At Creative Biolabs, we specialize in cutting-edge lipid-based drug delivery solutions tailored for porphyria-related challenges. With our deep-seated expertise and a commitment to excellence, we provide tailored delivery platforms that can significantly advance your porphyria projects, helping you achieve remarkable results in porphyria research.
Heme, an iron-containing compound that gives blood its red color, is synthesized in the bone marrow (80%) and liver (15%) through a complex process involving eight different enzymes. Porphyria is a group of metabolic disorders caused by specific enzyme deficiencies in the heme biosynthesis pathway. This results in the abnormal accumulation of porphyrins and heme precursors, including 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) and porphobilinogen (PBG), in the body's tissues and organs, subsequently causing cellular damage. The neurotoxic heme precursors can result in acute hepatic porphyrias, while the photoreactive porphyrins, when excess, cause skin porphyrias characterized by photosensitivity.
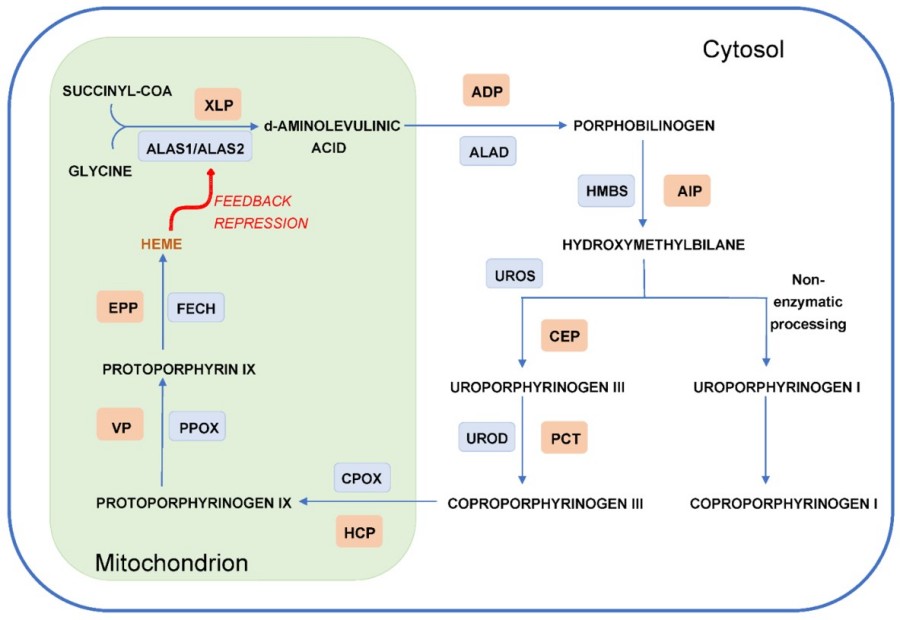 Fig. 1 The heme biosynthetic pathway.1
Fig. 1 The heme biosynthetic pathway.1
Based on the primary source of excess porphyrins or heme precursors, porphyrias are classified as either hepatic or erythropoietic.
| Porphyria | Porphyrin Origin | Related enzymes |
|---|---|---|
| Acute Hepatic Porphyrias (AHP) | ||
| ALA-dehydratase deficiency porphyria (ADP) | Hepatic | Delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (ALAD) |
| Acute intermittent porphyria (AIP) | Hepatic | Hydroxymethylbilane synthase (HMBS) |
| Hereditary Coproporphyria (HCP) | Hepatic | Coproporphyrinogen oxidase (CPOX) |
| Variegate Porphyria (VP) | Hepatic | Protoporphyrinogen oxidase (PPOX) |
| Cutaneous Erythropoietic Porphyrias | ||
| Erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP) | Erythropoietic | Ferrochelatase (FECH) |
| X-linked protoporphyria (XLP) | Erythropoietic | Delta-aminolevulinic acid synthase 2 (ALAS2) |
| Congenital erythropoietic porphyria (CEP) | Erythropoietic | Uroporphyrinogen III synthase (UROS) |
| Cutaneous Hepatic Porphyrias | ||
| Porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT) | Hepatic | Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase (UROD) |
| Hepato-erythropoietic porphyria (HEP) | Erythropoietic, hepatic | Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase (UROD) |
Creative Biolabs can utilize its advanced lipid-based drug delivery systems, including liposomes and lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), to enhance the therapeutic effects of these treatment strategies for porphyria.
Our advanced technology offers innovative solutions to improve drug delivery, enhance therapeutic outcomes, and overcome challenges associated with porphyria. By choosing Creative Biolabs, you can leverage our expertise to advance your porphyria research and develop more effective therapies.
With our expertise, customized solutions, and collaborative approach, Creative Biolabs can help you overcome challenges and achieve breakthroughs in porphyria research. We ensure consistent quality and reliable data in every project, which is crucial for advancing porphyria therapies. If you're ready to overcome research obstacles and drive innovation in porphyria treatment, contact us today.
Reference
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseApplications
Online Inquiry