilized to activate dendritic cells, enhance antigen presentation, and provoke anti-tumor immune responses.
Infectious diseases
Infectious diseases are pathological conditions instigated by pathogenic microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites, which can propagate via cross-infection. These microorganisms can enter the body and cause diseases by disrupting the homeostasis of the body. Monoclonal antibodies targeting dendritic cells, despite not being the primary targets of infectious agents, hold significant functions for enhancing the body's defense mechanisms against pathogens. They have potential applications in combating infectious diseases by modulating dendritic cell functions, through which these antibodies can amplify the host's capacity to recognize and eradicate microbial pathogens. Therefore, monoclonal antibodies directed towards dendritic cells have the potential to impact the immune system's ability to combat infections through several mechanisms, including enhancing antigen presentation, modulating innate immune responses, and promoting adaptive immunity.
Autoimmune disorders
Autoimmune disorders, or autoimmune diseases, denote pathological conditions characterized by aberrant immune responses wherein the immune system erroneously directs its attack towards healthy cells, tissues, and organs within the body. These conditions can affect the body in terms of the integumentary system, musculoskeletal system, vascular system, endocrine glands, and internal organs.
Monoclonal antibodies directed at dendritic cells specifically target molecules pivotal in their activation, co-stimulation, and cytokine secretion processes. This approach holds promise for therapeutic intervention by potentially reinstating immune tolerance mechanisms and regulating deviant immune reactions. Consequently, these antibodies may exert an influence on immune responses and hold the potential to mitigate autoimmune pathology.
Chronic inflammatory conditions
Chronic inflammatory conditions denote enduring or prolonged inflammatory phenomena within the body, surpassing the typical response to injuries or infections. Such conditions may induce persistent discomfort, edema, and tissue injury, leading to effects on organ functionality and overall well-being. They frequently coexist with autoimmune disorders, metabolic dysregulations, and other intrinsic health maladies. Therapeutic interventions commonly involve a multifaceted approach encompassing anti-inflammatory pharmaceuticals, immunomodulatory agents, and holistic management strategies targeting underlying health intricacies. Effective management of chronic inflammation holds paramount importance in averting further tissue compromise and mitigating consequential complications associated with these pathologies.
Dendritic cells serve as pivotal regulators of immune responses and hold a critical position in the orchestration of chronic inflammation across a spectrum of diseases, encompassing autoimmune disorders, inflammatory bowel diseases, and rheumatoid arthritis. Monoclonal antibodies directed towards dendritic cells possess the capacity to modulate inflammatory processes and immune responses in these pathological states through modulation of dendritic cell activation, induction of immune tolerance, inhibition of cytokine production, implementation of antigen-specific therapeutic approaches. etc.
Monoclonal antibodies targeting CD40
CD40 serves as a co-stimulatory receptor expressed predominantly on dendritic cells. It initiates intracellular signaling pathways upon engagement by its ligand, CD40L (CD154), which is expressed on activated T cells. This results in the upregulation of co-stimulatory molecules, particularly CD80 and CD86, as well as the secretion of cytokines such as interleukin-12 (IL-12) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), within the antigen-presenting cells. These events facilitate T cell activation, differentiation, and the acquisition of effector functions.
Monoclonal antibodies targeting CD40 have demonstrated the capacity to stimulate dendritic cells, enhance antigen presentation and initiate T cells. This activation promotes anti-tumor immune responses, making it a promising tool in cancer immunotherapy. Notably, monoclonal antibodies targeting CD40, such as dacetuzumab and lucatumumab, have been investigated for their ability to modulate dendritic cell functionality and mitigate autoimmune responses.
