
Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs) are lipid vesicles with a uniform lipid core, prepared from ionizable/cationic lipids, helper/structural lipid, cholesterol, and PEGylated lipids, with a diameter of around 100 nm. Their unique structure and size give them special physical and chemical properties, making them effective for encapsulating and protecting nucleic acid drugs like mRNA, siRNA, and DNA. LNPs can adhere to negatively charged cell membranes and are taken up by cells via endocytosis, forming endosomes. These mature endosomes fuse with lysosomes, where the acidic environment triggers the protonation of ionizable lipids, giving them a positive charge. This allows LNPs to escape the endosomes and release their nucleic acid cargo into the cytoplasm.
| SORT Molecule | Charge | Lipid | Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cationic Lipid | Positive | 50% DOTAP | Lung |
| Anionic Lipid | Negative | 10-40% 18PA | Spleen |
Ionizable/cationic lipids are key to LNP development. We offer off-the-shelf LNPs with diverse ionizable lipids, customizable with capped/modified nucleic acids.
For specific needs, explore our LNP development services or email us at info@creative-biolabs.com for details.
Please refer to our detailed list of LNP products:
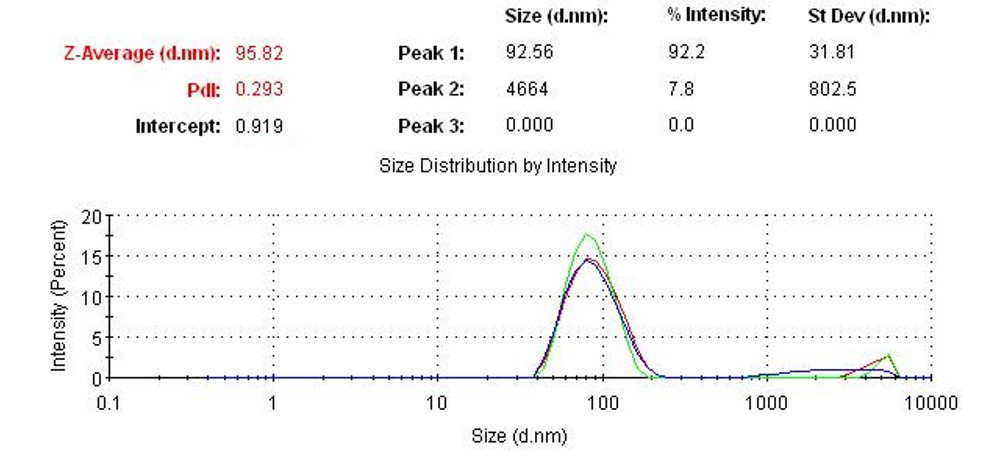
Creative Biolabs guarantees the supply of LNPs with uniform particle size and exceptional stability, ensuring dependable and effective genetic material delivery for a wide range of research applications.
| Item | Method | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | Dynamic light scattering | Uniform size distribution (typically around 100nm) |
| Poly Dispersity Index (PDI) | Dynamic light scattering | < 0.3 |
| Zeta Potential | Dynamic light scattering | Varies with different lipid compositions |
| Encapsulation Efficiency | RiboGreen | >85% |
| Concentration | RiboGreen | Customizable concentration |
| *For more testing items, please contact us. | ||
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use| Cat | Product name | Ionizable/Cationic Lipid | Cargo | Modification | Application | Data sheet | MSDS | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDLY-0325-LD890 | LP-01 LNP-DLL3 CAR mRNA | LP-01 | DLL3 CAR mRNA | mRNA delivery; CAR-T |
|
|
Inquiry | |
| LDLY-0325-LD891 | ALC-0315 LNP-DLL3 CAR mRNA | ALC-0315 | DLL3 CAR mRNA | mRNA delivery; CAR-T |
|
|
Inquiry | |
| LDLY-0325-LD892 | SM102 LNP-DLL3 CAR mRNA | SM102 | DLL3 CAR mRNA | mRNA delivery; CAR-T |
|
|
Inquiry | |
| LDLY-0325-LD893 | DLin-MC3-DMA LNP-MSLN CAR mRNA | DLin-MC3-DMA | MSLN CAR mRNA | mRNA delivery; CAR-T |
|
|
Inquiry | |
| LDLY-0325-LD894 | LP-01 LNP-MSLN CAR mRNA | LP-01 | MSLN CAR mRNA | mRNA delivery; CAR-T |
|
|
Inquiry | |
| LDLY-0325-LD895 | ALC-0315 LNP-MSLN CAR mRNA | ALC-0315 | MSLN CAR mRNA | mRNA delivery; CAR-T |
|
|
Inquiry | |
| LDLY-0325-LD896 | SM102 LNP-MSLN CAR mRNA | SM102 | MSLN CAR mRNA | mRNA delivery; CAR-T |
|
|
Inquiry | |
| LDLY-0325-LD897 | DLin-MC3-DMA LNP-TACSTD2 CAR mRNA | DLin-MC3-DMA | TACSTD2 CAR mRNA | mRNA delivery; CAR-T |
|
|
Inquiry | |
| LDLY-0325-LD898 | LP-01 LNP-TACSTD2 CAR mRNA | LP-01 | TACSTD2 CAR mRNA | mRNA delivery; CAR-T |
|
|
Inquiry | |
| LDLY-0325-LD899 | ALC-0315 LNP-TACSTD2 CAR mRNA | ALC-0315 | TACSTD2 CAR mRNA | mRNA delivery; CAR-T |
|
|
Inquiry | |
| LDLY-0325-LD900 | SM102 LNP-TACSTD2 CAR mRNA | SM102 | TACSTD2 CAR mRNA | mRNA delivery; CAR-T |
|
|
Inquiry | |
| LDLY-0325-LD901 | DLin-MC3-DMA LNP-HER3 CAR mRNA | DLin-MC3-DMA | HER3 CAR mRNA | mRNA delivery; CAR-T |
|
|
Inquiry | |
| LDLY-0325-LD902 | LP-01 LNP-HER3 CAR mRNA | LP-01 | HER3 CAR mRNA | mRNA delivery; CAR-T |
|
|
Inquiry | |
| LDLY-0325-LD903 | ALC-0315 LNP-HER3 CAR mRNA | ALC-0315 | HER3 CAR mRNA | mRNA delivery; CAR-T |
|
|
Inquiry | |
| LDLY-0325-LD904 | SM102 LNP-HER3 CAR mRNA | SM102 | HER3 CAR mRNA | mRNA delivery; CAR-T |
|
|
Inquiry |
Online Inquiry