At Creative Biolabs, we are dedicated to addressing the challenges of Alzheimer's disease (AD) through our innovative lipid-based drug delivery systems. Our pioneering intranasal administration approach effectively overcomes the blood-brain barrier (BBB), enabling efficient treatment for Alzheimer's disease and offering a novel pathway for researchers in this field.
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder and the most common form of dementia. It is characterized by cognitive decline, memory impairment, and behavioral changes. Several hypotheses attempt to explain the underlying mechanisms of AD:
| Hypothesis | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Amyloid cascade hypothesis | Amyloid-β peptide (Aβ) overproduction and insufficient clearance lead to cerebral aggregation, causing inflammation, oxidative stress (OS), and neurodegeneration. |
| Tau hypothesis | Tau protein hyperphosphorylation and aggregation into paired helical filaments/neurofibrillary tangles disrupt microtubule function. |
| Cholinergic hypothesis | Loss of cholinergic neurons and activity reduces choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) function, causing cognitive issues. |
| Metal ion hypothesis | Metal dyshomeostasis can accelerate the aggregation of Aβ, aggravate OS and disrupt normal neural functions. |
| Calcium hypothesis | Calcium ion dysregulation impairs synaptic plasticity and transmission, increasing Aβ/tau production and causing neuron death. |
| OS hypothesis | OS induces Aβ accumulation, mitochondrial dysfunction, metal metabolism issues, tau hyperphosphorylation, and inflammation. |
| Inflammation hypothesis | Inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-1β/18 damage neurons. |
| Mitochondrial cascade hypothesis | Mitochondrial dysfunction triggers Aβ buildup, tau hyperphosphorylation, synaptic loss, and neurodegeneration. |
| Presenilin hypothesis | Presenilin mutations disrupt synaptic and signaling functions, causing familial AD. |
A major obstacle in AD treatment is the blood-brain barrier (BBB), which protects the brain from harmful substances and invading microbes in the blood. Most potent AD therapeutics, including small molecules and biologics, cannot effectively cross the BBB.
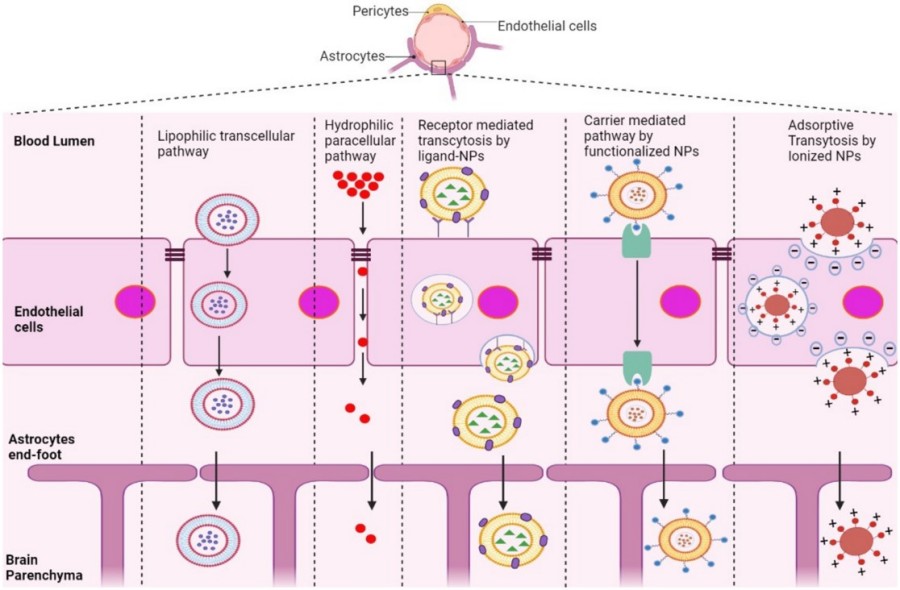 Fig. 1 Lipid-based drug delivery systems overcoming BBB for AD Treatment. 1
Fig. 1 Lipid-based drug delivery systems overcoming BBB for AD Treatment. 1
To overcome the barrier effect of BBB, current lipid-based drug delivery strategies include:
Creative Biolabs' lipid-based drug delivery systems present a promising solution. These systems can encapsulate drugs, enhance their solubility and stability, and facilitate their transport across the BBB, potentially improving the efficacy of AD treatments.