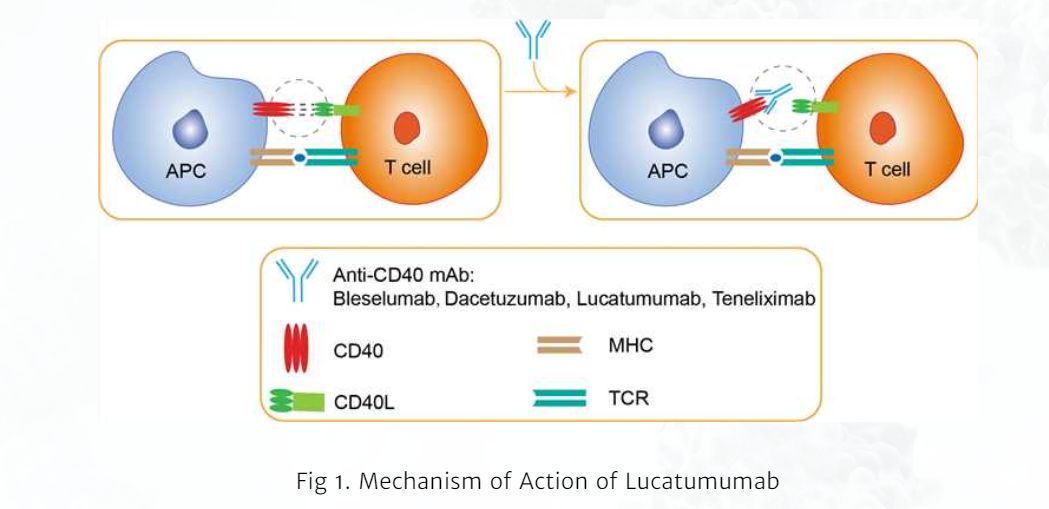 Fig. 1 Mechanism of Action of Lucatumumab (Creative Biolabs)
Fig. 1 Mechanism of Action of Lucatumumab (Creative Biolabs)
Monoclonal antibodies targeting DEC-205
DEC-205, also referred to as CD205, is a type I transmembrane protein within the C-type lectin receptor family, mostly expressed on dendritic cells. Its pivotal role lies in facilitating antigen uptake and subsequent presentation by dendritic cells. DEC-205 acts as a receptor for diverse ligands that can mediate the internalization of antigens into dendritic cells. Following internalization, antigens are processed and presented to T cells, triggering adaptive immune responses. Given its critical role in antigen presentation, DEC-205 has emerged as a promising target for immunotherapeutic interventions.
Monoclonal antibodies directed against DEC-205 offer a means to selectively deliver antigens or immunomodulatory agents to dendritic cells, that improve antigen presentation and elicit immune activation. This targeted therapeutic strategy holds considerable promise for combating infectious diseases, malignancies, and autoimmune disorders. Additionally, it offers potential for inducing immune tolerance in settings such as transplantation and autoimmune conditions.
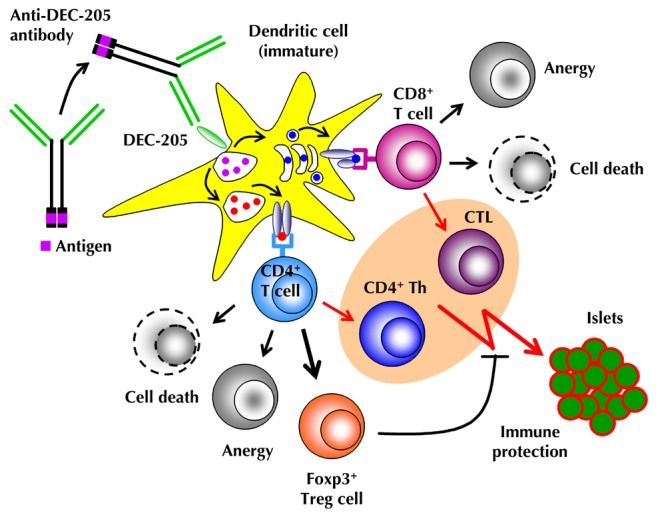 Fig. 2 Mechanisms of Ag-specific induction of peripheral T cell tolerance through DEC-205+ DCs (Cathleen, 2012)
Fig. 2 Mechanisms of Ag-specific induction of peripheral T cell tolerance through DEC-205+ DCs (Cathleen, 2012)
Monoclonal antibodies targeting DC-SIGN
DC-SIGN (dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule 3-grabbing non-integrin), or CD209, is a type II transmembrane protein belonging to the C-type lectin receptor family. Its expression is predominantly confined to dendritic cells. Through its interactions with pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), DC-SIGN facilitates the internalization and processing of pathogens by dendritic cells, that can initiate immune responses. DC-SIGN plays an important role in the pathogenesis of infectious diseases, as it acts as a receptor for viral entry into dendritic cells and supports viral dissemination within the host. As a result, DC-SIGN emerges as a promising target for therapies against infectious diseases.
