Schizophrenia, a devastating neuropsychiatric disorder, presents profound challenges in its treatment due to its complex nature and the inherent difficulties in delivering therapeutic agents effectively to the brain. Given these complexities, the development of advanced drug delivery systems, particularly lipid-based drug delivery systems, is crucial for achieving effective therapeutic outcomes. Creative Biolabs is uniquely positioned to solve these challenges for our clients through our comprehensive suite of delivery systems-related services.
Schizophrenia is a chronic and complex psychiatric disorder characterized by a wide range of debilitating symptoms, including positive symptoms (hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thought and speech), negative symptoms (apathy, social withdrawal, anhedonia), and cognitive deficits (impaired memory, attention, and executive function). Its etiology is multifactorial, involving a complex interplay between genetic predispositions, neurobiological abnormalities, and environmental factors such as prenatal infections and psychosocial stress. The profound impact on daily functioning and quality of life for affected individuals and their families highlights the critical need for more effective and tolerable treatment strategies.
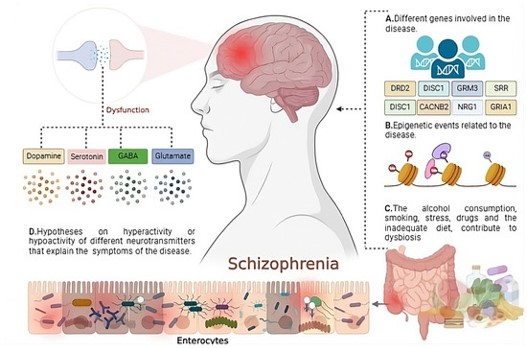 Fig. 1 Diagram of neuroinflammation in schizophrenia.1
Fig. 1 Diagram of neuroinflammation in schizophrenia.1
Current therapeutic strategies for schizophrenia primarily revolve around modulating neurotransmitter systems, particularly dopamine. However, emerging research points towards a multi-target approach, exploring novel pathways beyond the traditional dopamine hypothesis to address the diverse symptomatology and underlying pathophysiology. These include serotoninergic, glutamatergic, and immunomodulatory systems, as well as targets aimed at improving cognitive function. Understanding these diverse targets is crucial for developing next-generation therapeutics.
| Hypothesis | Target | Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dopamine | Dopaminergic stabilizers | Enhance medication adherence |
| Glutamate |
AMPA receptor NMDAR, AMPA receptor Metabotropic receptors |
Mitigate negative symptoms and cognitive deficits |
| Serotonin |
Agonists (5-HT1A, 5-HT2C) Antagonists (5-HT2C, 5-HT3, 5-HT6, 5HT7) 5-HT reuptake inhibitors |
Reduce extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) Alleviate negative symptoms and cognitive deficits |
| Acetylcholine | Agonists and positive allosteric modulators (α-7 nicotinic and M1 muscarinic) | Target cognitive deficits via nicotinic agonism; Target positive symptoms via muscarinic agonism |
| Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) |
Selective GABA-A agonists GABA-B antagonists |
Augment antipsychotic efficacy |
| Inflammation | Cytokines | Possibly the early period of the psychosis |
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) constitutes a highly selective, semipermeable interface that segregates the systemic circulation from the brain parenchyma and the extracellular fluid within the central nervous system (CNS). Formed by specialized endothelial cells with tight junctions, the BBB meticulously regulates the passage of ions, molecules, and cells, protecting the brain from pathogens and toxins while maintaining a stable environment for neuronal function. While essential for brain health, this protective barrier poses a significant challenge for drug delivery to the CNS.
Mechanisms of Drug Transport
Across the BBB
Despite the various natural mechanisms for substances to cross the BBB, conventional oral or intravenous administration of antipsychotics often leads to several significant limitations in schizophrenia treatment.
These multifaceted limitations underscore the critical need for advanced drug delivery systems that can intelligently overcome the BBB's formidable defenses, protect the drug payload from degradation, ensure sustained release, and enable targeted delivery to the CNS. Choosing an appropriate delivery system is paramount to realizing the full therapeutic potential of novel and existing antipsychotics. This is precisely where Creative Biolabs' expertise in lipid-based drug delivery systems becomes invaluable, offering tailored solutions to bypass these challenges.
We assist in different links of schizophrenia treatment by facilitating drug delivery through multiple advanced methods:
Discover How We Can Help - Request a Consultation
The ongoing advancements in lipid-based drug delivery systems technology are poised to redefine the landscape of schizophrenia treatment. By offering targeted, efficient drug delivery, lipid-based drug delivery systems are not just an alternative but a cornerstone for the next generation of therapeutics. Creative Biolabs is committed to leading this charge, leveraging our expertise to unlock the full potential of lipid-based systems for schizophrenia. Our solutions address key challenges, ensuring efficient drug delivery and enhanced therapeutic outcomes. For comprehensive support, including system functionalization and efficacy validation, reach out to our expert team.
Reference
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseApplications
Online Inquiry