Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Treatment
Background Mechanisms Challenges Creative Biolabs' Solutions Workflow Published Data Related Services Resources
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a challenging neurodegenerative disease with limited treatment options due to barriers like the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and poor drug bioavailability. Creative Biolabs' lipid-based delivery systems offer innovative solutions to enhance drug efficacy and targeting in ALS. Our services include advanced formulation development, tailored targeting strategies, and comprehensive preclinical support to overcome these hurdles and accelerate your ALS research.
Background of ALS
ALS is a serious neurological condition involving the gradual deterioration of motor neurons in the brain and spine. This deterioration results in muscle atrophy, weakness, and eventually paralysis. It is a terminal illness with an average survival period of about 3 years from when symptoms first appear. Furthermore, ALS is classified among motor neuron diseases and affects both upper motor neurons (UMN) and lower motor neurons (LMN). Common complications include spasticity, hyper-reflexia, fasciculation, and difficulties with speech, swallowing, and breathing.
|
Clinical Phenotypes
|
Regions
|
Symptoms
|
|
Limb-onset
|
UMN
|
Spasticity
Weakness
Brisk deep tendon reflexes
|
|
LMN
|
Fasciculations
Distal weakness
|
|
Bulbar-onset
|
UMN
|
Spastic dysarthria
|
|
LMN
|
tongue wasting, weakness, and fasciculations
Flaccid dysarthria
Dysphagia
|
|
Primary lateral sclerosis
|
Pure UMN
|
Ascending spastic tetraparesis
|
|
Progressive muscular atrophy
|
Pure LMN
|
Asymmetrical weakness and wasting
|
|
ALS-frontal lobe dementia syndrome
|
UMN
LMN
Brain cortex
|
Frontotemporal dementia
|
The complex etiology significantly hinder effective drug therapy. Creative Biolabs is dedicated to providing innovative solutions to these critical challenges, offering customers comprehensive strategies to address the complex mechanisms underlying ALS.
Understanding the Disease Mechanisms
Oxidative Stress & Mitochondrial Dysfunction
An imbalance between oxidants and antioxidants leads to cellular damage from reactive oxygen species (ROS), often linked to mitochondrial dysfunction, contributing to neuron death.
Gene Defects
Mutations in genes such as SOD1, FUS/TLS, and C9orf72 are identified in familial ALS, leading to toxic protein gain-of-function or altered protein processing and aggregation.
Protein Aggregation
Abnormal accumulation and aggregation of proteins like mutant SOD1 and TDP-43 inside motor neurons disrupt critical cellular functions, leading to toxicity and cell death.
Glutamate Excitotoxicity
Overstimulation of glutamate receptors causes excessive calcium to enter motor neurons. This influx is toxic, leading to cellular damage and contributing to the neurodegenerative cascade.
Challenges of Delivering ALS Therapeutic Drugs to Central Nervous System (CNS)
Despite the development of promising new therapeutic agents, including antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), proteins, and vital nutritional factors, their clinical efficacy in ALS is severely constrained.
-
BBB and BSCB Barrier: The BBB and blood-spinal cord barrier (BSCB) are highly selective physiological barriers that protect the CNS from circulating toxins and pathogens. They restrict the passage of most large molecules, hydrophilic compounds, and even many small lipophilic drugs, making it exceptionally difficult to achieve therapeutic concentrations in the brain and spinal cord.
-
Biostability and Bioavailability: Many advanced therapeutic molecules, particularly biologics like proteins and nucleic acids, are highly susceptible to enzymatic degradation in the bloodstream and peripheral tissues. This rapid breakdown significantly reduces their biostability and, consequently, their bioavailability at the intended site of action.
-
Systemic Distribution: Without targeted delivery, therapeutic agents distribute widely throughout the body, leading to off-target effects and potential systemic toxicity.
-
Clearance:Rapid systemic clearance by the liver and kidneys can further diminish the effective concentration of the drug available to cross the BBB and reach the CNS, necessitating higher doses that exacerbate side effects.
Creative Biolabs' lipid-based drug delivery systems are specifically engineered to address these multifaceted challenges. By encapsulating and protecting therapeutic agents, facilitating their passage across the BBB/BSCB, and enabling targeted delivery, our solutions aim to overcome these critical barriers and unlock the full therapeutic potential of novel ALS treatments.
How Creative Biolabs' Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems Can Assist Your Project
Creative Biolabs specializes in overcoming the formidable challenges of drug delivery to the central nervous system (CNS), particularly for complex neurodegenerative disorders like ALS.
