By reducing intracellular drug accumulation, ABCC1 enables tumor survival. It also effluxes tyrosine kinase inhibitors, complicating targeted therapies.
ABCC1 Introduction
ABCC1 (ATP-Binding Cassette Subfamily C Member 1) is a pivotal ATP-dependent efflux transporter belonging to the ABC superfamily. Its primary function is to protect cells by exporting xenobiotics, chemotherapeutic agents, and endogenous signaling molecules. Overexpression in cancers such as breast, lung, and ovarian tumors correlates with poor prognosis due to multidrug resistance (MDR). Beyond oncology, ABCC1 regulates neurotransmitter clearance, heavy metal detoxification, and inflammatory responses, linking it to neurodegenerative diseases, asthma, and environmental toxicity.
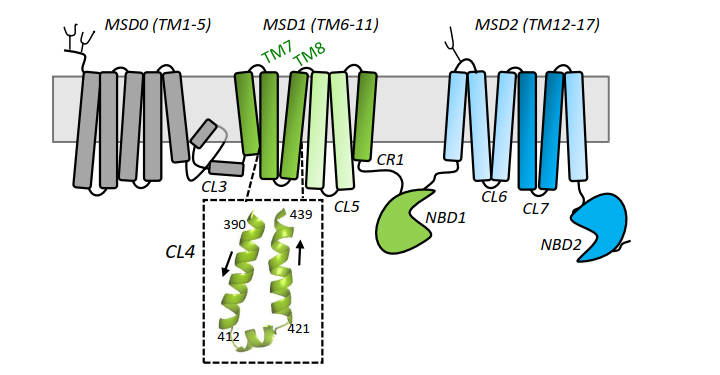 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the secondary structure of human MRP1 highlighting CL4.1
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the secondary structure of human MRP1 highlighting CL4.1
Key Pathways & Biological Functions
ABCC1's influence spans cellular defense, signaling, and homeostasis:
Chemotherapy Resistance
Inflammatory & Immune Modulation
Transports prostaglandin E2 and leukotriene C4, exacerbating airway inflammation in asthma and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis.
Neuroprotection
Clears neurotoxic metabolites across the blood-brain barrier, offering potential in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease research.
Heavy Metal Detoxification
Exports arsenic and cadmium conjugates, protecting against environmental toxicity.
Redox Regulation
Modulates glutathione homeostasis, influencing cellular redox status and apoptosis.
Cutting-Edge Analysis Platforms & Technologies
Our ABCC1 analysis service leverages a range of advanced, state-of-the-art methodologies to comprehensively decode the functions of ABCC1.
Gene Editing
We employ cutting-edge gene editing techniques to precisely perform knockout or knock-in of the ABCC1 gene in diverse cell lines and transgenic mice. This facilitates in-depth exploration of ABCC1's role and the impacts of its genetic modification at both cellular and organismal levels, creating tailored models for detailed study.
High-Throughput Screening
Our high-throughput screening platform is used to swiftly identify ABCC1 modulators, including small molecules and biological agents that can affect its function. We also offer custom screens to find factors contributing to drug resistance.
Western Blot
Using highly specific antibodies, we accurately quantify ABCC1 protein levels in various samples, assessing changes under different experimental conditions.
Immunohistochemistry
This technique maps ABCC1 localization in FFPE or frozen tissue sections, providing insights into its expression patterns in different cell types and tissue compartments.
Flow Cytometry
With PE-conjugated antibodies, we measure membrane-bound ABCC1 in live cells, offering quantitative data on its surface expression and enabling analysis of heterogeneous cell populations.
Metabolomics
UPLC-MS/MS precisely quantifies ABCC1 substrates and maps its interaction networks, revealing metabolic changes associated with its activity and the substrates it transports.
Proteomics
Proteomic profiling identifies ABCC1-interacting proteins, uncovering new regulatory mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets, as well as post-translational modifications that may influence its function.