Creative Biolabs' advanced lipid-based delivery systems are designed to cross the BBB efficiently. Our surface-modified liposomes can deliver drugs directly to brain cells, improving cognitive function and reducing amyloid plaques. This innovative approach not only achieve targeted delivery but also enhance drug delivery across the BBB. Additionally, our biomimetic systems, like cell membrane-coated liposomes, ensure effective drug delivery across the BBB. Our gene therapy platform also leverages lipid-based drug delivery systems to deliver nucleic acid that boost dopamine production or protect neurons, potentially slowing disease progression.
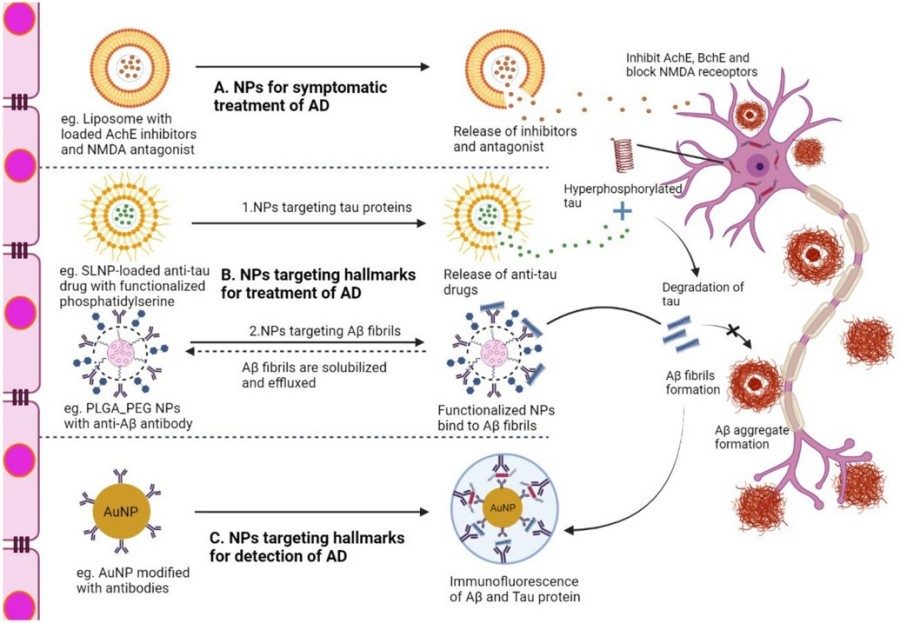 Fig. 2 The interaction of lipid-based drug delivery systems with AD-related neurons after crossing the BBB.1
Fig. 2 The interaction of lipid-based drug delivery systems with AD-related neurons after crossing the BBB.1
| Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems | Drug | Strategies for Brain-Targeting | Targets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Creative Biolabs offers various customized delivery systems. For more information, please contact us. | Osthole |
|
BACE1 |
| Galantamine HBr | Aβ | ||
| Donepezil | Neuroinflammation | ||
| Curcumin | Tau | ||
| Resveratrol | NMDA receptors | ||
| Rivastigmine | AchE | ||
| Quercetin | ROS |
Creative Biolabs' lipid-based drug delivery systems represent a cutting-edge solution for AD research. If you are working on projects related to AD treatment and are seeking to enhance drug delivery efficiency, please contact us. We not only provide customized drug delivery system development services for AD but also offer a range of spot products to simplify AD treatment. Our team is ready to collaborate with you to advance scientific progress and contribute to the development of new therapies for AD.
Reference
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseApplications
Online Inquiry