Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Fungal Infections Treatment
Background Treatment Strategies Creative Biolabs' Solutions Why Choose Us? Workflow Published Data Related Services Resources
Fungal infections are becoming a more serious global health problem, covering everything from minor skin issues to deadly body-wide fungal diseases. While conventional antifungal therapies have long been the mainstay, their limitations—including poor drug solubility, systemic toxicity, rapid degradation, and the ominous rise of antimicrobial resistance—underscore an urgent need for innovative solutions. At Creative Biolabs, we are at the forefront of this revolution, leveraging the unparalleled potential of lipid-based drug delivery systems to redefine antifungal drug delivery.
Background of Fungal Infections
Fungal infections, also known as mycoses, encompass a broad spectrum of diseases instigated by fungi. These infections span from prevalent superficial afflictions targeting the skin, hair, and nails to deeply entrenched systemic infections that pose a severe threat to life. Epidemiologically, fungal infections are a growing concern globally, particularly among immunocompromised individuals (e.g., HIV/AIDS patients, organ transplant recipients, cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy) and those in intensive care units. Common complications include severe tissue damage, organ failure, and high mortality rates in systemic cases. Current treatment difficulties often arise from the limited number of effective antifungal drugs, their associated toxicities, and the increasing problem of antifungal drug resistance.
Superficial Mycoses
Affecting the outermost layers of skin and hair. Generally not life-threatening but can be persistent and widespread.
Onychomycosis
Cutaneous Mycoses
Infections that extend deeper into the epidermis, hair, and nails, often causing chronic conditions.
Athlete's foot, Ringworm
Subcutaneous Mycoses
Involve the dermis, subcutaneous tissues, and muscle, typically from traumatic implantation of fungi.
Sporotrichosis
Systemic Mycoses
