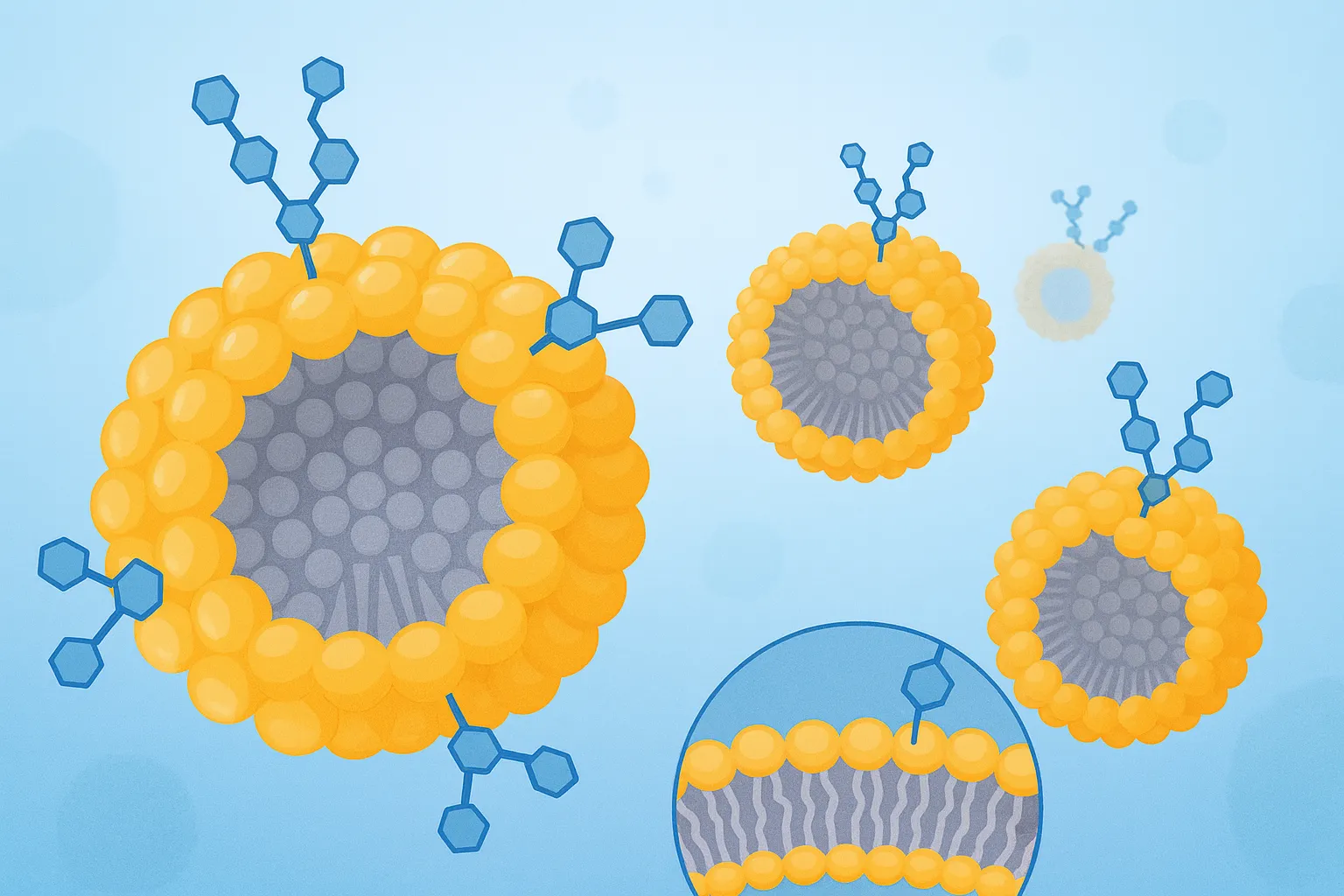
Liposome Surface Glycoengineering Service
Build glycan-decorated liposomes that speak the language of cells—precise, stable, and ready for rigorous research.
