Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Viral Infections Treatment
Background Treatment Strategies Challenges Creative Biolabs' Solutions Workflow Published Data Related Services Resources
Are you currently facing challenges in achieving targeted delivery, overcoming limited efficacy, managing systemic toxicity, or combating the rapid degradation of therapeutics in antiviral research? Creative Biolabs' advanced lipid-based drug delivery systems help you enhance therapeutic payload stability, improve bioavailability, achieve precise targeted delivery, and significantly reduce off-target effects through innovative lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulation and encapsulation techniques.
Background of Viral Infections
Viral infections belong to the category of infectious diseases, characterized by pathogens (viruses) that hijack host cellular machinery for their proliferation. They are characterized by obligate intracellular parasitism, diverse genetic material (DNA or RNA), small size, and high mutation rates, leading to challenges like antiviral resistance. Common complications can range from acute organ damage (e.g., viral hepatitis leading to liver failure) to chronic conditions, immune system suppression, and increased susceptibility to secondary bacterial infections. Viral infections represent a significant global health challenge, causing a wide spectrum of diseases from common colds to life-threatening conditions like HIV/AIDS, influenza, and hepatitis. Epidemiologically, these infections contribute to substantial morbidity and mortality worldwide, often leading to pandemics and large-scale public health crises. The intricate nature of viral replication within host cells and their rapid evolutionary capacity pose immense difficulties for effective treatment.
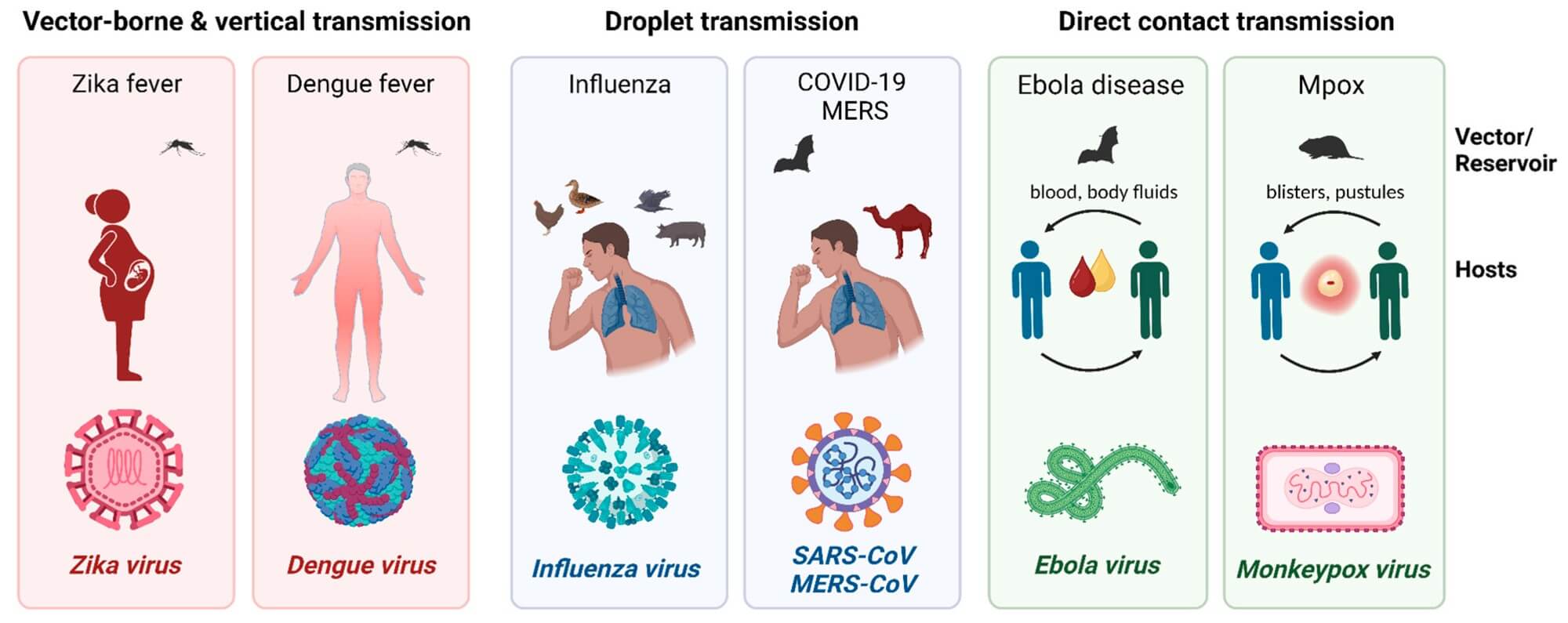 Fig. 1 Viral Infections: vectors, reservoirs, and routes of transmission.1,4
Fig. 1 Viral Infections: vectors, reservoirs, and routes of transmission.1,4
Treatment Strategies for Viral Infections
Current antiviral treatment strategies for viral infections are multifaceted, aiming to inhibit viral replication, boost host immunity, or prevent infection.
