Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Epilepsy Treatment
Background Treatment Strategies Creative Biolabs' Solutions Workflow Published Data Related Services Resources
Creative Biolabs is at the forefront of lipid-based drug delivery innovations. Our expertise enables researchers to explore new frontiers in epilepsy treatment. We provide comprehensive solutions to enhance the efficacy of epilepsy therapies through advanced lipid-based delivery systems, helping you overcome formulation challenges and accelerate your research progress.
Explore Our Solutions
Background of Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures, which are caused by abnormal and excessive synchronized activities among brain neurons. It is the second most prevalent neurological disease worldwide, affecting approximately 1% of the global population. If not promptly controlled, the epileptic discharges originating in specific areas can rapidly spread throughout the brain, leading to severe neurological consequences. Common complications include cognitive impairment, mood disorders, and injury from seizures. Current treatments often face difficulties due to the blood-brain barrier (BBB), blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier (BCSFB), and drug resistance, which severely limits drug access to the brain, leading to suboptimal therapeutic concentrations and systemic side effects. The complexity of epilepsy necessitates innovative drug delivery solutions to improve patient outcomes.
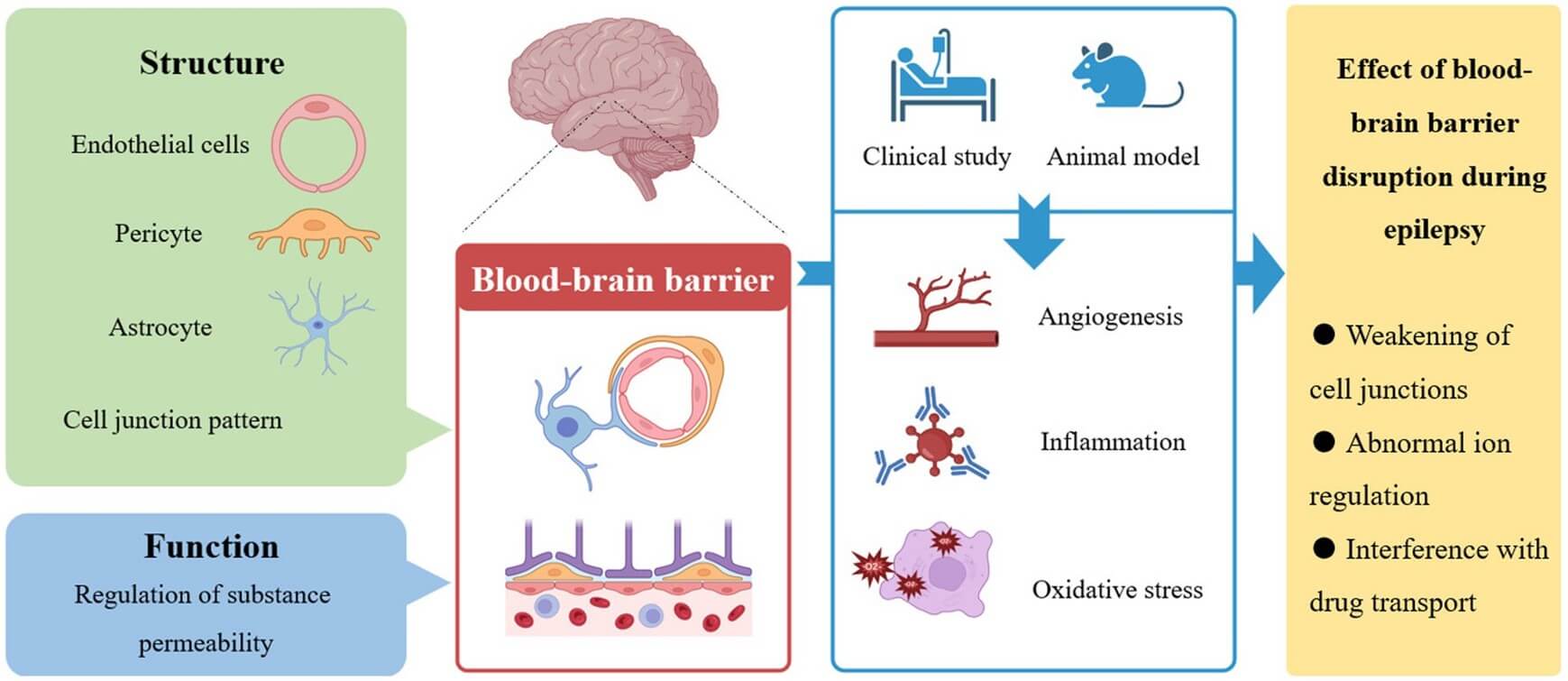 Fig. 1 Unveiling the hidden connection: the blood-brain barrier's role in epilepsy. 1,4
Fig. 1 Unveiling the hidden connection: the blood-brain barrier's role in epilepsy. 1,4
-
Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB): This protective barrier, composed of tightly packed endothelial cells, severely limits drug access, leading to suboptimal therapeutic concentrations and high systemic toxicity from the large doses required. It also contains efflux transporters that actively pump drugs back into the bloodstream, thereby limiting the concentration of antiepileptic drugs that can reach the brain.