Partnered with Industry Leaders
Creative Biolabs supports global R&D teams with ISO-standardized lipid platforms, end-to-end method development, and transparent data packages.





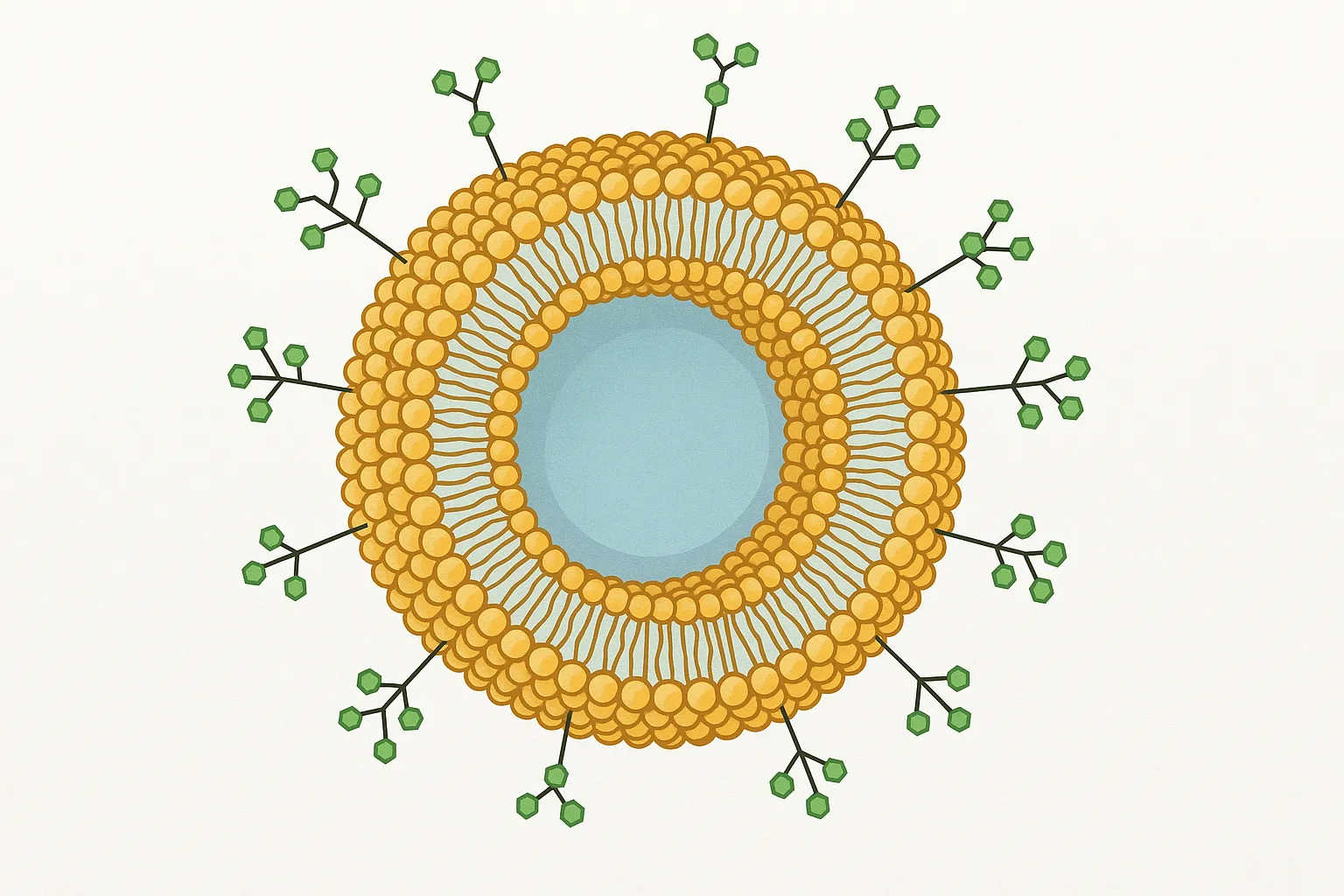
Why Liposome Surface Glycoengineering Matters
Cellular recognition frequently begins at the glycocalyx. Receptors such as ASGPR, mannose receptor (CD206), DC-SIGN, selectins, Siglecs, and galectins read specific sugar “codes” to coordinate uptake, adhesion, and signaling. Decorating liposome surfaces with well-defined glycans translates those codes into practical tools for receptor-mediated uptake, improved biodistribution in models, and tunable immune interactions—without compromising core formulation stability.