-
Antiviral Drugs: These drugs work by targeting specific viral proteins or processes essential for replication, such as remdesivir, ribavirin, and favipiravir.
-
Vaccines: Prophylactic vaccines stimulate the host immune system to recognize and neutralize viruses, preventing infection, including DNA vaccines, mRNA vaccines, purified inactivated virus vaccines, and viral vector vaccines. While highly effective, vaccine development can be time-consuming, and their efficacy can be compromised by rapidly evolving viral strains.
-
Immunomodulators: These treatments aim to modulate the host immune response to better combat the infection or mitigate inflammation.
Challenges in Antiviral Treatment
While these approaches have seen considerable success, significant challenges persist. The emerging field of nanotechnology, like functionalized nanoparticles, highlights the potential for materials engineered at the nanoscale to directly interact with and disrupt viral components, offering a promising avenue beyond conventional physical and chemical methods. Creative Biolabs' lipid-based drug delivery systems offer a path to overcome these difficulties by precisely delivering therapeutics.
-
Viral Mutation
-
Drug Resistance
-
Narrow Spectrum of Activity
-
Systemic Toxicity
-
Poor Cellular Uptake
-
Rapid Degradation for sensitive therapeutic molecules (such as mRNA or siRNA)
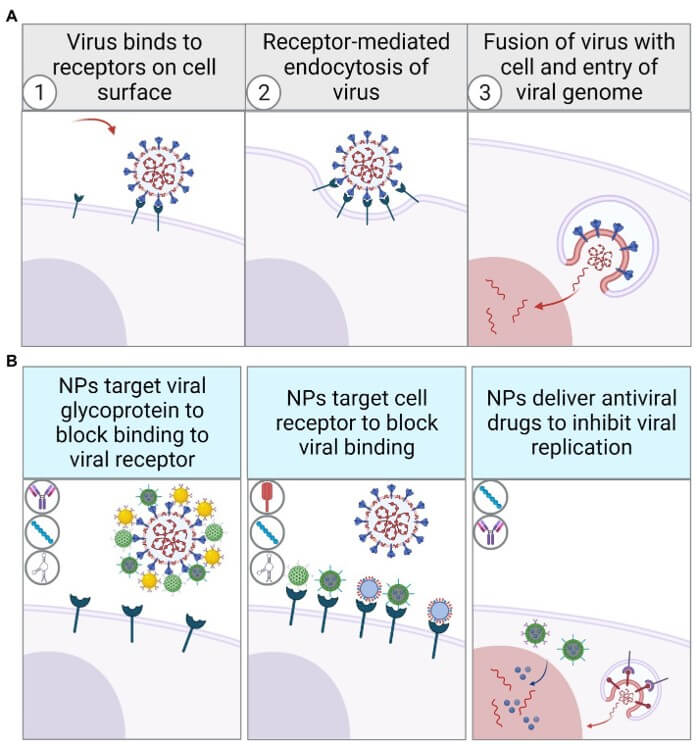 Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of virus invasion via receptor-mediated endocytosis and inhibition by functionalized nanoparticles. 2,4
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of virus invasion via receptor-mediated endocytosis and inhibition by functionalized nanoparticles. 2,4
How Creative Biolabs' Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems Can Assist Your Project
The efficacy of many promising treatments for viral infections is often limited because they cannot reach the lesion at a sufficient concentration. Our lipid-based drug delivery systems are engineered to address this critical bottleneck. By leveraging the unique properties of lipids – their ability to interact with biological membranes and their biocompatibility – we can design formulations with enhanced cellular uptake capacity and drug delivery efficiency.
Creative Biolabs offers a range of lipid-based drug delivery solutions tailored for antiviral research projects. Our systems can effectively encapsulate and deliver antiviral drugs, improving their pharmacokinetic properties and reducing side effects.
