Reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, a hallmark of myocardial ischemia, is a leading cause of global morbidity and mortality. Despite advancements in medicine, current therapies face challenges like poor drug absorption, non-targeted delivery, and side effects. Creative Biolabs is tackling this issue with cutting-edge lipid-based drug delivery systems, featuring our proprietary ATP-load liposomes.
Myocardial ischemia results in inadequate oxygenation and metabolic instability, thereby compromising cardiac function. Restoring blood flow to ischemic myocardial tissue is essential, but paradoxically, reperfusion can exacerbate cardiac injury, a phenomenon known as myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (MIRI).
The complex and multifaceted pathophysiology of myocardial ischemia necessitates a deep understanding of its mechanisms in order to develop targeted therapies that effectively mitigate ischemic injury.
Inflammatory Response
Acute myocardial ischemia induces a pro-inflammatory cascade via necrotic cell-derived signals, such as complement activation, ROS production, and DAMP release. DAMPs binding to TLRs drive myocardial cell death and cytokine secretion, with TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6 being pivotal in ischemic injury.
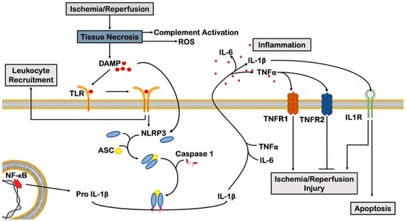 Fig.1 Schematic of inflammation-related signaling in myocardial ischemia.1
Fig.1 Schematic of inflammation-related signaling in myocardial ischemia.1
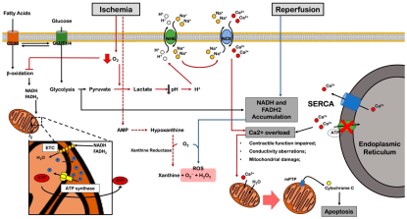 Fig.2 Schematic of metabolic pathways in myocardial ischemia.1
Fig.2 Schematic of metabolic pathways in myocardial ischemia.1
Cellular Metabolism
The heart's function relies on a substantial energy supply, predominantly ATP, generated via oxidative phosphorylation. During ischemia, cardiomyocytes are deprived of nutrients and oxygen, leading to a rapid decline in ATP levels. This directly affects the contractile function of cardiomyocytes, reducing the heart's pumping capacity.
ROS
Excessive production of ROS is a key pathophysiological event in myocardial infarction and ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury, causing damage to proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, and leading to membrane injury. Reperfusion oxygenation intensifies oxidative stress and impairs the antioxidant defense system.
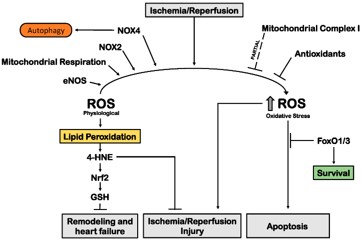 Fig.3 Schematic of oxidative stress pathways in myocardial ischemia.1
Fig.3 Schematic of oxidative stress pathways in myocardial ischemia.1
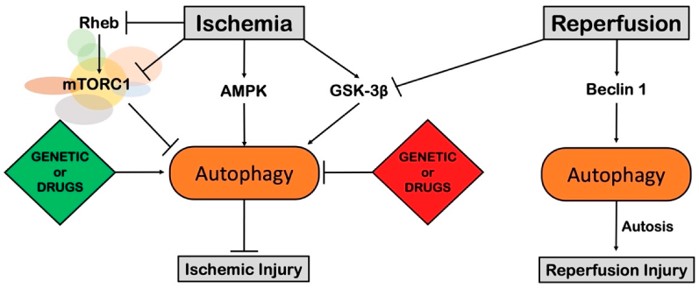 Fig.4 Role of autophagy in myocardial ischemia.1
Fig.4 Role of autophagy in myocardial ischemia.1
Autophagy
Autophagy is essential for maintaining cardiac homeostasis under stress, limiting damage and preserving heart function. Generally, reduced autophagy is associated with cardiac aging and injury, while stimulating autophagy has protective effects. However, in certain conditions, excessive autophagy can trigger harmful cellular mechanisms, increasing cardiac damage.
Mitochondrial Dynamics
Mitochondrial dynamics, involving biogenesis, fusion, fission, and degradation, are vital for cardiac homeostasis and pathology, given their role in ROS generation and metabolism.