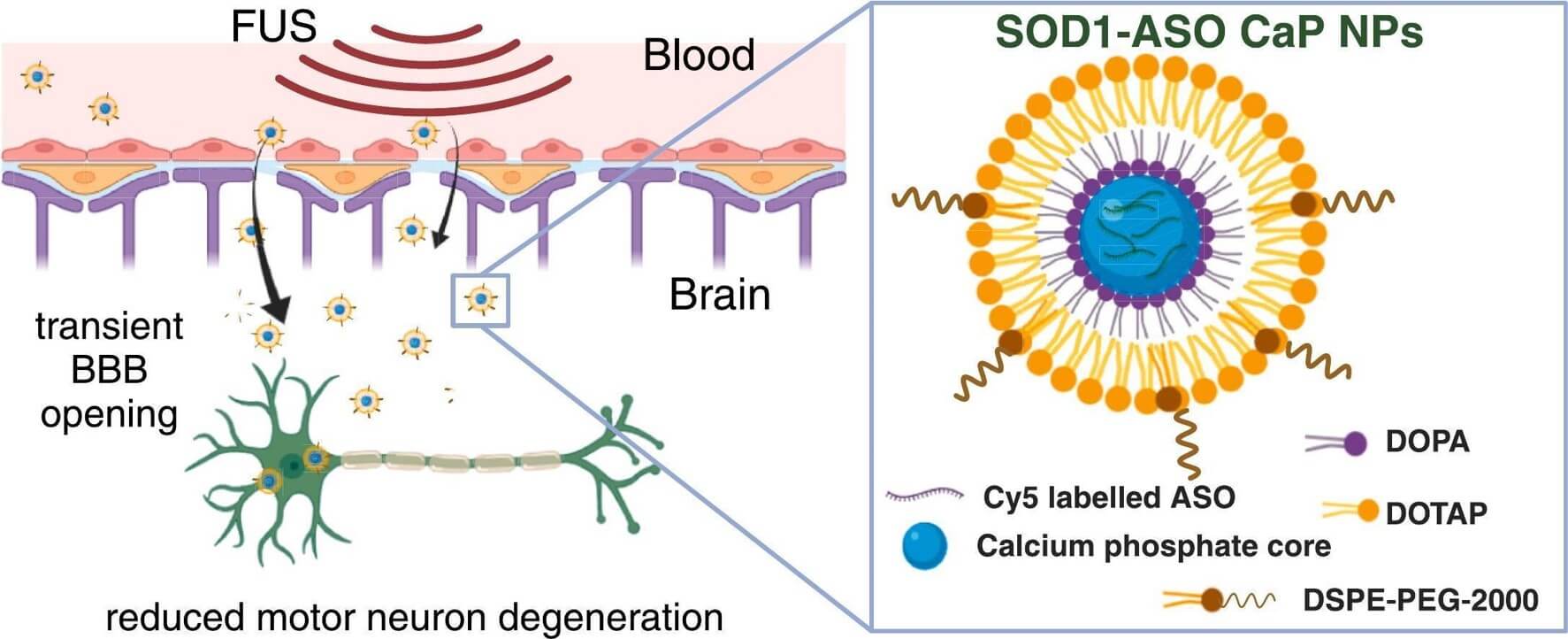 Fig. 1 Lipid nanoparticles enhance the brain delivery of ASO for ALS treatment. 1,3
Fig. 1 Lipid nanoparticles enhance the brain delivery of ASO for ALS treatment. 1,3
-
CNS Penetration: Our lipid-based nanocarriers are engineered to efficiently traverse the BBB/BSCB, ensuring that therapeutic agents reach the affected motor neurons at optimal concentrations.
-
Targeted Delivery: We employ advanced targeted modification strategies, utilizing multiple ligands on the nanocarrier surface to achieve highly specific and efficient delivery to diseased cells or tissues within the CNS. This maximizes therapeutic impact while minimizing off-target effects.
-
Gene Therapy: Our expertise extends to formulating lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) capable of encapsulating and delivering nucleic acids, such as ASOs, mRNA, CircRNA and siRNA, for gene therapy approaches in ALS.
-
Improved Biostability and Sustained Release: By encapsulating active pharmaceutical ingredients within liposomes or LNPs, we significantly increase their stability against enzymatic degradation and prolong their circulation time. This leads to sustained drug release, maintaining therapeutic concentrations over extended periods and reducing the frequency of administration.
-
Robust Pre-clinical Model Support: Creative Biolabs leverages mature in vivo and in vitro models relevant to ALS research, allowing for comprehensive evaluation of drug efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and biodistribution of our lipid-based delivery systems, thereby accelerating your path to clinical translation.
-
Versatile Administration Routes: Our systems are adaptable to various administration routes, including non-invasive options like intranasal delivery, which can bypass the BBB effect and offer a direct pathway to the brain.