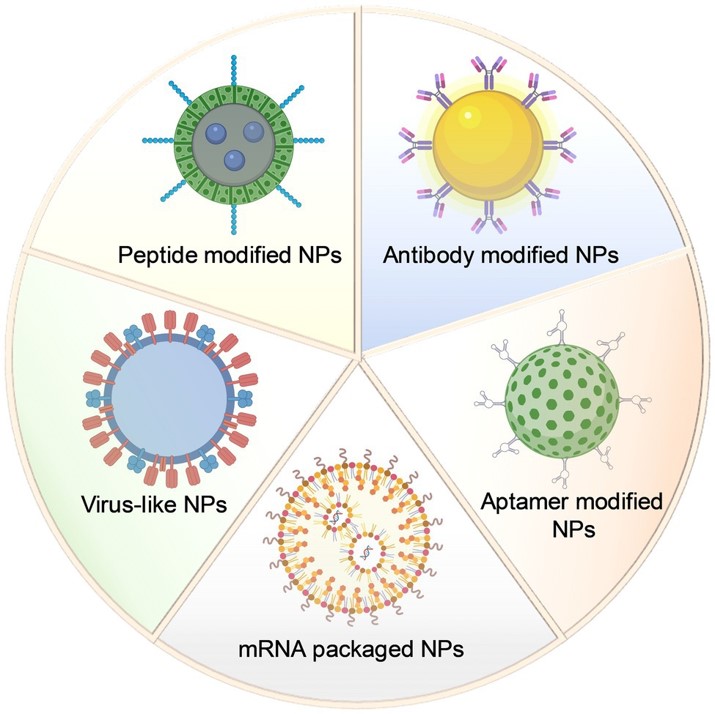 Fig. 3 Schematic design of different types of nanoparticles in antiviral targeted therapy research. 2,4
Fig. 3 Schematic design of different types of nanoparticles in antiviral targeted therapy research. 2,4
Creative Biolabs' Targeted Delivery System
We can conjugate lipid-based delivery systems (such as liposomes, LNPs, micelles, solid lipid nanoparticles) with peptides, aptamer, polymer, antibodies, nucleic acid fragments, and antigenic components to target viral antigens/receptors, enabling targeted treatment of viral infections.
How Our Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems Overcome Viral Barriers
Viruses often hide within cells or possess protective coatings. Creative Biolabs' LNPs can penetrate these barriers, delivering therapeutic payloads precisely to viral replication sites or presenting antigens to immune cells, thereby enhancing the efficacy of antiviral strategies.
Applications in Antiviral Research
Lipid-based drug delivery systems are particularly effective for delivering antiviral agents targeting RNA viruses such as Influenza, SARS-CoV-2, and HIV. The LNPs can encapsulate nucleoside analogs and protease inhibitors, facilitating their entry into host cells where viral replication occurs.
Our systems have been shown to enhance the intracellular delivery of RNA interference (RNAi) therapeutics, providing a powerful tool for studying viral gene expression and identifying novel therapeutic targets.
Explore RNA Virus Research
For DNA viruses like herpes simplex virus (HSV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), and human papillomavirus (HPV), our lipid-based drug delivery systems improve the delivery of nucleotide analogs and other antiviral compounds to infected cells. The targeted nature of our formulations allows for higher concentrations of drug at the site of infection, enhancing efficacy in research models.
Additionally, LNPs can be used to deliver CRISPR-Cas9 systems for gene editing applications in studying DNA virus latency and persistence.
Explore DNA Virus Research
Workflow for Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems Development for Viral Infections
Published Data
A novel lipid-based drug delivery system, utilizing liposomes encapsulating α-linolenic acid (ALA) and acetate, has demonstrated significant antiviral potential, particularly against emergent Coronaviridae viruses like SARS-CoV-2 and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Research highlights the synergistic action of ALA and acetate in inhibiting viral replication and reducing inflammation. In cellular models (Calu-3 and A549 cells), the ALA-acetate combination synergistically suppressed CoV2-N expression, reduced viral plaque formation, and modulated cytokine responses by decreasing IL-6 and IL-1β while increasing IFN-β. In vivo studies in murine models of SARS-CoV-2 infection further supported these findings, showing reduced viral load in lung tissue and diminished infection-associated inflammation and cytokine levels following treatment with the ALA-acetate liposomes. This research underscores the potential of lipid-based drug delivery systems, such as those developed by Creative Biolabs, for addressing viral infections.