3D & Organoid Models
Our 3D and organoid models, using patient-derived organoids (PDOs), realistically mimic the tumor microenvironment. This allows us to study ABCC1-mediated drug resistance in a more physiologically relevant context, investigating how the tumor microenvironment influences ABCC1 expression and function.
Diverse Applications
Cancer Drug Resistance & Therapeutic Development
ABCC1 analysis aids in cancer research by identifying its expression in cancers like triple-negative breast cancer. It helps screen inhibitors to reverse multidrug resistance, enhancing chemotherapy efficacy.
Neurological Disorder Therapy Optimization
ABCC1 is involved in amyloid-beta clearance in Alzheimer's. Analysis of its role guides therapeutic strategies to slow disease progression. It also optimizes CNS drug delivery by identifying compounds that utilize or bypass ABCC1 transport.
Pharmacokinetic & Drug-Drug Interaction Studies
ABCC1 analysis is crucial for understanding drug ADME processes, especially in tissues with high expression. It predicts drug-drug interactions in polypharmacy, ensuring safety and efficacy by avoiding altered drug levels or toxicity.
Immunotherapy Development & Immune Response Modulation
ABCC1 affects dendritic cell function in antigen presentation. Analysis guides immunotherapy development, like cancer vaccines, by modulating ABCC1 to enhance immune responses against tumors or pathogens.
Why Choose Our ABCC1 Analysis Service?
1. Top-tier Expertise & Advanced Tech
Our team boasts leading ABCC1 researchers with extensive experience. We utilize cutting-edge tools like high-throughput sequencing and advanced mass spectrometry. These enable precise and comprehensive ABCC1 analysis, offering reliable data for informed decisions. For instance, our high-throughput platforms can swiftly screen for ABCC1 inhibitors from large libraries, saving time in drug discovery.
2. Tailored Analysis for Your Needs
We know each project is unique. So, we offer customized ABCC1 analysis. Whether it's studying ABCC1 in a specific tissue, its role in cancer drug resistance, or the impact of toxins on its function, we'll design a plan just for you.
3. In-depth Data Analysis & Interpretation
We don't just give raw data. Our bioinformaticians and molecular biologists analyze it using advanced stats and tools. Then, we present clear findings, highlighting key insights and their implications.
4. Quick Turnaround & Efficient Management
Time is crucial in research. We promise fast turnaround times. Our efficient project management keeps your project on track. We've streamlined processes to reduce delays and keep you updated. For a basic ABCC1 expression analysis, we can finish it in a few weeks, depending on complexity.
5. Strict Quality Control & Data Integrity
Quality is our priority. We have strict quality control at every step, from sample handling to data analysis. Our labs have the latest systems, and staff follow standard procedures. We also protect your data's confidentiality and security, giving you confidence in the results for research or regulatory use.
6. Outstanding Customer Support & Collaboration
We value long-term client relationships. Our customer support team is always ready to answer questions, offer technical help, and address concerns. We encourage collaboration and welcome your feedback.
FAQs
-
What cell lines are available for ABCC1 knockout studies?
We offer HEK293T, HeLa, MCF7, HepG2, U87, and patient-derived xenograft (PDX) cells. Custom lines can be engineered.
-
How is ABCC1 expression quantified in tissues?
Protein: Western blot and IHC;
mRNA: qRT-PCR with probes.
-
Are your antibodies validated for clinical use?
No. All antibodies and kits are strictly for research use only (RUO) and not approved for diagnostics.
ABCC1's dual role in physiology and pathology makes it a high-value target for drug discovery and biomarker development. Our ABCC1 analysis service provides the tools to dissect its mechanisms, overcome resistance, and pioneer personalized therapies. Contact us today to explore customized solutions.
Reference
- Conseil, Gwenaëlle, and Susan PC Cole. "The first cytoplasmic loop in the core structure of the ABCC1 (Multidrug Resistance Protein 1; MRP1) transporter contains multiple amino acids essential for its expression." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22.18 (2021): 9710. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189710
For Research Use Only.