For research programs that already rely on PEGylation, charge modulation, or ligand peptides, glycoengineering adds a complementary axis of control: multivalent, spatially organized carbohydrate motifs that engage lectins with high avidity. Creative Biolabs combines synthetic chemistry, enzymology, and lipid formulation know-how so you can compare targeting hypotheses head-to-head under consistent analytical standards.
Our Liposome Surface Glycoengineering Solutions
Chemoselective Glycan Conjugation
We engineer glycan displays through clean, orthogonal chemistries that preserve liposome integrity and carbohydrate structure.
- Headgroup modification. Reactive lipids (e.g., DSPE-PEG-NHS, maleimide, azide-PEG) allow controlled coupling to amino-, thiol-, or azide-bearing glycans. Spacer length and grafting density are optimized for receptor access and stability.
- Click strategies. SPAAC, CuAAC, and iEDDA ligations enable fast, selective attachment with adjustable valency.
- Glycan panel. Mannose, Gal/GalNAc, sialic acids, fucosylated motifs, Lewis-type structures, and custom oligosaccharides. Glycolipids and glycopolymers are also available.
- Analytics: HPLC/UPLC, lectin binding assays, DLS/PDI, Z-potential, cryo-TEM, ICP-MS for trace catalysts, and endotoxin testing.
Enzymatic Remodeling
For precise glycocalyx mimicry, we apply glycosyltransferases and glycosidases directly on liposome surfaces.
- Extension. Controlled addition of sialyl, fucosyl, galactosyl, or GalNAc units for exact motifs.
- Editing. Trimming by exoglycosidases to reveal or mask termini.
- Support. Cofactor regeneration and optimized conditions for liposome stability.
Use cases: Siglec-biased liposomes, selectin-binding panels, galectin interaction models.
Advanced Assembly Strategies
We integrate hybrid or bio-inspired systems for complex applications.
- Metabolic bridges. Incorporation of azido-sugar derivatives for click-enabled hybrid vesicles.
- Proteo/glycoliposomes. Co-embedding proteins with glycans for cooperative receptor clustering studies.
- Multivalency control. Microfluidic mixing ensures consistent ligand spacing and reduced nonspecific binding.
Advantages of Our Liposome Surface Glycoengineering Service
Our platform integrates advanced chemistry and enzymology with precise lipid formulation to provide superior, reliable glycoengineering services.
Precise glycan control
Defined motifs, linkages, and valencies—validated by orthogonal analytics.
Clean surface chemistry
Bioorthogonal ligations and stringent impurity control to protect sensitive cargos and preserve colloidal stability.
Multimodal expertise
Chemistry, enzymology, and lipid formulation under one roof for faster iteration.
Manufacturability in mind
Reagent choices, workups, and process parameters aligned with robust scale-up.
Data you can trust
Transparent QC, traceable reagents, and complete method reporting.
Flexible engagement
From discovery-scale screening sets to larger batches for advanced studies.
Applications of Glycoengineered Liposomes
Receptor-guided uptake studies
Build mannosylated or fucosylated liposomes to compare CD206 or DC-SIGN engagement across primary cells and engineered lines. Titrate ligand density and PEG spacer length to separate affinity effects from steric constraints in uptake kinetics.
Hepatocyte and hepatocyte-like model targeting
Display galactose or GalNAc to engage ASGPR on liver-derived models. Use multivalency and mid-length PEG spacers to boost avidity while maintaining circulation stability in biodistribution studies.
Selectin-mediated adhesion under flow
Present sialyl Lewis-type motifs to probe rolling and adhesion on E-/P-selectin substrates in microfluidic channels. Evaluate detachment forces and the impact of valency on shear-resistant binding.
Siglec-biased immune modulation research
Sialylated surfaces with defined α-2,3 or α-2,6 linkages help interrogate Siglec-dependent recognition on myeloid and lymphoid cells, enabling side-by-side comparisons of motif preference and downstream signaling readouts.
Galectin interaction mapping
Create galactoside-rich coronae to quantify galectin binding and crosslinking propensity. Combine with cryo-TEM and light scattering to correlate network formation with colloidal behavior.
Biomimetic membrane models
Incorporate glycolipids or enzymatically extended chains to emulate cell glycocalyces for protein corona studies or complement activation assessments, using consistent surface analytics to pinpoint structure–function relationships.
Mucosal adhesion and barrier transport research
Tune charge and hydration with sulfated glycans or sialylated motifs to investigate mucus penetration versus adhesion. Adjust PEG length and glycan density to optimize residence time in ex vivo models.
Combinatorial targeting
Co-display glycans with peptides, aptamers, or antibodies on the same liposome to study cooperative binding and receptor clustering, while monitoring aggregation risk with titrated ligand ratios and surface passivation.
Liposome Surface Glycoengineering Workflow
Design Consultation
Define target receptors, glycan motifs, desired valency, particle size, charge, and stability constraints.
Formulation Prototyping
Prepare base liposomes (e.g., HSPC/Chol/PEG variants) with predefined reactive handles; screen particle size distribution and PDI.
Glycan Conjugation or Enzymatic Build
Execute chemoselective coupling or stepwise enzymatic extension; control grafting density and spacer length.
Characterization & Acceptance Criteria
DLS/PDI, Z-potential, cryo-TEM snapshots, conjugation degree, lectin binding, residual catalysts, and endotoxin.
Stability & Functional Readouts
Stress testing under salt/pH/serum, accelerated and real-time studies; cell-based uptake or binding (optional).
Scale-Up & Tech Transfer
Batch-to-batch reproducibility assessment, method documentation, and optional transfer to your facility.
Deliverables from Our Service
- ✓Formulation vials at agreed concentrations and buffer compositions, with lot-matched controls.
- ✓Certificate of Analysis covering DLS/PDI, Z-potential, conjugation metrics, residuals, endotoxin, and visual inspection.
- ✓Analytical report with methods, raw data, and acceptance criteria; lectin binding/bio-layer interferometry traces when included.
- ✓Stability summary with conditions, time points, and specification outcomes.
- ✓Method documentation supporting repeatability and optional scale-up notes.
All services are strictly For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Explore Related Liposome Development Services
To support diverse research goals, Creative Biolabs offers a range of complementary lipid-based delivery and liposome engineering services. Clients often combine our liposome surface glycoengineering service with the following solutions:
Frequently Asked Questions
Glycoengineering enables precise presentation of biologically relevant sugar motifs, offering receptor-specific recognition and multivalency unmatched by simple PEGylation or peptide conjugation. It provides tunable control over uptake, biodistribution, and cellular interactions in research models.
Other Resources
References
- Torchilin, Vladimir P. "Multifunctional, stimuli-sensitive nanoparticulate systems for drug delivery." Nature reviews Drug discovery 13.11 (2014): 813-827. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4333
- Torres-Pérez, Sergio Andrés, et al. "Glycosylated nanoparticles for cancer-targeted drug delivery." Frontiers in Oncology 10 (2020): 605037. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.605037
- Hütter, Julia, and Bernd Lepenies. "Carbohydrate-based vaccines: an overview." Carbohydrate-Based Vaccines: Methods and Protocols (2015): 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2874-3_1
Online Inquiry
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.