ABCA7 deficiency disrupts lipid homeostasis by impairing phospholipid efflux from neuronal membranes, destabilizing lipid rafts, key structures for synaptic function and mitochondrial integrity. This leads to mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative damage to biomolecules, and impaired neurotransmitter receptor clustering, weakening synaptic plasticity.
Introduction to ABCA7
ABCA7 (ATP-Binding Cassette Subfamily A Member 7) is a transmembrane protein belonging to the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. It plays a critical role in lipid homeostasis, phagocytosis, and neuroinflammation by regulating the transport of phospholipids and cholesterol across cellular membranes. In addition, mutations in ABCA7 are strongly linked to late-onset Alzheimer's Disease (AD), schizophrenia, and postoperative cognitive dysfunction.
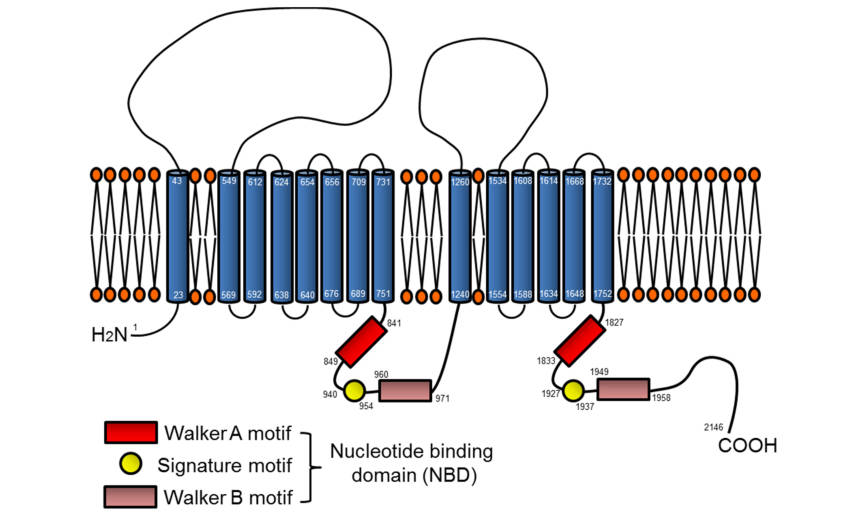 Fig.1 Topological model of ABCA7.1
Fig.1 Topological model of ABCA7.1
ABCA7-Related Pathways
Lipid Dysregulation & Neurodegeneration
Neuroinflammation & Microglial Activation
ABCA7 modulates microglial polarization, shifting from pro-inflammatory (M1) to anti-inflammatory (M2) states. Promoting cholesterol efflux via apolipoprotein E (APOE) lipidation, it suppresses M1 markers and enhances M2 markers, fostering Aβ clearance and tissue repair.
Genetic Variants & Disease Risk
ABCA7 variants influence AD risk through diverse mechanisms. Rarer loss-of-function mutations cause early-onset AD with aggressive pathology.
Core Technology
| Technique | Application |
|---|---|
| ELISA | Quantifies ABCA7 protein levels in brain tissue, CSF, or blood. |
| Western Blot | Detects ABCA7 expression changes under inflammatory or lipid-depleted conditions. |
| qPCR/RNA Sequencing | Analyzes ABCA7 mRNA levels in neurodegenerative disease models. |
| Single-Cell RNA Seq | Maps cell-type-specific ABCA7 expression in AD brains. |
| Immunohistochemistry | Visualizes ABCA7 localization in glial cells and neurons. |
Significance of ABCA7 Analysis
Advancing AD Care
ABCA7 levels in blood/CSF act as biomarkers for AD, correlating with amyloid-beta buildup and cognitive decline.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
ABCA7 stabilizes the blood-brain barrier and suppresses microglia-driven inflammation, protecting brain health.
Small-Molecule Screening
High-throughput platforms identify compounds that boost ABCA7 stability, offering treatments for AD, Parkinson's, and vascular dementia.