-
Blood-Cerebrospinal Fluid Barrier (BCSFB): Located in the choroid plexus of the brain ventricles and formed by epithelial cells with tight junctions, the BCSFB regulates the movement of substances between the blood and cerebrospinal fluid. This barrier further limits the entry of antiepileptic drugs into the central nervous system.
-
Drug Resistance: Approximately 30% of epilepsy patients develop drug resistance, where their seizures do not respond adequately to existing medications. This can be due to various factors, including genetic variations, alterations in drug targets, and enhanced drug metabolism.
These barriers strictly regulate transport and metabolic processes to protect the brain from peripheral harm. However, they also limit the entry of most large molecules and over 90% of small-molecule drugs into the brain, thereby affecting epilepsy treatment efficacy.
Treatment Strategies for Epilepsy
Current treatment for epilepsy primarily relies on antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) administered orally or intravenously. While these methods aim to reduce seizure frequency and severity, their effectiveness is often hampered by the brain's natural defenses, particularly the BBB. To overcome the inherent limitations of conventional treatments, several innovative strategies are being explored and developed to enhance the delivery of therapeutic agents to the brain for epilepsy. These approaches aim to bypass, modify, or leverage the body's natural systems to achieve more effective drug concentrations at the site of action.
Drug Modification
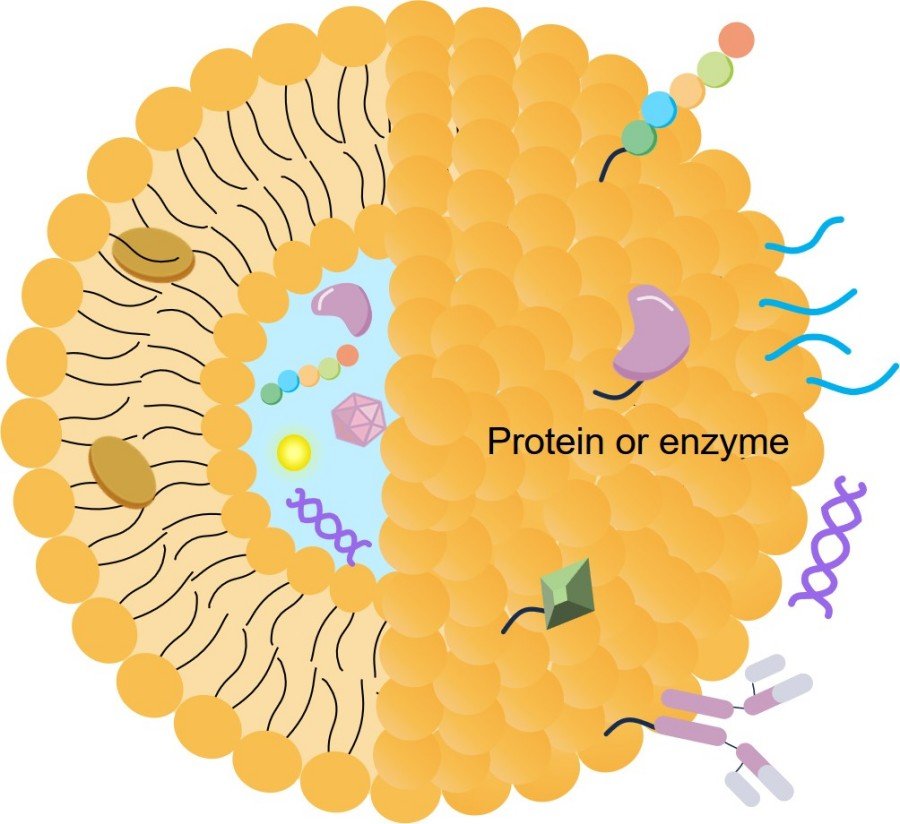
This strategy involves encapsulating AEDs within nanoscale carriers, such as polymeric-based nanoparticles and lipid-based nanoparticles (e.g., liposomes, lipid nanoparticles, solid lipid nanoparticles, nanostructured lipid carriers), or creating prodrugs. These systems offer enhanced drug stability, enable controlled and sustained release of the therapeutic agent over time, and can significantly reduce systemic toxicity by localizing drug action. They also hold the potential for targeted delivery to specific brain regions or cell types.