The most severe type, affecting internal organs and capable of spreading throughout the body. Often life-threatening.
Aspergillosis, Candidemia
Understanding the specific fungi responsible for these infections is crucial for developing targeted treatments. By identifying the specific fungi involved in these infections, researchers can better tailor their approaches to combat fungal infections.
|
Diseases
|
Fungal Species
|
|
Dimorphic mycoses
|
B. dermatitidis
|
|
C. immitis
|
|
C. posadasii
|
|
H. capsulatum
|
|
P. brasiliensis
|
|
T. marneffei
|
|
Disseminated cryptococcosis
|
C. neoformans
|
|
C. gattii
|
|
Aspergillosis
|
A. fumigatus
|
|
A. flavus
|
|
A. terreus
|
|
A. nidulans
|
|
A. niger
|
|
A. clavatus
|
|
Candidiasis
|
C. albicans
|
|
C. tropicalis
|
|
C. glabrata
|
|
C. parapsilosis
|
|
C. krusei
|
|
C. auris
|
|
Mucormycosis
|
Rhizopus spp.
|
|
Mucor spp.
|
|
Cunninghamella bertholletiae
|
Treatment Strategies for Fungal Infections
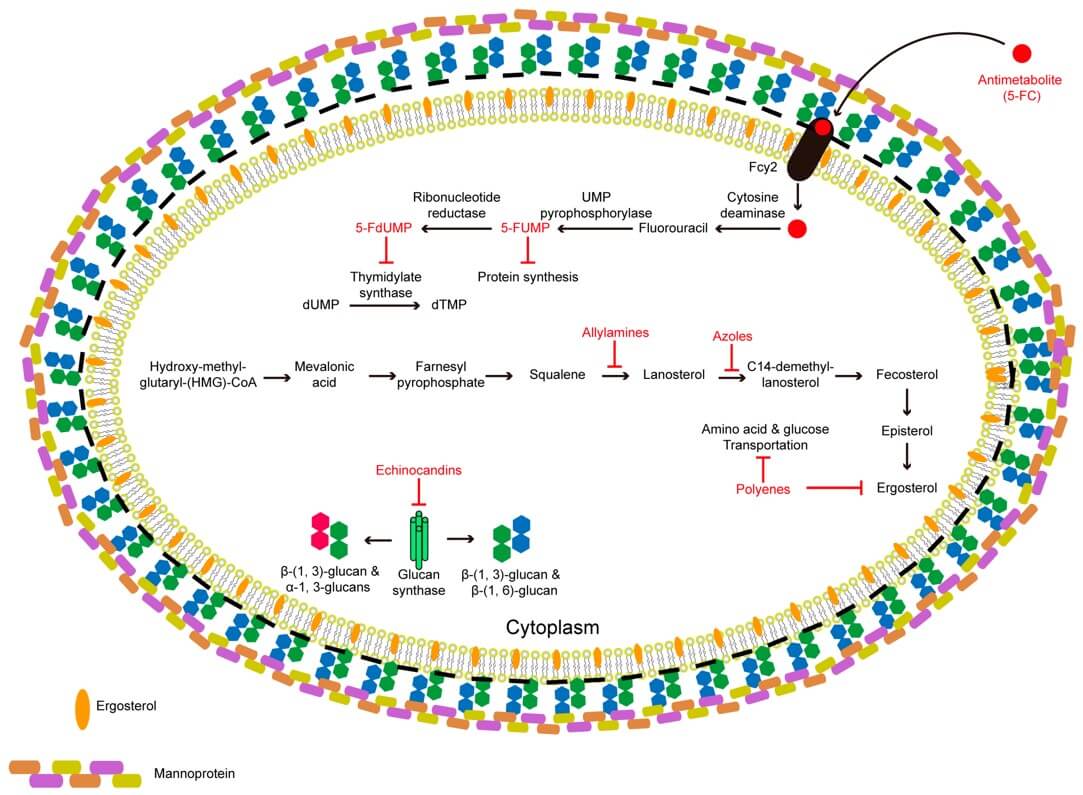 Fig. 1 Schematic representation of the conventional antifungal
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of the conventional antifungal
agents, their targets, and actions.1,4
-
Treatment Strategies
Traditional treatment strategies for fungal infections involve the use of antifungal medications such as azoles, polyenes, echinocandins, and flucytosine. However, these drugs may have limitations such as low solubility, poor bioavailability, and potential side effects.
-
High Systemic Toxicity: Can lead to severe side effects, including kidney and liver damage.
-
Poor Bioavailability: Inefficient absorption requires higher, more toxic doses.
-
Growing Drug Resistance: Decreasing efficacy against resilient fungal strains.
-
Limited Tissue Penetration: Difficulty reaching deep-seated infection sites.
-
Advanced lipid-based drug delivery systems
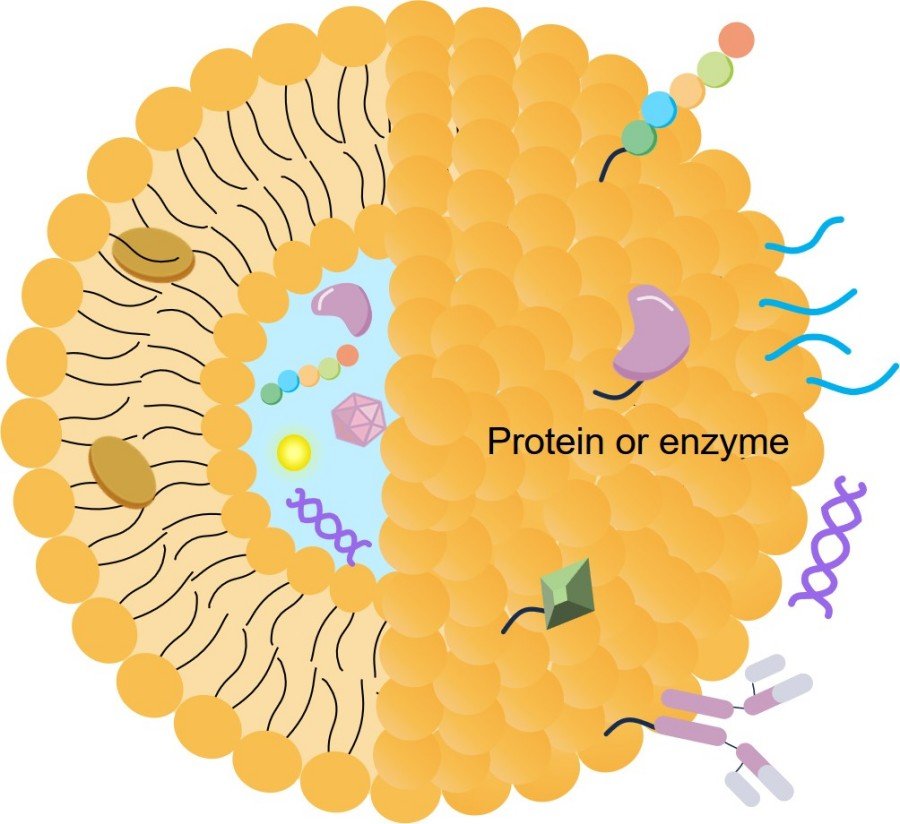
Lipid-based drug delivery systems like liposomes, and ethosomes are engineered to overcome the hurdles of traditional therapies. By encapsulating antifungal agents, these nanosystems enhance solubility, protect the drug from degradation, and enable targeted, sustained release, transforming the therapeutic landscape.
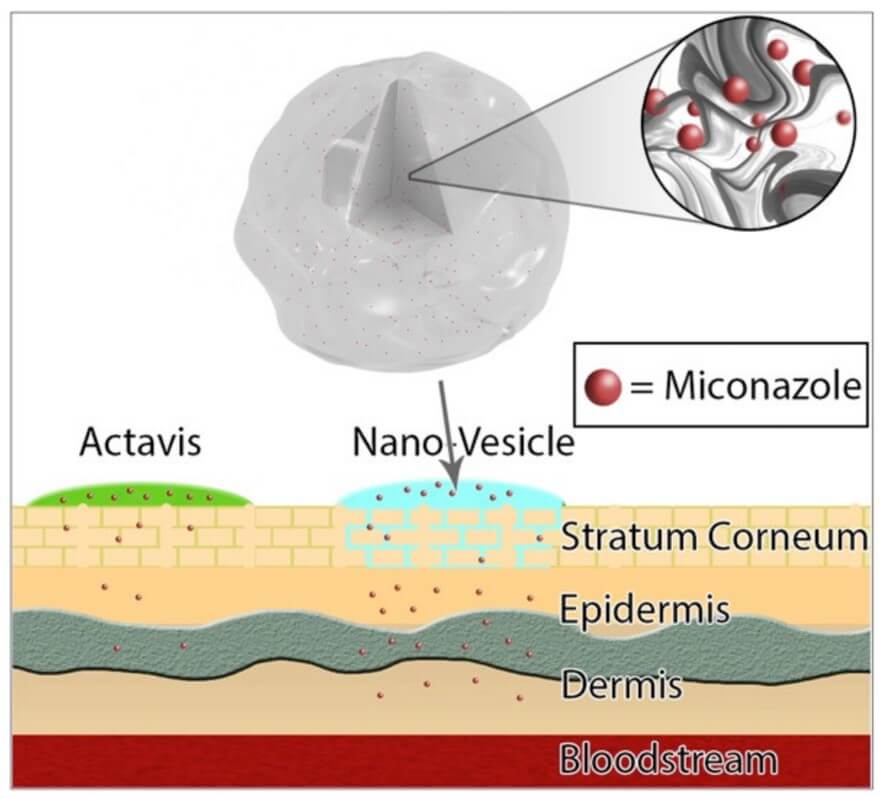 Fig. 2 Miconazole loaded nano-vesicles offer a higher delivery of drug content through the epidermis to the target site of fungal infection.2,4
Fig. 2 Miconazole loaded nano-vesicles offer a higher delivery of drug content through the epidermis to the target site of fungal infection.2,4
*Click on a lipid-based system above to learn more about its unique properties and advantages.
|
Antifungal Agents
|
Drugs
|
Targets
|
|
Azoles
|
Sertaconazole
|
Epidermophyton
Trichophyton
|
|
Tioconazole
|
Candida spp.
|
|
Luliconazole
|
Epidermophyton, Trichophyton
|
|
Posaconazole
|
Aspergillus spp.
Candida spp.
|
|
Efinaconazole
|
Trichophyton
|
|
Polyenes
|
Amphotericin B
|
Aspergillus spp.
Candida spp.
Cryptococcus spp.
|
|
Nystatin B
|
Candida spp.
|
|
Echinocandins
|
Anidulafungin
|
Candida spp.
|
|
Micafungin
|
Candida spp.
|
|
Allylamins
|
Naftifine
|
Trichophyton
|
|
Terbinafine
|
Trichophyton
|
|
Antimetabolites
|
5-flucytosine
|
Candida spp.
Cryptococcus spp.
|
How Creative Biolabs' Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems Can Assist Your Project
Creative Biolabs provides end-to-end solutions to overcome the most pressing challenges in antifungal drug development. Our expertise in formulation, targeting, and delivery enables you to accelerate your research and enhance your therapeutic candidates.
Protecting the Drug
Many antifungal compounds are susceptible to degradation in biological environments or have poor solubility. Our lipid-based delivery systems act as protective shells, shielding the drug from premature degradation by enzymes or pH changes. This protection ensures that a higher percentage of the administered drug reaches its target site in its active form, improving therapeutic efficacy.
Promoting Cellular Uptake
Fungal cells often possess mechanisms to limit drug uptake or actively pump drugs out. Our delivery systems can enhance cellular uptake through various mechanisms, including fusion with the fungal cell membrane, endocytosis, or passive diffusion. This improved uptake increases the intracellular concentration of the antifungal agent, overcoming resistance mechanisms that rely on reduced drug entry.
Enhanced Transdermal & Topical Delivery
We engineer advanced delivery systems like ethosomes and transfersomes that dramatically improve skin penetration. These deformable vesicles navigate the skin's layers to deliver antifungal agents directly to deep-seated infections, increasing local concentration and efficacy while minimizing systemic exposure.
Precision Targeted Therapy
Achieve site-specific drug delivery with our functionalized nanoparticles. We conjugate antibodies or fungi-targeting peptides (e.g., P-113 analogs) to the surface of liposomes, guiding your therapeutic directly to the pathogen. Our in-house peptide synthesis capabilities allow for fully customized targeting ligands to meet your project's unique needs.
Passive Targeting
Our lipid-based delivery systems can accumulate preferentially in infected tissues due to their size and surface properties. In systemic fungal infections, for example, the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect can lead to higher concentrations of the drug in infected organs like the lungs or kidneys.
Optimized Secondary Formulations
We integrate our advanced lipid-based drug delivery systems into secondary formulations. By incorporating nanoparticles into hydrogels (e.g., chitosan-based), we create stable, cosmetically elegant products with enhanced skin adherence and sustained-release profiles, improving both therapeutic outcomes.
Request a Consultation
Why Partner with Creative Biolabs?
Our dedication to innovation, quality, and client success makes us the ideal partner to advance your antifungal research.
Decades of Expertise
Our team brings over 20 years of specialized experience in drug delivery, biology, and pharmaceutical sciences.
Cutting-Edge Technology
We utilize state-of-the-art instrumentation and proprietary methods for nanoparticle formulation and characterization.
Collaborative Partnership
We work as an extension of your team, providing transparent communication and customized support to ensure your project's success from start to finish.
Workflow for Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems Development for Fungal Infections
Published Data
This research highlights the significant therapeutic benefits achieved by encapsulating Sphaeropsidin A (SphA) within liposomes. The study explored the ability of SphA-loaded liposomes (SphA-L) to reduce cytotoxicity while preserving antifungal activity against Candida auris. Researchers comparing the inhibitory effect of free SphA versus SphA-L against a panel of bacterial strains, including C. auris. Such data would typically show that while free SphA exhibits some antifungal activity, SphA-L maintains comparable or even enhanced antifungal potency. Crucially, the liposomal formulation would be demonstrated to achieve this activity with significantly reduced cytotoxicity (e.g., HaCaT cell).