Atherosclerosis Control
ABCA7 promotes cholesterol efflux, reducing plaque formation and cardiovascular risk.
Diabetes-Linked Cognition
ABCA7 dysregulation ties metabolic disorders to cognitive decline, highlighting dual-target therapy opportunities.
FAQs
-
What are the key technical challenges in ABCA7 protein quantification?
ABCA7 protein quantification faces hurdles due to its low abundance in biological fluids, post-translational modifications, and tissue-specific expression patterns. Standard immunoassays like ELISA often lack sensitivity for CSF or plasma samples, requiring ultra-sensitive techniques. Additionally, ABCA7's instability during sample processing can lead to degradation, necessitating optimized protocols for rapid freezing, protease inhibitor use, and minimal freeze-thaw cycles.
-
What role does ABCA7 play in cardiovascular health?
ABCA7 is a key regulator of reverse cholesterol transport, a process by which macrophages expel excess cholesterol via high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles. Reduced ABCA7 activity leads to cholesterol accumulation in arterial walls, promoting foam cell formation and atherosclerotic plaque development.
-
What is the role of ABCA7 in immune cell function beyond the brain?
ABCA7 is critical for peripheral immune homeostasis. In macrophages, it regulates cholesterol efflux, preventing foam cell formation and atherosclerosis. ABCA7 deficiency alters cytokine production, promoting pro-inflammatory M1 polarization. In T cells, ABCA7 modulates lipid raft composition, affecting TCR signaling and autoimmune disease susceptibility.
-
What are the limitations of animal models in ABCA7 research?
Animal models, while invaluable, have limitations. Mice lacking ABCA7 exhibit milder AD-like phenotypes than humans, possibly due to species-specific lipid metabolism. Non-human primates better replicate human ABCA7 function but face ethical and cost barriers. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from AD patients with ABCA7 mutations offer human-relevant models but lack systemic context. Combining animal, cellular, and organoid models may overcome these gaps.
-
What types of biological samples are most suitable for conducting comprehensive ABCA7 analysis?
A wide range of biological specimens can be utilized for ABCA7 analysis, each offering unique insights. These include postmortem brain tissue for examining localized protein expression and pathological changes, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for detecting soluble ABCA7 fragments and associated biomarkers, blood plasma or serum for non-invasive monitoring of systemic ABCA7 levels, induced iPSC-derived neurons for modeling disease mechanisms in a human-relevant context, and animal models for studying in vivo physiological and pathological roles of ABCA7. The choice depends on research goals, ethical considerations, and technical feasibility.
-
Could you elaborate on the mechanisms through which ABCA7 dysfunction contributes to the pathogenesis of AD?
ABCA7 dysfunction plays a multifaceted role in AD progression. Firstly, it impairs amyloid-beta (Aβ) clearance by reducing lipidation of APOE, a critical chaperone for Aβ efflux from the brain. This leads to Aβ accumulation and plaque formation. Secondly, ABCA7 disrupts lipid homeostasis in neurons and glial cells, compromising membrane integrity and synaptic function. Thirdly, ABCA7 deficiency exacerbates neuroinflammation by promoting pro-inflammatory cytokine release from microglia and astrocytes, which further damages neuronal networks. These interconnected pathways collectively drive neurodegeneration and cognitive decline in AD.
-
What is the approximate cost range for ABCA7 ELISA testing, and how does it vary based on different factors?
The cost of ABCA7 ELISA testing is influenced by several variables, including sample type, sample volume, assay sensitivity requirements, and additional services. Please contact our technical support team with details about your study design and sample specifications.
Unlock the potential of ABCA7 research with our state-of-the-art services. Contact us today!
Reference
- Aikawa, Tomonori, Marie-Louise Holm, and Takahisa Kanekiyo. "ABCA7 and pathogenic pathways of Alzheimer's disease." Brain Sciences 8.2 (2018): 27. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8020027
For Research Use Only.