Liposomes are spherical vesicles composed of phospholipid bilayers that can encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs. Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are lipid-based nanocarriers primarily used for encapsulating nucleic acid drugs (such as mRNA) and certain small molecule drugs. Kits designed for the preparation of liposomes and LNPs can enhance drug delivery efficiency and offer the following advantages:
As a supplier focused on lipid-based delivery systems, Creative Biolabs has developed optimized formulations and processes to create kits that efficiently prepare liposomes or lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) in a short time frame. These kits are designed for the direct preparation of liposomes or LNPs and offer excellent reproducibility. You can choose the appropriate kit based on the active substances you wish to encapsulate or the lipids of interest. Once you contact us, you will receive professional technical support and consulting services.
Please refer to our detailed list of kit products:
Optimizing mRNA-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles as a Potential Tool for Protein-Replacement Therapy
Author: Gambaro, Rocío, et al.
This study explored the impact of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) formulated with different lipid mixtures on mRNA delivery efficiency. Researchers utilized microfluidics to prepare four types of LNPs (LM1, LM2, LM3, and LM4) encapsulating EGFP mRNA, based on various lipid compositions. Subsequently, they evaluate the transfection efficiencies of a commercial formulation (GV) and the four LNPs in delivering EGFP mRNA to HepG2 cells. The results from the EGFP+ cells (figure a) indicated that all LNPs demonstrated high transfection efficiencies, with percentages of 93%, 87%, 96%, 87%, and 98% for GV, LM1, LM2, LM3, and LM4, respectively. Fluorescence microscopy results (figure b and c) revealed that the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of the positive control group was significantly higher than that of the other groups. In comparison, LM4 (DLin-MC3-DMA/DSPC/Cholesterol/ALC-0159) exhibited a higher MFI than GV, LM1, LM2, and LM3. Overall, the results suggest that the LNPs effectively delivered EGFP-encoding mRNA to HepG2 cells.
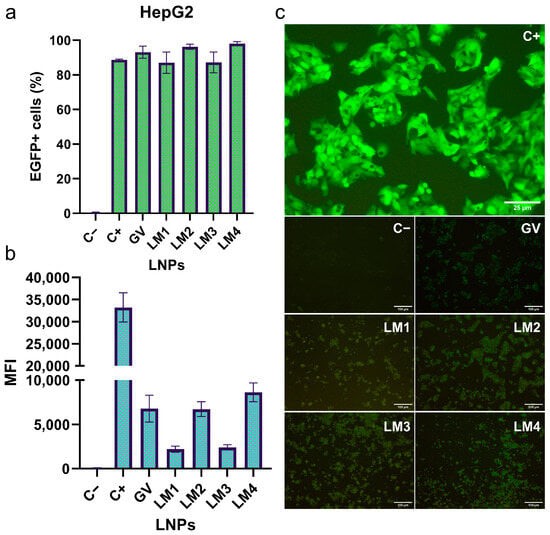 Fig.1 Efficiency of different LNP formulations in transfecting EGFP mRNA into HepG2 cells.1,2
Fig.1 Efficiency of different LNP formulations in transfecting EGFP mRNA into HepG2 cells.1,2
References
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use| Cat | Product name | Lipid Composition | Data sheet | MSDS | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDLY-0724-LD136 | Liposome Preparation Kit | Cholesterol, Egg PC, Stearylamine |
|
|
Inquiry |
| LDLY-0325-LD1012 | Liver-Targeted LNP Preparation Kit | Exclusive Liver-Targeting Lipid Mixture |
|
|
Inquiry |
| LDLY-0325-LD1013 | Lung-Targeted LNP Preparation Kit | Exclusive Lung-Targeting Lipid Mixture |
|
|
Inquiry |
| LDLY-0325-LD1014 | Spleen-Targeted LNP Preparation Kit | Exclusive Spleen-Targeting Lipid Mixture |
|
|
Inquiry |
| LDLY-0325-LD1015 | Muscle-Targeted LNP Preparation Kit | Exclusive Muscle-Targeting Lipid Mixture |
|
|
Inquiry |
| LDLY-0325-LD1016 | T Cell-Targeted LNP Preparation Kit | Exclusive T Cell-Targeting Lipid Mixture |
|
|
Inquiry |
Online Inquiry