Myocardial infarction (MI) and its associated complications, such as malignant arrhythmias and pathological ventricular remodeling, pose a significant threat to human health. Lipid-based drug delivery systems have emerged as a unique solution due to their excellent biocompatibility, high bioavailability, and ability to carry both hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds. With their broad physicochemical properties that enable tunable biological functions, and the added benefits of straightforward formulation, cost-effective production, and scalability further enhance its potential in targeted therapies. Building on these strengths, Creative Biolabs' lipid-based drug delivery system thus emerges as a highly promising solution, providing precise and efficient drug delivery to the infarcted myocardium and driving advancements in cardiovascular disease treatment.
Myocardial infarction (MI) is commonly a consequence of the long-term progression of atherosclerosis (As). When atherosclerotic plaques rupture, they release thrombogenic components that activate platelets and trigger the coagulation cascade, leading to thrombus formation and occlusion of distal coronary arteries. This hypercoagulable state can also cause additional plaque ruptures, resulting in multiple lesions, myocardial cell necrosis, fibrosis, and potentially heart failure. Common treatment approaches include pharmacotherapy, antithrombotic therapy, and coronary artery bypass grafting.
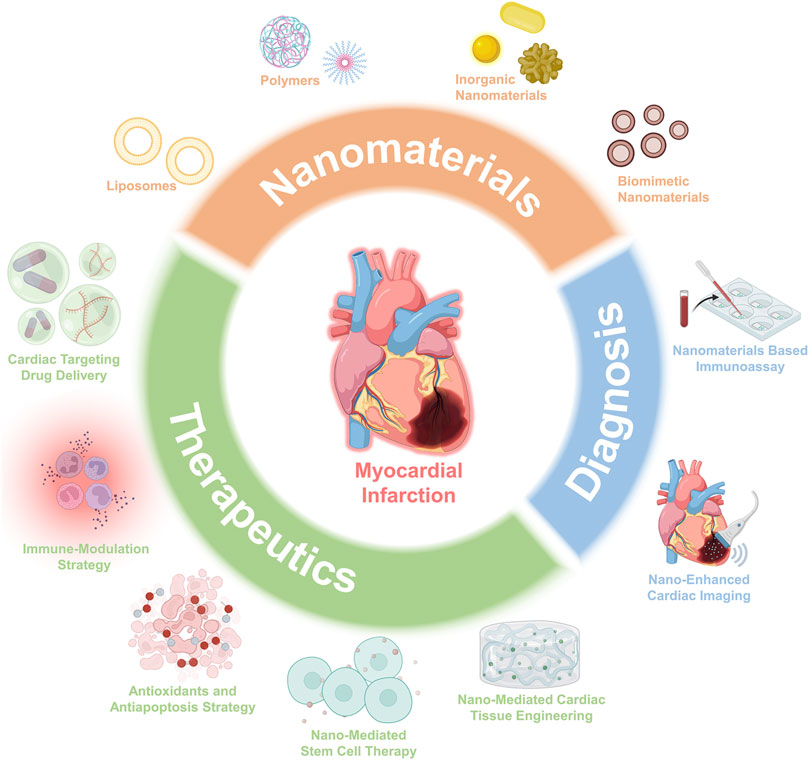 Fig.1 Schematic overview of the advances of nanomaterials and applications for both therapeutics and diagnosis.1
Fig.1 Schematic overview of the advances of nanomaterials and applications for both therapeutics and diagnosis.1
The pathological damage in MI primarily involves inflammatory responses and the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Therefore, mitigating inflammation, combating ROS damage, and enhancing myocardial tissue repair and regeneration are key strategies for protecting myocardial cells.
Lipid-based drug delivery systems are transforming MI therapy. These advanced systems encapsulate therapeutic molecules within lipid carriers such as liposomes and lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), thereby bypassing biological barriers and achieving direct delivery to affected cardiomyocytes. Creative Biolabs formulates its lipid-based delivery systems with biocompatible and biodegradable lipids, ensuring minimal toxicity and optimal bioavailability. We go beyond standard formulations by offering customized development of functionalized liposomes. Whether you require surface modifications with antibodies, peptides, or other targeting ligands, or need stimuli-responsive release mechanisms, our team of experts is ready to provide one-on-one technical support tailored to your specific needs.
Table 1 Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems for MI Therapy
| Lipid-Based Delivery System | Therapeutic agent | Modification | Administration Route | Therapeutic Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liposomes | AZ7379 (PARP-1 inhibitor) | Cardiomyocyte-specific I-1 peptide | IV | Encapsulation of AZ7379 in liposomes significantly prolongs its circulation time and enhances PARP-1 inhibition by 3-fold across multiple cell types. |
| Liposomes | AMO-1 | / | IV | Liposomes deliver AMO-1 to ischemic myocardium in rats, alleviating ischemic arrhythmias by silencing miR-1. |
| Liposomes | Berberine | / | IV | Prolonged circulation effectively mitigates adverse myocardial remodeling, improving cardiac dysfunction in MI-induced mice. |
| Liposomes | Rapamycin and MI antigens | PEGylation | ID | Reduces adverse remodeling and cardiac dysfunction post-myocardial infarction. |
| Liposomes | Anti-miR-1 antisense oligonucleotides (AMO-1) | anti-cardiac troponin I (cTnI) antibody | IV | Enables targeted delivery to ischemic myocardial tissue, minimizing off-target effects of AMO-1. |
| Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs) | Total Flavonoid Extract of Dracocephalum Moldavia L. (TFDM) | / | PO | Significantly reduces infarct size, myocardial enzymes, and inflammatory factors. |
The development of Creative Biolabs' lipid-based delivery system for MI therapy is an ongoing endeavor. Our extensive research and development efforts have focused on optimizing the formulation and targeting mechanisms to achieve maximum therapeutic efficacy. Discover the potential of our lipid-based delivery system for your MI treatment strategies—contact us today.
Reference
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseApplications
Online Inquiry