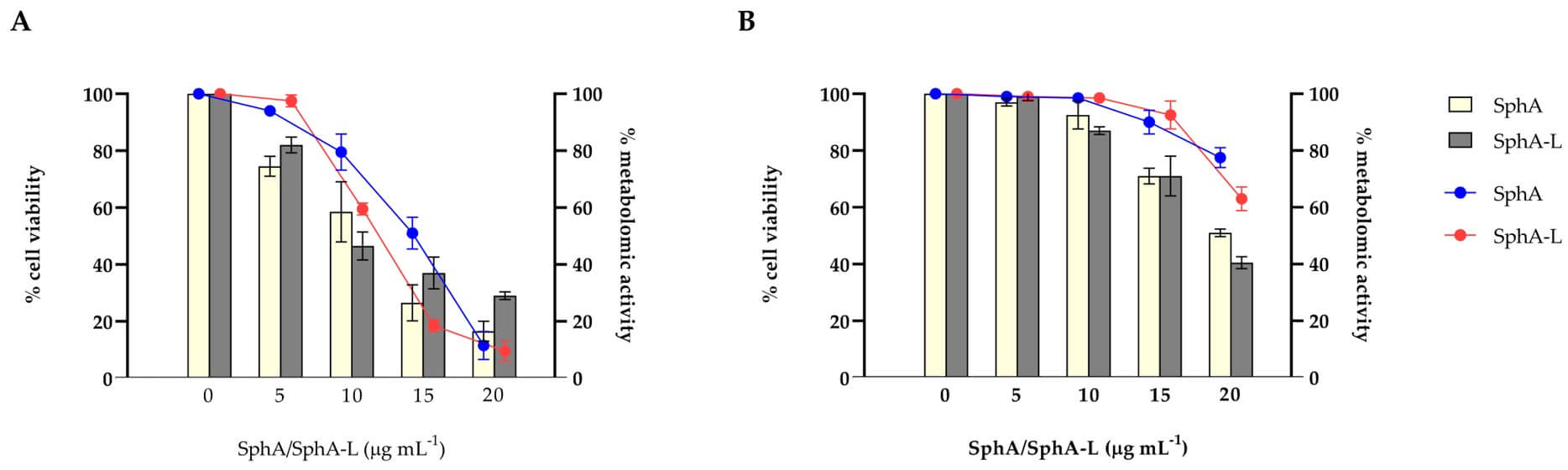 Fig. 3 Efficacy of SphA and SphA-L on C. auris at different stages of biofilm development.3,4
Fig. 3 Efficacy of SphA and SphA-L on C. auris at different stages of biofilm development.3,4
By leveraging sophisticated lipid delivery systems techniques, Creative Biolabs can replicate and advance such achievements, providing solutions that effectively address the inherent toxicity and delivery challenges of potent antifungal (and potentially antibacterial) agents, ultimately leading to safer and more effective treatments for various infections.
Lipid-based drug delivery systems represent a pivotal evolution in drug delivery, offering a robust and versatile platform to address the persistent challenges in antifungal therapy. By overcoming limitations of conventional formulations—such as poor solubility, systemic toxicity, and inadequate tissue penetration—liposomes empower the development of safer, more effective, and precisely targeted treatments. At Creative Biolabs, our expertise, honed over two decades in advanced biology and pharmaceutical innovation, allows us to harness lipid-based drug delivery systems technology to develop therapies that are more effective, safer, and precisely targeted. Contact us for a one-on-one consultation and see how our proficiency in lipid-based drug delivery systems can drive your therapeutic innovations forward.
Related Services
Resources
References
-
Du, Wei, et al. "Striking back against fungal infections: The utilization of nanosystems for antifungal strategies." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22.18 (2021): 10104. doi:10.3390/ijms221810104.
-
Deaguero, Isaac G., et al. "Nano-vesicle based anti-fungal formulation shows higher stability, skin diffusion, biosafety and anti-fungal efficacy in vitro." Pharmaceutics 12.6 (2020): 516. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics12060516.
-
Buonanno, Annalisa, et al. "Sphaeropsidin A Loaded in Liposomes to Reduce Its Cytotoxicity and Preserve Antifungal Activity Against Candida auris." Molecules 29.24 (2024): 5949. doi:10.3390/molecules29245949.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.

For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use

 Fig. 1 Schematic representation of the conventional antifungal
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of the conventional antifungal Fig. 2 Miconazole loaded nano-vesicles offer a higher delivery of drug content through the epidermis to the target site of fungal infection.2,4
Fig. 2 Miconazole loaded nano-vesicles offer a higher delivery of drug content through the epidermis to the target site of fungal infection.2,4
 Fig. 3 Efficacy of SphA and SphA-L on C. auris at different stages of biofilm development.3,4
Fig. 3 Efficacy of SphA and SphA-L on C. auris at different stages of biofilm development.3,4



 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use