Monoclonal antibodies targeting DC-SIGN provide versatile means for modulating immune responses and combating immune-related conditions like cancer. Ongoing research endeavors persistently explore the possible applications of these antibodies across various therapeutic domains.
Monoclonal antibodies targeting CD83
CD83, a cell surface glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, is mostly expressed on mature dendritic cells and plays a pivotal role in initiating and regulating immune responses. Under the T cell activation, CD83 expression on dendritic cells has been observed to increase T cell proliferation and cytokine production, thus facilitating robust immune responses against pathogens or neoplastic cells. Additionally, CD83 contributes to immune tolerance mechanisms to mitigate autoimmune responses.
Monoclonal antibodies targeting CD83 have received attention for their therapeutic potential in diverse immune-related disorders, encompassing autoimmune diseases, transplant rejection, and graft-versus-host disease. These antibodies exert their effects by modulating dendritic cell functionality, T cell responses, and immune tolerance mechanisms, presenting a novel therapeutic avenue for the management of immune-mediated conditions.
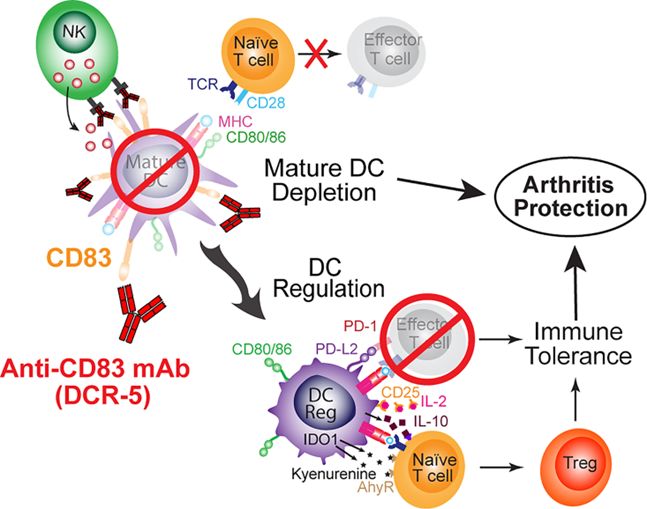 Fig. 3 Schematic mechanisms of anti-CD83 mAb mediated immune suppression leading to protection from arthritis. (Pablo,2022)
Fig. 3 Schematic mechanisms of anti-CD83 mAb mediated immune suppression leading to protection from arthritis. (Pablo,2022)
Empowered by our state-of-the-art CellRapeutics™ Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) Technology, Creative Biolabs offers world-leading CAR-macrophage development services, aiming to improve the ability of CAR cells to attack solid tumors. Our one-stop services covering Target Identification & Selection, High-Affinity Antigen Binder Generation, CAR-MA Design & Construction, CAR-MA Preparation, Macrophages Activation and Expansion, In Vitro Assessments, Preclinical Tests and Clinical Trials. We also provide CAR-MA Vector Products, CAR-MA Cell Products, and a proprietary online system for customizing CAR and CAR cell products, which offers full options to meet all unique needs.
References
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION