The cAMP/PKA pathway activates CREB via phosphorylation, driving ABCC5 transcription. Elevated cAMP levels increase ABCC5 expression, enhancing drug efflux in cancer cells. PKA may also phosphorylate ABCC5 directly, altering its membrane localization or function.
Introduction to ABCC5
ABCC5, also known as Multidrug Resistance-Associated Protein 5 (MRP5), is a prominent member of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. These transporters are characterized by their ability to harness the energy from ATP hydrolysis to actively transport a wide array of substances across cellular membranes. ABCC5 is ubiquitously expressed in various tissues throughout the body, including the liver, kidney, intestine, and brain. In the liver, it plays a role in the detoxification process by effluxing organic anions and endogenous metabolites. In the kidney, ABCC5 is involved in the reabsorption and secretion of substances, contributing to the maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance. In the intestine, it can influence the absorption of drugs and nutrients. In the brain, ABCC5 may be involved in the regulation of neurotransmitter levels and the protection of the central nervous system from potentially harmful substances.
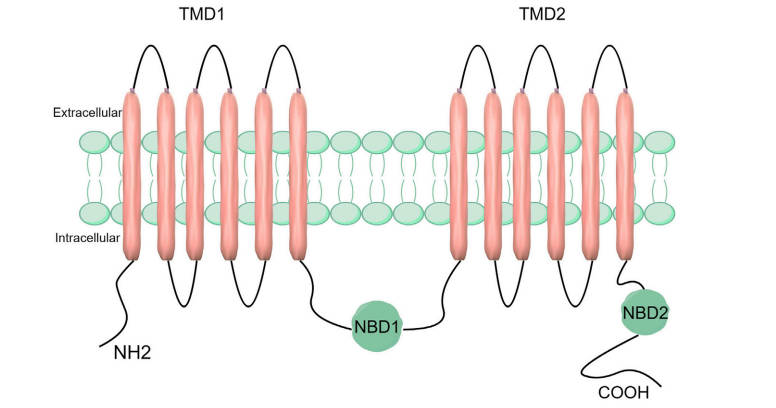 Fig.1 Structure of the ABCC5 transporter protein. ABCC5 consists of two TMDs and two NBDs.1
Fig.1 Structure of the ABCC5 transporter protein. ABCC5 consists of two TMDs and two NBDs.1
Related Pathways
cAMP/PKA Pathway
PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway
Hyperactivation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR stabilizes ABCC5 protein by inhibiting degradation, prolonging its role in drug efflux. This pathway correlates with ABCC5 overexpression in cancers resistant to chemotherapy.
Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway
Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes ABCC5 transcription via nuclear β-catenin/TCF complexes, driving drug resistance in cancer stem cells (CSCs). Disrupting Wnt lowers ABCC5 expression, sensitizing CSCs to therapy.
NF-κB Pathway
Pro-inflammatory cytokines activate NF-κB, which binds ABCC5 promoter regions to enhance transcription. This mechanism is critical in tumor microenvironments, where inflammation-driven ABCC5 upregulation confers chemoresistance. NF-κB inhibitors may attenuate this effect.
HIF-1α Pathway
Under hypoxia, HIF-1α stabilizes and binds hypoxia-response elements (HREs) in the ABCC5 promoter, upregulating drug efflux in solid tumors. Targeting HIF-1α reduces ABCC5 levels, improving therapeutic outcomes.
JAK/STAT Pathway
Cytokines activate JAK/STAT, leading to STAT3-mediated ABCC5 transcription. Elevated ABCC5 in leukemias/lymphomas correlates with resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. JAK/STAT inhibitors may suppress ABCC5 upregulation.
Notch Pathway
Notch signaling indirectly regulates ABCC5 via downstream targets, which bind ABCC5 regulatory regions. This pathway is linked to aggressive phenotypes in breast/pancreatic cancers. Gamma-secretase inhibitors may reduce ABCC5 expression.