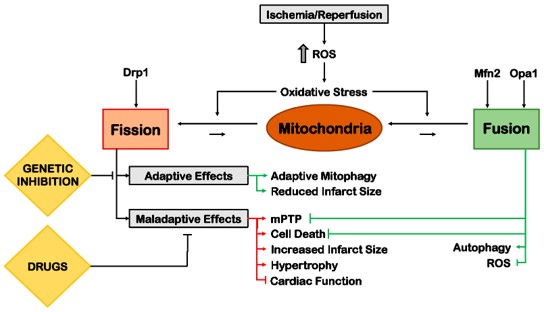 Fig.5 Role of mitochondrial dynamics in myocardial ischemia.1
Fig.5 Role of mitochondrial dynamics in myocardial ischemia.1
While a variety of anti-myocardial ischemia drugs are currently in clinical use, traditional formulations face limitations such as short plasma half-life, insufficient specificity to myocardial tissue, and susceptibility to degradation and elimination at the site of disease, which hinder the effective delivery of drugs to the target area for therapeutic effect. To address these challenges, lipid-based drug delivery systems have emerged as a promising strategy, significantly enhancing drug targeting and stability, thereby improving therapeutic outcomes. Creative Biolabs, leveraging its innovative liposomal delivery technology, has successfully achieved precise delivery of drugs such as ATP, offering a more efficient and targeted solution for myocardial ischemia treatment.
In myocardial ischemia, the insufficient supply of ATP is a critical factor that impairs myocardial function. Delivering exogenous ATP to restore normal intracellular ATP levels in cardiomyocytes holds promise for cardioprotection. However, delivering exogenous ATP faces significant challenges: ATP is highly susceptible to hydrolysis in the body, breaking down into adenosine monophosphate (AMP), adenosine diphosphate (ADP), and adenosine, which rapidly diminishes its bioactivity. Additionally, as a hydrophilic and negatively charged molecule, ATP struggles to cross the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane to enter cells, which limitations severely hinder the application of ATP in myocardial ischemia treatment.
To address these challenges, developing a delivery system that can protect ATP from hydrolysis and facilitate its transmembrane transport is crucial. Lipid-based drug delivery systems, with their excellent biocompatibility and high drug-loading capacity, can effectively encapsulate ATP, prevent its hydrolysis, and promote its uptake by cardiomyocytes, thereby increasing intracellular ATP levels and enhancing therapeutic efficacy.
Our lipid-based drug delivery systems not only enhance the bioavailability of ATP but also enables precise targeting of myocardial tissue through surface modification, minimizing potential side effects.
| Cat | Product Name | Applications | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDLY-0724-LD5 | DOPG:Chol:PEG2000-ATP Liposome (PEGylated) | For improving myocardial ischemia | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0724-LD6 | DOPG:DOPC:Chol:PEG2000-ATP Liposome (PEGylated) | For improving myocardial ischemia | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0724-LD15 | PS:Chol:PEG2000-ATP Liposome (PEGylated) | For improving myocardial ischemia | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0724-LD16 | PS:PC:Chol:PEG2000-ATP Liposome (PEGylated) | For improving myocardial ischemia | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0724-LD25 | PC:Chol:PEG2000-ATP Liposome (PEGylated) | For improving myocardial ischemia | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0724-LD26 | DOTAP:Chol:PEG2000-ATP Liposome (PEGylated) | For improving myocardial ischemia | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0724-LD27 | DOTAP:DOPC:Chol:PEG2000-ATP Liposome (PEGylated) | For improving myocardial ischemia | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0724-LD36 | DOPG:Chol-ATP Liposome | For improving myocardial ischemia | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0724-LD37 | DOPG:DOPC:Chol-ATP Liposome | For improving myocardial ischemia | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0724-LD47 | PS-ATP Liposome | For improving myocardial ischemia | Inquiry |
A diverse range of mature delivery systems
High encapsulation efficiency and stability
A robust quality control (QC) system
Suitable for both in vitro and in vivo experiments
High customization and rapid delivery

Plain ATP-loaded liposomes
ATP-loaded long-circulating liposomes
ATP-loaded Immunoliposomes
ATP-loaded targeted liposomes
ATP-loaded stimuli-responsive liposomes
Creative Biolabs' lipid-based drug delivery systems, with its unique ATP-load liposomes, offers a groundbreaking solution for the treatment of myocardial ischemia. To explore how our lipid-based drug delivery systems can enhance your research or therapeutic development initiatives for myocardial ischemia, contact us today.
Reference
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseApplications
Online Inquiry