Liposome-Microbiome Interaction Profiling Service
Accelerate rational liposome design with data that reveals how gut (and other barrier) microbiomes shape carrier stability, surface coronas, mucus transport, and payload release—under rigorously controlled in vitro, ex vivo, and organ-on-chip conditions.
Trusted by Innovators across Biopharma and Academia
Creative Biolabs supports discovery teams worldwide with end-to-end lipid carrier analytics and microbiome modeling.





Importance of Liposome–Microbiome Interaction Profiling
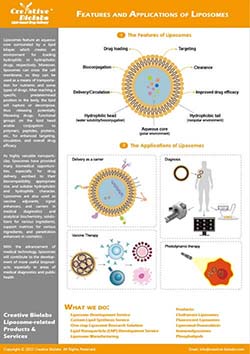
Liposomes are highly versatile nanocarriers, yet their stability and functionality are significantly influenced by complex gastrointestinal environments. Factors such as intestinal mucus, bile salts, digestive enzymes, and the microbiome play critical roles in shaping liposome behavior. These interactions can alter particle size, surface charge, bilayer integrity, and encapsulation stability.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for:
- Optimizing oral and mucosal liposome formulations.
- Reducing risks of unpredictable release or degradation.
- Ensuring consistency in preclinical and translational research.
Creative Biolabs’ liposome–microbiome interaction profiling service provides in-depth experimental data to guide rational design, reduce development risks, and accelerate decision-making.
Comprehensive Service Offerings
Microbiome–Liposome Interaction Assays
- Ex vivo fecal incubation to evaluate stability, surface changes, and leakage in the presence of microbial enzymes.
- In vitro defined consortia to investigate species-specific effects on lipid bilayers.
- Mucus penetration analysis to determine transport efficiency across gastrointestinal barriers.
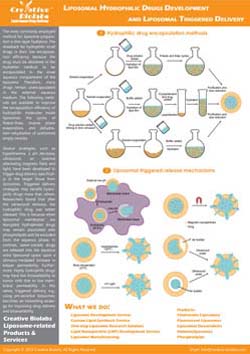
Digestive Stress and Bile Salt Compatibility
- Bile salt exposure panels to measure liposome integrity under physiological concentrations.
- Enzyme stability tests with pancreatic lipases to assess leakage and degradation.
- Formulation optimization with bile-salt-enriched systems for enhanced oral delivery research.
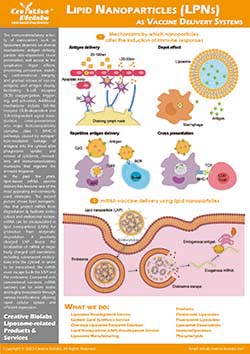
Omics-Based Profiling and Corona Analysis
- Microbiome sequencing (16S/shotgun) to detect structural shifts in microbial communities.
- Metabolomics profiling of short-chain fatty acids and bile acid pools.
- Biocorona characterization using proteomic and lipidomic approaches to identify biomolecules adsorbed on liposome surfaces.
Key Advantages of Our Service
Integrated Expertise
Integrated lipid and microbiome expertise for streamlined analysis.
Physiologically Relevant Models
Including mucus and organ-on-chip systems.
High-Resolution Analytics
With AF4-MALS, DLS, and LC-MS/MS platforms.
Comparability & Reproducibility
Through standardized protocols.
Customizable Modules
Tailored to client-specific research goals.
Actionable Results
With clear decision-making guidance.
Applications of Liposome–Microbiome Profiling
Oral Liposome Research
Evaluate the impact of bile salts and digestive enzymes on liposome stability and optimize lipid compositions for gastrointestinal environments.
Mucus Penetration Studies
Compare PEGylated or surface-modified liposomes to determine efficiency in crossing mucus barriers while retaining structural integrity.
Microbiome Compatibility Screening
Screen for potential effects of liposomes on microbiome composition and metabolite production to ensure minimal disruption.
Biocorona and Uptake Analysis
Characterize the adsorption of microbiome-derived biomolecules onto liposomes, which can influence uptake and biodistribution.
Organ-on-Chip Validation
Confirm findings in dynamic gut-on-chip models simulating physiologic conditions and microbiome co-culture.
Probiotic and Postbiotic Delivery
Assess the role of liposome encapsulation in stabilizing probiotics or modulating postbiotic release within microbiome environments.
Step-by-step Workflow
Project Consultation
Define research goals and experimental design.
Sample Preparation
Use client-supplied or Creative Biolabs-prepared liposomes.
Baseline Characterization
Particle size, zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency, and morphology.
Interaction Studies
Microbiome, mucus, and digestive stress exposure testing.
Omics Analysis
Sequencing, metabolomics, and corona profiling.
Comprehensive Reporting
Data interpretation and recommendations for formulation optimization.
Deliverables Provided
- ✓Full experimental plan and methods documentation.
- ✓Physicochemical characterization reports with particle size and morphology data.
- ✓Graphical dashboards showing stability, leakage, and mucus penetration results.
- ✓Detailed microbiome and metabolite analysis.
- ✓Surface corona composition data with relevance to uptake and stability.
- ✓Final comprehensive report with data-driven recommendations.
Related Services from Creative Biolabs
Our Lipid-Based Delivery platform provides a broad range of complementary solutions, including:
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, we can test multiple liposome batches simultaneously, comparing particle size, encapsulation efficiency, mucus penetration, and microbiome effects. Parallel evaluation reduces project timelines and provides head-to-head data to support rational formulation optimization.
Other Resources
References
- Vitulo, Manuela, et al. "Interactions between nanoparticles and intestine." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.8 (2022): 4339. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084339
- Subramanian, Deepak A., Robert Langer, and Giovanni Traverso. "Mucus interaction to improve gastrointestinal retention and pharmacokinetics of orally administered nano-drug delivery systems." Journal of nanobiotechnology 20.1 (2022): 362. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-022-01539-x
- Bohsen, Mette Sloth, et al. "Interaction of liposomes with bile salts investigated by asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation (af4): A novel approach for stability assessment of oral drug carriers." European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 182 (2023): 106384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2023.106384
Online Inquiry
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.