Common ABCC5 Analysis Technologies
qRT-PCR
qRT-PCR is a highly sensitive and specific technique for measuring the expression levels of ABCC5 mRNA. It is based on the principle of amplifying a specific region of the ABCC5 gene using fluorescently labeled primers. As the PCR reaction progresses, the fluorescence intensity increases proportionally to the amount of amplified DNA. This method allows for quantitative analysis of ABCC5 mRNA expression in different samples, such as cell lines, tissue biopsies, and blood samples.
Western Blotting
Western blotting is a widely used technique for detecting and quantifying the ABCC5 protein. Western blotting provides information about the protein's expression level, molecular weight, and post - post-translational modifications. It can also be used to study the subcellular localization of ABCC5 by separating different cellular fractions.
Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry is a powerful technique for analyzing ABCC5 expression on the cell surface. Flow cytometry can quickly analyze large numbers of cells, allowing for the quantification of ABCC5-expressing cells in a heterogeneous population. This is particularly useful in studying ABCC5 expression in blood samples or tumor samples, where different cell types may be present. Additionally, flow cytometry can be used to sort ABCC5-positive and ABCC5-negative cells for further analysis.
Applications
Cancer Research
In cancer research, ABCC5 analysis plays a crucial role in understanding the mechanisms of drug resistance. By identifying ABCC5-overexpressing cancer cells, researchers can gain insights into how cancer cells evade the effects of chemotherapy. This knowledge can be used to develop strategies to overcome drug resistance, such as the use of ABCC5 inhibitors in combination with chemotherapy.
Pharmacology Research
ABCC5 analysis is essential in pharmacology for studying drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME). Understanding how ABCC5 affects the transport of drugs can help in optimizing drug dosages, reducing side effects, and improving drug efficacy.
Toxicology Research
In toxicology, ABCC5 analysis can be used to assess the toxicity of environmental pollutants and xenobiotics. Many environmental toxins, such as heavy metals and organic pollutants, can interact with ABCC5 and affect its function. By studying the interaction between these substances and ABCC5, researchers can predict their potential health risks.
Service Advantages
High-Quality Data
Our ABCC5 analysis service is carried out by a team of experienced scientists with in-depth knowledge of ABC transporter biology and molecular biology techniques. We use state-of-the-art equipment, such as high-precision qRT-PCR machines, advanced Western blotting systems, and flow cytometers.
Customized Solutions
We understand that every research project with its own set of requirements. That's why we offer customized analysis packages tailored to your specific needs. Whether you require a comprehensive analysis of ABCC5 expression and function in a particular tissue type or a focused study on the interaction between ABCC5 and a specific drug, we can design a solution that meets your requirements.
Fast Turnaround Time
We recognize the importance of time in research. Our efficient workflow and dedicated team enable us to provide fast turnaround times without compromising on quality. We have optimized our processes to minimize delays at every stage of the analysis, from sample receipt to result delivery.
FAQs
-
What sample types are suitable for ABCC5 analysis?
We can analyze a variety of sample types, including cell lines (both adherent and suspension cells), tissue biopsies (fresh or frozen), blood samples (whole blood, peripheral blood mononuclear cells), and animal tissues (from various species). Each sample type may require specific preparation methods, and our team will guide you through the process.
-
How long does it take to get the results?
The turnaround time depends on the complexity of the analysis. For basic expression analysis using qRT-PCR, it typically takes 2 - 3 weeks. Western blotting and flow cytometry analyses may take a bit longer, usually 3 - 4 weeks. More complex functional studies, such as drug-transporter interaction studies, may take 4 - 6 weeks. We will provide you with a detailed timeline at the beginning of the project.
-
Are the results confidential?
Yes, we take data confidentiality very seriously. All your research data and results are kept strictly confidential and are only shared with you as per your instructions.
Contact us for more details on ABCC5 analysis.
Reference
- Pan, Yinlong, Mengmeng Wu, and Huazhong Cai. "Role of ABCC5 in cancer drug resistance and its potential as a therapeutic target." Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 12 (2024): 1446418. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2024.1446418
For Research Use Only.