Advantages
-
Enhanced drug stability and solubility.
-
Enables controlled and sustained release.
-
Reduces systemic toxicity by localizing drug action.
-
Potential for precise targeting to specific cells.
BBB Modification
This strategy aims to temporarily enhance BBB permeability for improved drug delivery, by either blocking efflux pumps like P-glycoprotein and MRPs that eject drugs from the brain, or using agents such as mannitol in hyperosmolar solutions to transiently open the barrier. This can lead to a direct increase in drug entry into the brain, potentially improving therapeutic concentrations.
Advantages
-
Directly increases drug entry into the brain.
-
Improve therapeutic concentrations of existing drugs.
Direct Drug Delivery
This strategy involves bypassing the blood-brain barrier altogether by administering drugs directly into the brain. It includes intracerebroventricular (ICV) administration (delivering drugs into the cerebrospinal fluid), intracerebral implants or injections (direct delivery into the brain parenchyma), and convection-enhanced delivery (CED), which uses a pressure gradient to enhance drug distribution.
Advantages
-
Precise targeting of epilepsy focus.
-
Completely avoids systemic toxicity.
-
Achieves higher local drug concentrations.
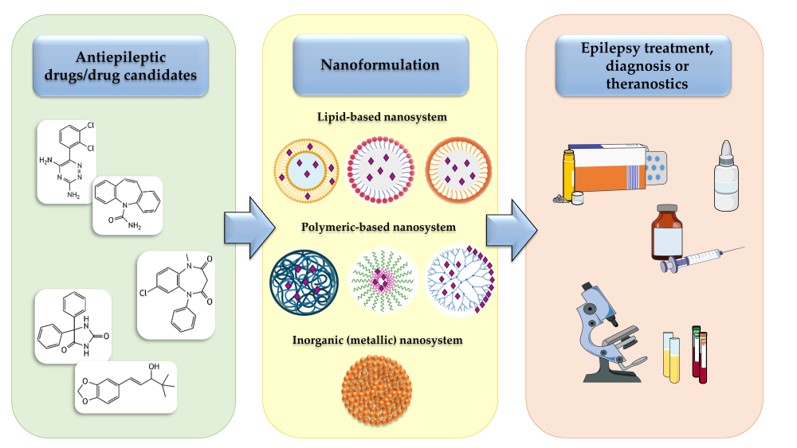 Fig. 2 Fighting epilepsy with nanomedicines. 2,4
Fig. 2 Fighting epilepsy with nanomedicines. 2,4
The persistent challenge in epilepsy treatment lies in safely and effectively delivering therapeutic concentrations of AEDs to the brain while minimizing systemic exposure. This difficulty underscores the critical need for innovative solutions. Creative Biolabs specializes in developing advanced lipid-based drug delivery systems, offering a precise and targeted approach to overcome these barriers.
How Creative Biolabs' Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems Can Assist Your Project
Creative Biolabs' lipid-based drug delivery systems are engineered to address the critical challenges of brain drug delivery for epilepsy, offering a robust platform for your therapeutic development. We provide comprehensive solutions designed to enhance the efficacy and safety of your drug candidates.
-
Enhanced Brain Penetration: Our proprietary lipid nanoparticle (LNP) and liposomal formulations are designed to efficiently traverse the blood-brain barrier, ensuring higher concentrations of your therapeutic agent reach the target neurological sites.
-
Targeted Delivery: We can functionalize lipid-based carriers with specific ligands to achieve receptor-mediated targeting, directing AEDs precisely to epileptic foci or specific brain cell types, maximizing therapeutic impact while minimizing off-target effects.
-
Sustained and Controlled Release: Our systems enable prolonged AEDs exposure at the site of action, reducing the frequency of administration and maintaining therapeutic levels over extended periods, which is crucial for managing chronic conditions like epilepsy.
