Heart failure (HF) often represents an advanced stage of various cardiovascular diseases, posing significant therapeutic challenges. At the forefront of this medical evolution, Creative Biolabs is pioneering advanced lipid-based drug delivery systems specifically engineered to tackle the complexities of heart failure therapy. Our innovative strategy aims to refine heart failure management through precise interventions.
Heart failure (HF) represents a multifaceted clinical condition marked by structural or functional cardiac impairments, typically arising from diverse etiological factors. These changes impair the ventricular contraction and/or relaxation, leading to symptoms such as fluid retention, dyspnea, and fatigue. Importantly, metabolic alterations in the failing heart typically precede functional impairments, suggesting that metabolic reprogramming may serve as an early hallmark in the pathogenesis of HF.
Given the heart's high demand for ATP turnover to maintain homeostasis, metabolic changes in the context of HF have long been a focal point of research. Metabolomic advances have elucidated new pathways, enhancing our understanding of HF progression and treatment target identification. Specifically, pathways and targets related to fatty acid metabolism and glucose metabolism have been identified as promising therapeutic avenues.
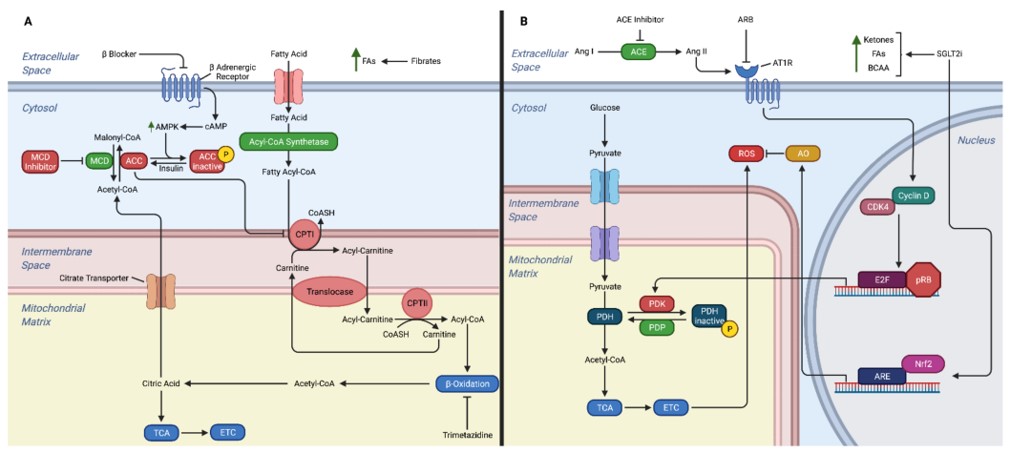 Fig.1 Mechanisms of action for heart failure medications on cardiac metabolism.1
Fig.1 Mechanisms of action for heart failure medications on cardiac metabolism.1
Here are some drugs targeting metabolic pathways in HF, which offer new therapeutic strategies by modulating fatty acid metabolism, glucose metabolism, and other metabolic pathways.
| Drug Category | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|
| β-Blocker | Inhibits CPTI activity to reduce fatty acid oxidation, thereby shifting cardiac metabolism towards a more efficient form of oxygen metabolism. |
| Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor | Prevents Angiotensin II-mediated upregulation of PDK4, which would otherwise increase glucose oxidation. |
| Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) | Prevents Angiotensin II-mediated upregulation of PDK4, which would otherwise increase glucose oxidation. |
| Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI) | Elevated levels of ANP promote lipolysis, prevent the proteolysis of GLP-1, and enhance the therapeutic effects of ARBs. |
| Sodium-glucose transport protein 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors | Enhances ketone body production in the liver and mitigates oxidative damage through Nrf2 nuclear translocation activation. |
| Decarboxylase (MCD) inhibitors | By increasing levels of cardiac malonyl-CoA, it inhibits CPT-I, leading to reduced mitochondrial fatty acid uptake and enhanced glucose oxidation pathways. |
| PPARα and PPARγ agonists | Decreases the supply of free fatty acids to the heart. |
Driven by innovative approaches and scientific rigor, Creative Biolabs is advancing therapeutic interventions for HF. Our lipid-based drug delivery systems are backed by rigorous research, state-of-the-art technology, and a team of experts in drug delivery and cardiovascular medicine. Discover the potential of our cutting-edge approaches to enhance therapeutic outcomes and transform HF management—contact us now.
Reference
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseApplications
Online Inquiry