Workflow for Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems Development for ALS
Published Data
The study explores the critical role of perivascular macrophages (PVMs) in ALS progression and investigates the potential of lipid-based drug delivery systems, specifically clodronate liposomes (CLO), to modulate these cells. By selectively depleting PVMs, the researchers aimed to alleviate neuroinflammation and improve disease outcomes in a well-established mouse model of ALS. The study's findings unequivocally reveal that continuous depletion of PVMs using CLO significantly delays disease progression and extends the lifespan of SOD1G93A mice.
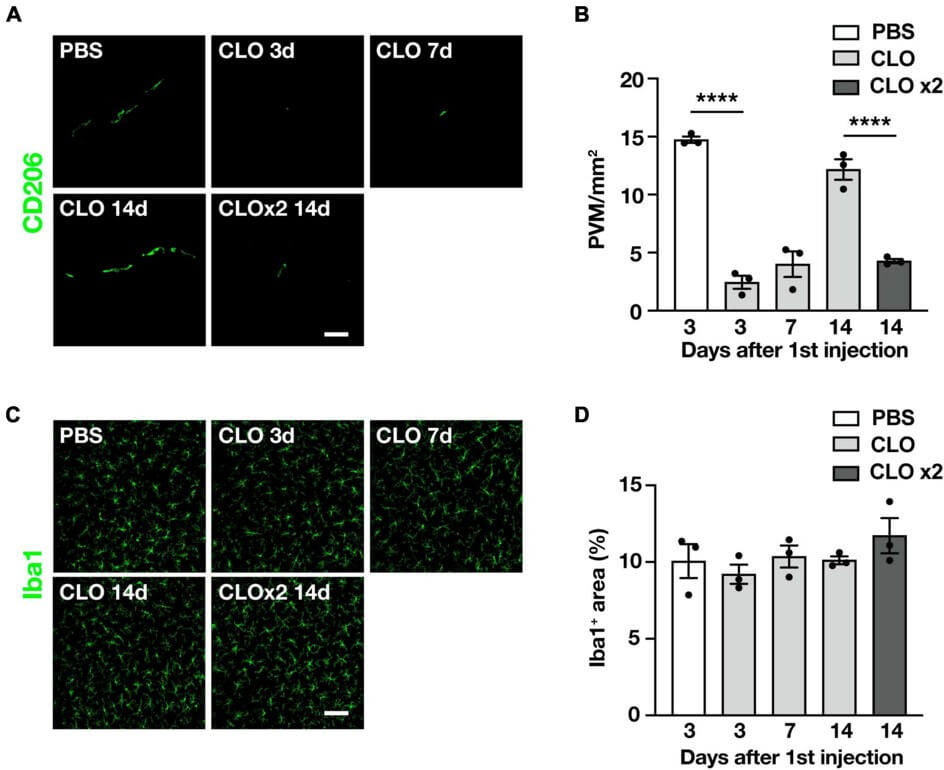 Fig. 2 Sustained and selective PVM depletion by repetitive CLO intracisternal injection into WT mice.2,3
Fig. 2 Sustained and selective PVM depletion by repetitive CLO intracisternal injection into WT mice.2,3
Creative Biolabs' clodronate liposomes offer researchers versatile tools to explore the role of macrophage populations in various disease models. Our offerings include a diverse range of ready-to-use clodronate liposomes, available in both neutral and anionic formulations.
Creative Biolabs is dedicated to advancing the field of neurodegenerative disease (such as ALS, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, huntington's disease, and multiple sclerosis) therapeutics through innovative lipid-based drug delivery systems. Our solutions are designed to enhance drug bioavailability, improve target specificity, and overcome the formidable blood-brain barrier, ultimately leading to more effective and safer therapies. For detailed information, to discuss your specific project requirements, or to request a consultation, please contact our team.
Related Services
Resources
References
-
Ediriweera, Gayathri R., et al. "Lipid nanoparticles and transcranial focused ultrasound enhance the delivery of SOD1 antisense oligonucleotides to the murine brain for ALS therapy." Journal of Controlled Release 378 (2025): 221-235. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.11.074.
-
Adachi, Kazuki, et al. "Depletion of perivascular macrophages delays ALS disease progression by ameliorating blood-spinal cord barrier impairment in SOD1G93A mice." Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 17 (2023): 1291673. doi:10.3389/fncel.2023.1291673
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.

For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
 Fig. 1 Lipid nanoparticles enhance the brain delivery of ASO for ALS treatment. 1,3
Fig. 1 Lipid nanoparticles enhance the brain delivery of ASO for ALS treatment. 1,3
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use