Analyzing ACACA is crucial for identifying and validating new therapeutic targets for metabolic diseases and cancer. Modulating ACACA activity can lead to novel treatments for obesity, diabetes, and various malignancies, making it a highly valuable target for pharmaceutical research and development.
With a seasoned team of scientists, Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive ACACA analysis services, offering tailored solutions to investigate its multifaceted role. Studies indicate ACACA is a predictive and therapeutic target for cancer, and our services help examine its roles in initiation, progression, and development for clients worldwide.
Introduction of ACACA
Acetyl-CoA carboxylases (ACCs) are enzymes that convert acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA, a crucial precursor for fatty acid synthesis. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase α (ACACA), or ACC1, is the primary member of this enzyme family in mammalian cells, localized in the cytosol. This enzyme, which has three functional domains—biotin carboxylase (BC), carboxyl transferase (CT), and biotin carboxyl carrier protein (BCCP)—is highly enriched in adipogenic tissues and vital for metabolic regulation.
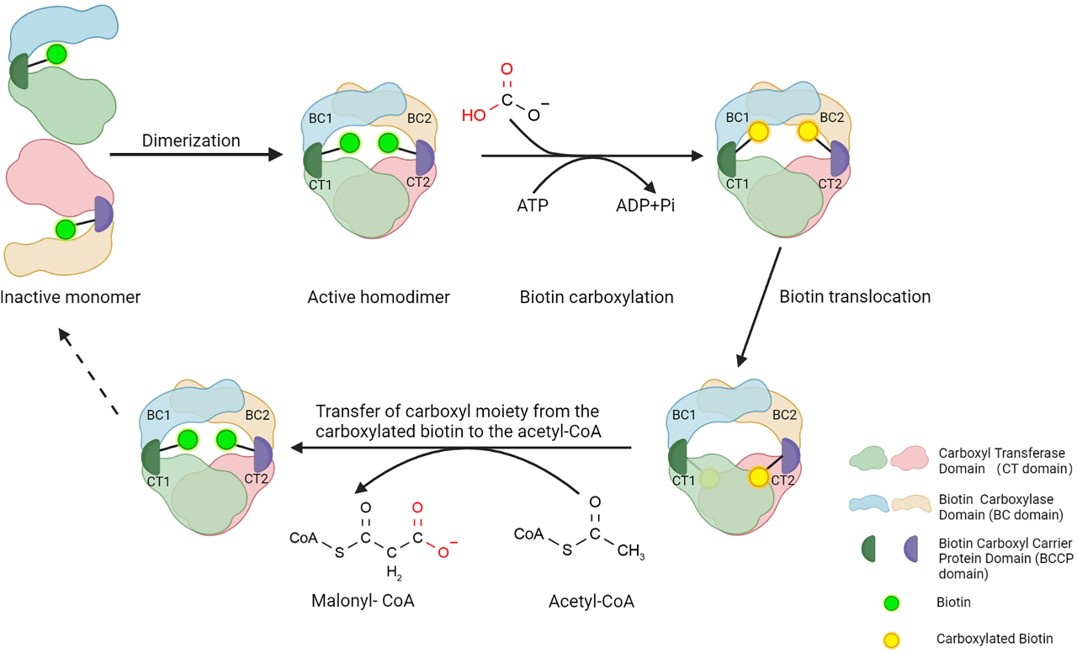 Fig.1 ACC1 architecture and the roles of its three principal domains.1
Fig.1 ACC1 architecture and the roles of its three principal domains.1
Studies highlight ACACA's role in various diseases, especially tumors. ACACA is an important antitumor target in colon cancer and is essential for breast cancer cell survival. Its overexpression in liver cancer contributes to cell proliferation, and its down-regulation in prostate cancer suppresses tumor growth by inhibiting mitochondrial potential. The higher expression of ACACA in prostate cancer patients compared to healthy individuals also underscores its potential as a diagnostic marker.
ACACA Analysis Services at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs provides specialized ACACA analysis services designed to meet the unique needs of your research. Our team leverages extensive experience and advanced methodologies to deliver precise and reliable data. We possess high-quality antibodies that can be utilized in several scientific applications, including WB, IHC, ICC, and ELISA for robust ACACA detection. Our popular services targeting ACACA include, but are not limited to the following:
- qRT-PCR and WB Analysis
We provide qRT-PCR and WB to quantify ACACA gene and protein expression, providing insights into its abundance within your samples.
- Cell Cycle Analysis
Our cell cycle analysis service assesses the effects of ACACA on cell proliferation, which is a critical measure for understanding its role in cancer and other diseases.
- In Vivo Tumor Formation Assays
We offer in vivo tumor formation assays to study the role of ACACA in tumor growth and development, providing a comprehensive view of its function in a living organism.
