Utilize ADMA and the L-Arginine/ADMA ratio to independently predict adverse cardiovascular events (MI, stroke, and heart failure) in high-risk patient groups. This offers robust predictive power and mechanistic insight that frequently surpasses traditional risk indicators like standard lipid profiles.
The usage of biomarkers in research or in pre-clinical routine practice as diagnostic tools has become commonplace. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) acts as a novel biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis in some diseases. Creative Biolabs provides customized ADMA analysis and quantification services for global clients.
Introduction of ADMA
ADMA is an endogenous amino acid inhibitor that directly competes with L-Arginine for the active site of nitric oxide synthase (eNOS). This competitive mechanism makes ADMA the most potent known molecular brake on the critical nitric oxide (NO) synthesis pathway, leading directly to reduced NO bioavailability. Consequently, elevated ADMA is a direct, measurable cause of endothelial dysfunction, which is recognized as a prerequisite for most chronic vascular diseases, establishing ADMA as an indispensable biomarker in clinical research.
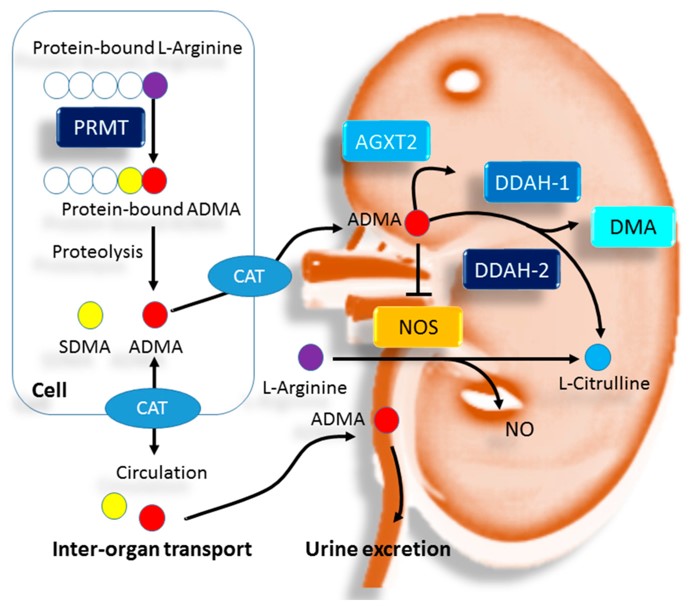 Fig.1 The biosynthesis and elimination of ADMA and the relation of ADMA to NO.1
Fig.1 The biosynthesis and elimination of ADMA and the relation of ADMA to NO.1
ADMA is primarily regulated by the enzyme dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase (DDAH), which degrades it into L-citrulline. Failure of DDAH activity, often caused by oxidative stress or renal impairment, leads to ADMA accumulation. Therefore, monitoring ADMA, along with its structural isomer SDMA (symmetric dimethylarginine, a key renal clearance marker), provides a comprehensive Arginine Metabolite Signature for evaluating both functional NO status and critical kidney health in parallel.
ADMA Analysis Services at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs offers a diverse suite of ADMA analysis platforms, tailored to your study phase and required quantitative rigor, ensuring optimal sensitivity and specificity to manage the challenge of ADMA's narrow concentration range.
- Gas Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
This highly selective technique employs derivatization for enhanced volatility, yielding exceptional separation, quantification, and structural confirmation for comprehensive dimethylarginine profiling in complex matrices.
- HPLC with Fluorescence Detection
A cost-effective, high-throughput method requiring chemical derivatization specifically for ADMA detection. It is optimally suited for rapid, large-scale screening and initial exploratory quantification projects.
- HPLC with LC-MS
This is our Gold Standard method, merging superior chromatographic separation with definitive Mass Spectrometry (MS) specificity. It is essential for reliable, high-accuracy, and regulatory-compliant ADMA data.
- Capillary Electrophoresis (CE) Coupled with Ultraviolet
This technique offers high separation efficiency for charged arginine metabolites, utilizing UV absorbance for rapid, high-resolution ADMA analysis from various complex matrices.
- CE Coupled with Mass-Spectrometric Detection
A powerful hybrid platform merging CE's high-resolution separation with the definitive identification and quantification power of MS, ensuring robust complementary specificity for dimethylarginine species.
- Customized ELISA
In-house competitive immunoassays developed for high-volume, rapid screening. They offer tailored specificity and high sensitivity for ADMA detection, ideal for initial biomarker validation and large-cohort epidemiological research.
Service Workflow
Our client-focused ADMA Analysis Service Workflow is engineered for compliance and efficiency, ensuring clarity from initial concept to final data.
Our scientific team aligns your study design, matrix type (e.g., plasma, serum), and report endpoints, confirming the optimal Arginine Metabolite Signature panel for your project.
Clients submit biospecimens under strict cold chain conditions. Our team immediately verifies sample integrity and volume upon receipt at our laboratory.