-
Reduced Systemic Toxicity: By encapsulating AEDs within lipid carriers, we can significantly lower systemic drug exposure, thereby mitigating dose-limiting side effects and improving patient tolerability.
-
Improved Drug Stability and Solubility: Our formulations protect sensitive drug molecules from degradation in biological environments and enhance the solubility of poorly soluble compounds, expanding the range of viable drug candidates.
-
Secondary Preparations: We can further develop lipid-based delivery systems, such as liposomes, into diverse secondary preparations like gels, offering versatile application methods tailored to specific therapeutic needs.
-
Stimulus-Responsive Release: Our advanced formulations can be designed for on-demand drug release triggered by specific stimuli such as light, pH changes, temperature, or electrical signals, allowing for highly precise and localized AEDs delivery.
-
Multiple Administration Routes: We explore and optimize various non-invasive administration routes beyond traditional intravenous methods, including nasal cavity and transdermal delivery, which are conducive to bypassing the BBB and achieving effective drug delivery to the brain.
Workflow for Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems Development for Epilepsy
Published Data
This article introduces a cutting-edge strategy for managing epilepsy through enhanced drug delivery. The study focuses on developing novel nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) designed to improve the biodistribution and therapeutic efficacy of antiepileptic drugs. The optimized phenobarbital-loaded NLCs were thoroughly characterized, demonstrating a high entrapment efficiency of 98.2% and a mean particle size of approximately 178 nm, confirming their suitability as nanoscale drug carriers. Furthermore, these NLCs exhibited good physical stability for over a month. Beyond physicochemical properties, the research investigated crucial aspects such as in vitro release kinetics, cytotoxicity, and, significantly, their in vivo anticonvulsant activity in an animal model of acute seizures. The demonstrated success of NLCs in encapsulating phenobarbital and exhibiting promising in vivo anticonvulsant activity showcases the potential of this technology.
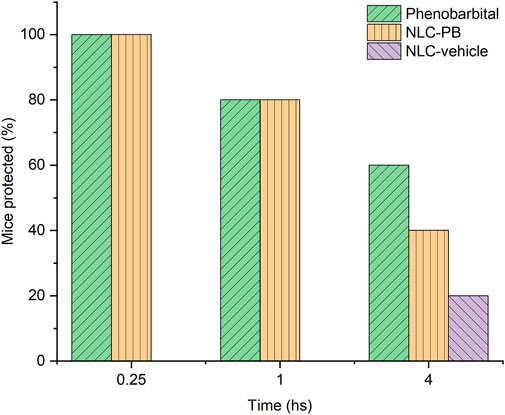 Fig. 3 Evaluate the anticonvulsant activity in vivo.3,4
Fig. 3 Evaluate the anticonvulsant activity in vivo.3,4
Through its mastery in developing cutting-edge lipid-based drug delivery systems, Creative Biolabs offers highly effective solutions designed to surmount the difficulties of managing epilepsy. Our expertise in enhancing brain penetration, enabling targeted and sustained release, and reducing systemic toxicity positions us as your ideal partner in bringing transformative neurotherapeutics. If you would like to learn more about our lipid-based drug delivery systems for epilepsy treatment or discuss potential collaborations, please feel free to contact us.
Related Services
Resources
References
-
Han, Jinkun, et al. "Unveiling the hidden connection: the blood-brain barrier's role in epilepsy." Frontiers in Neurology 15 (2024): 1413023. doi:10.3389/fneur.2024.1413023.
-
Matias, Mariana, et al. "Fighting epilepsy with nanomedicines—is this the right weapon?." Pharmaceutics 15.2 (2023): 306. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15020306.
-
Scioli-Montoto, Sebastian, et al. "Novel phenobarbital-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for epilepsy treatment: from QbD to in vivo evaluation." Frontiers in Chemistry 10 (2022): 908386. doi:10.3389/fchem.2022.908386.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.

For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use

 Fig. 1 Unveiling the hidden connection: the blood-brain barrier's role in epilepsy. 1,4
Fig. 1 Unveiling the hidden connection: the blood-brain barrier's role in epilepsy. 1,4
 Fig. 2 Fighting epilepsy with nanomedicines. 2,4
Fig. 2 Fighting epilepsy with nanomedicines. 2,4
 Fig. 3 Evaluate the anticonvulsant activity in vivo.3,4
Fig. 3 Evaluate the anticonvulsant activity in vivo.3,4



 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use