- ELISA Assays
Our ELISA assays allow for the quantitative detection of ACACA, providing a sensitive and specific method for measuring protein levels in various biological fluids and cell lysates.
Service Workflow
Our ACACA analysis service workflow is a streamlined, step-by-step process designed for efficiency and precision.
The process begins with a detailed consultation to understand your specific research objectives and experimental needs. Our team will work with you to design a customized plan for your ACACA analysis project.
You will provide us with your starting materials, such as cell lines, tissue samples, or purified proteins. We will provide clear guidelines for sample preparation and shipping to ensure sample integrity upon arrival.
Our expert team will perform the requested ACACA analysis using our cutting-edge platforms and proprietary protocols. We ensure the highest standards of quality control throughout this phase, with all assays tailored to your specific project.
The final deliverables include a comprehensive report containing all raw data, detailed analytical results, and a professional interpretation of the findings. This provides you with actionable insights to drive your research forward, with our team available for follow-up discussions.
Applications
Drug Discovery and Development
Biomarker Discovery and Diagnostics
The expression and phosphorylation state of ACACA can serve as a potent biomarker for disease progression and response to treatment. Our analysis services can help identify and validate ACACA as a diagnostic marker for early disease detection and for monitoring therapeutic efficacy in clinical trials.
Fundamental Research in Metabolism
ACACA analysis provides deep insights into lipid metabolism, cellular energy balance, and signaling pathways. By studying ACACA, researchers can uncover new mechanisms of metabolic regulation and dysfunction, advancing our fundamental understanding of cell biology.
Personalized Nutrition
The activity of ACACA is influenced by dietary factors, making its analysis valuable for personalized nutrition strategies. Understanding an individual's ACACA profile can help in developing tailored dietary recommendations to optimize metabolic health and prevent disease.
Service Highlights
- Expertise and Precision
With decades of experience, our team provides unparalleled expertise and a meticulous approach to biomarker analysis. We deliver highly precise, reproducible results for your most critical research decisions.
- Comprehensive Platforms
We use advanced platforms like qPCR, Western Blot, ELISA, and high-throughput technologies. This allows for multifaceted analysis of ACACA's role, from gene expression to protein function.
- Tailored Solutions
We offer flexible, customized service packages to meet your specific research goals, timeline, and budget. This ensures you receive the most impactful data for your study.
- Rigorous Quality Control
We implement strict quality control measures throughout our analysis. Our proprietary protocols ensure every result is accurate, reliable, and trustworthy, giving you full confidence in your data.
FAQs
-
How do you ensure the specificity and accuracy of your ACACA detection methods?
We ensure the specificity and accuracy of our ACACA detection methods through several rigorous quality control steps. Our antibodies are thoroughly validated for their specificity to the ACACA protein and its phosphorylation sites. We utilize positive and negative controls in all our assays to confirm the validity of our results and perform multiple replicates to ensure the reproducibility and statistical significance of the data.
-
Can your services distinguish between ACACA and other isoforms, such as ACC2?
Our services are designed to distinguish between ACACA and other isoforms like ACC2. We use specific antibodies that target unique epitopes on the ACACA protein, ensuring no cross-reactivity with ACC2. This allows for the precise measurement of ACACA levels and activity without confounding signals from other related proteins, providing a clear and accurate assessment.
-
Can you help with the interpretation of the results from the ACACA analysis?
We provide comprehensive support with the interpretation of the results from your ACACA analysis. Our final report includes not only the raw data and a detailed methodology section but also an expert analysis of the findings. Our team of scientists is available for follow-up consultations to discuss the biological implications of your data and to help plan your next steps.
-
Do you offer customized or multiplex ACACA analysis services?
We offer both customized and multiplex ACACA analysis services to cater to your specific research needs. We can develop a tailored plan that combines various analytical techniques, such as measuring ACACA expression, phosphorylation, and enzymatic activity, in a single study. We can also integrate ACACA analysis with other biomarker assays to provide a broader metabolic profile.
-
What types of controls do you use in your ACACA analysis assays?
We use a variety of controls in our ACACA analysis assays to ensure the validity and reliability of the results. For Western blotting, we use loading controls like GAPDH or Beta-Actin to normalize protein levels. For other assays, we use positive controls with known ACACA expression and negative controls to rule out any non-specific binding, ensuring the accuracy of our data.
Ready to take your biomarker research to the next level? Get in contact with our experts - We are happy to answer any question! Please feel free to contact us for more information.
Reference
- Wang, Yu, et al. "Acetyl-CoA carboxylases and diseases." Frontiers in oncology 12 (2022): 836058. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.836058
For Research Use Only.