Samples undergo necessary preparation steps, which may include protein precipitation or derivatization. We then execute the agreed-upon high-resolution quantification method (LC-MS/MS, GC-MS, or CE) using stable isotopic internal standards for precise ADMA measurement.
Raw data is processed, quantified, and subjected to a strict quality control review, including standard curve validation, performed by two independent scientists.
The client receives a comprehensive, ready-for-submission report, detailing ADMA and related metabolite concentrations, quality control metrics, and the critical L-Arginine/ADMA functional ratio.
Applications
Cardiovascular Risk Stratification
Therapeutic Efficacy Monitoring
Measure changes in ADMA levels and the critical L-Arginine/ADMA ratio to confirm the mechanism of action and functional impact of novel therapeutic agents targeting endothelial function, such as DDAH activators, specific NO donors, or innovative antihypertensives during preclinical and clinical phases.
Renal Health Assessment
We quantify SDMA levels alongside ADMA. SDMA serves as a non-creatinine-based marker highly correlated with the estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR), providing a powerful and necessary dual assessment of renal function and associated systemic endothelial damage in cohorts with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Preeclampsia and Vascular Research
Apply ADMA analysis to accurately characterize the severity of placental dysfunction and vascular compromise in gestational diseases, including preeclampsia. This supports the development of better diagnostic protocols, risk prediction models, and targeted interventions for high-risk pregnancies and related vascular conditions.
Service Highlights
- Regulatory-Ready Service Pipeline: All ADMA analysis projects adhere strictly to standard guidelines, ensuring data release is suitable for minimizing client risk during regulatory submissions.
- Integrated Arginine Metabolite Panel: We provide simultaneous quantification of ADMA, SDMA, and L-Arginine. This integrated approach guarantees accurate interpretation of NO status and renal function without requiring multiple independent assays.
- Guaranteed Precision and Sensitivity: Our commitment ensures coefficient of variation (CV) values consistently remain below 5%. This high precision allows clients to confidently detect subtle, pathologically relevant changes in ADMA's narrow concentration window.
- Actionable and Transparent Reporting: Our final deliverable is a comprehensive analytical report, including all concentration values, QC chromatograms, standard curves, and the calculated L-Arginine/ADMA functional ratio, providing immediate utility and complete data transparency.
FAQs
-
Can you measure the critical L-Arginine/ADMA ratio, and why is this functional metric so important in clinical studies?
We consistently quantify both L-Arginine and ADMA simultaneously in a single LC-MS/MS run, providing the necessary data to calculate this critical ratio; this functional metric is important because it directly reflects the competitive balance at the eNOS active site, offering a better mechanistic indicator of actual Nitric Oxide bioavailability than the absolute ADMA level alone.
-
How does the inclusion of SDMA quantification benefit the interpretation of ADMA results in patients with kidney conditions?
The simultaneous quantification of SDMA is a significant benefit because, unlike ADMA which is cleared both enzymatically and renally, SDMA is cleared almost exclusively by the kidneys; therefore, a high SDMA level serves as an indispensable marker for decreased renal clearance, which aids in precisely attributing the cause of elevated ADMA in patients, particularly those with CKD.
-
What is the lowest limit of quantification (LLOQ) achieved by your high-resolution ADMA LC-MS/MS assay?
The high-resolution ADMA LC-MS/MS assay utilized by our laboratory reliably achieves a low limit of quantification (LLOQ) in the low nanomolar (nM) range, offering the requisite sensitivity to accurately measure ADMA concentrations even in healthy control populations and minimizing false negative results in highly diluted samples.
-
Do you require clients to use a specific type of anti-coagulant for plasma collection before sample submission?
We recommend that clients use EDTA or Heparin as the preferred anti-coagulants for plasma sample collection, as these have been fully validated with our extraction and quantification protocols; it is imperative that clients avoid the use of arginine-containing buffers or collection materials to prevent artificial elevation of L-Arginine and skewed ratio results.
-
How do you ensure data reliability and consistency, specifically regarding inter-assay variability across multiple clinical sites?
Data reliability across multiple clinical sites is ensured through the strict application of GLP-compliant quality control measures, which include running blinded quality control samples and calibration standards with every batch; this rigorous process consistently demonstrates an excellent inter-assay CV below the 5% threshold.
-
How should samples be prepared and shipped to Creative Biolabs to maintain ADMA and L-Arginine integrity?
Samples must be prepared by immediately separating plasma or serum from blood cells following collection, and they must be shipped frozen on dry ice in properly sealed, cryo-labeled vials; adherence to this strict cold chain integrity protocol is crucial for preventing potential ex vivo metabolism that could artificially alter the measured concentrations of ADMA and L-Arginine.
If you are interested in our services at Creative Biolabs, please contact us for more information.
Reference
- Hsu, Chien-Ning, and You-Lin Tain. "Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) in pediatric renal diseases: from pathophysiological phenomenon to clinical biomarker and beyond." Children 8.10 (2021): 837. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8100837
For Research Use Only.