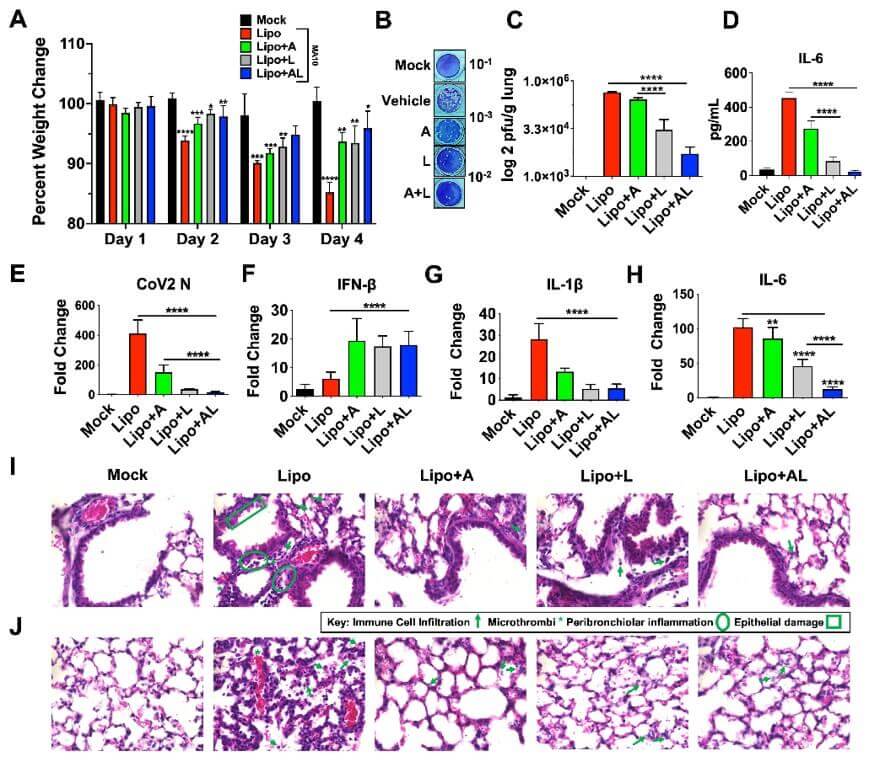 Fig. 4 Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infected with ALA liposomes ablates infection and COVID-19 associated cytokines.3,4
Fig. 4 Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infected with ALA liposomes ablates infection and COVID-19 associated cytokines.3,4
Creative Biolabs is dedicated to advancing antiviral therapeutic development through our cutting-edge lipid-based drug delivery systems. Our comprehensive services are designed to address the critical challenges of drug stability, targeted delivery, and bioavailability, empowering your projects with enhanced efficacy and reduced toxicity. For more information and to discuss how our lipid-based drug delivery systems can transform your antiviral research, please contact our expert team.
Related Services
Resources
References
-
Han, Jasmine J., et al. "Emerging infectious diseases are virulent viruses—Are we prepared? An overview." Microorganisms 11.11 (2023): 2618. doi:10.3390/microorganisms11112618.
-
Ren, Meishen, et al. "Functionalized nanoparticles in prevention and targeted therapy of viral diseases with neurotropism properties, special insight on COVID-19." Frontiers in Microbiology 12 (2021): 767104. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2021.767104.
-
McGill, Andrew R., et al. "Acetate-encapsulated linolenic acid liposomes reduce SARS-CoV-2 and RSV infection." Viruses 15.7 (2023): 1429. doi:10.3390/v15071429.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.

For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use

 Fig. 1 Viral Infections: vectors, reservoirs, and routes of transmission.1,4
Fig. 1 Viral Infections: vectors, reservoirs, and routes of transmission.1,4
 Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of virus invasion via receptor-mediated endocytosis and inhibition by functionalized nanoparticles. 2,4
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of virus invasion via receptor-mediated endocytosis and inhibition by functionalized nanoparticles. 2,4
 Fig. 3 Schematic design of different types of nanoparticles in antiviral targeted therapy research. 2,4
Fig. 3 Schematic design of different types of nanoparticles in antiviral targeted therapy research. 2,4
 Fig. 4 Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infected with ALA liposomes ablates infection and COVID-19 associated cytokines.3,4
Fig. 4 Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infected with ALA liposomes ablates infection and COVID-19 associated cytokines.3,4



 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use