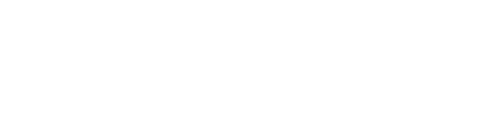Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome Treatment
Background Treatment Strategies Lipid Delivery Systems Creative Biolabs’ Solutions Workflow Published Data Related Services Resources
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) remains a critical global health challenge. Creative Biolabs provides cutting-edge lipid-based drug delivery systems to accelerate your AIDS treatment research! We offer comprehensive services from custom lipid nanoparticle design to full-scale formulation development, helping you optimize drug solubility, target infected cells precisely, and reduce toxicity in your AIDS projects. Our expertise in lipid technology can transform how antiretrovirals are delivered, making your research breakthroughs possible faster.
78 Million +
People Infected with HIV
39 Million +
Deaths from HIV-Related Causes
35 Million +
People Living with HIV
Background of AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a member of the lentivirus within the retroviridae family, is the causative agent of AIDS, a global health crisis profoundly impacting economic development and social stability. It is primarily transmitted through sexual intercourse, shared intravenous drug injection paraphernalia, and mother-to-child transmission. Common complications of AIDS stem from the compromised immune system, leading to opportunistic infections (e.g., pneumonia, candidiasis, tuberculosis) and malignancies (e.g., kaposi's sarcoma, non-hodgkin lymphoma, cervical cancer). HIV typically presents as a spherical particle approximately 120 nm in diameter, targeting crucial immune cells such as CD4+ T cells, macrophages, and microglial cells, leading to severe immunodeficiency. A hallmark characteristic of HIV is its rapid mutation rate, enabling it to efficiently evade both humoral (antibody-mediated) and cellular (T cell-mediated) adaptive immune responses.
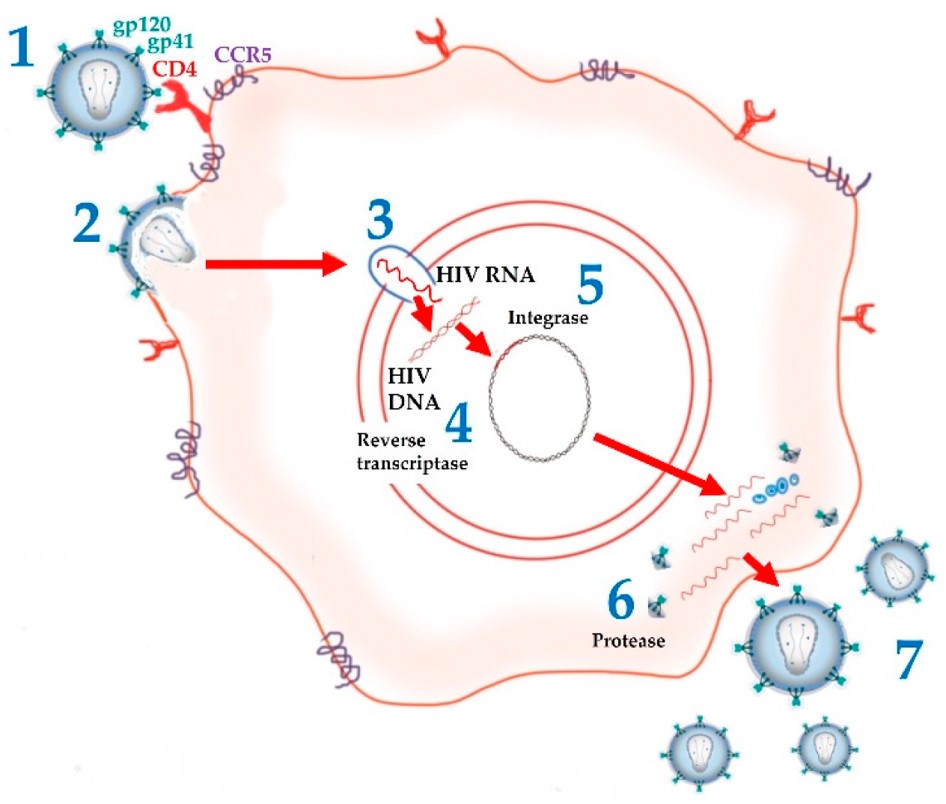 Fig. 1 Stages in HIV lifecycle.1,3
Fig. 1 Stages in HIV lifecycle.1,3
The HIV infection process can be summarized in several key steps:
-
Entry: HIV glycoproteins bind to host cell receptors, leading to viral envelope fusion and release of viral RNA and enzymes into the cell.
-
Replication/Transcription: Viral reverse transcriptase converts HIV RNA into complementary DNA (cDNA).
-
Integration: HIV DNA inserts into the host cell's nuclear DNA, aided by viral integrase.
-
Recombination: Genetic exchange occurs between the two HIV RNA genomes during replication.
-
Assembly/Release: New viral proteins are transported to the cell membrane, forming new viral particles that bud from the host cell.
-
Spread: HIV propagates via cell-free or cell-to-cell transmission to infect new T cells.
Treatment Strategies for AIDS
The primary goal of HIV treatment is to suppress viral replication, preserve or restore immune function, and reduce the risk of transmission. Antiretroviral therapy (ART) is the standard treatment approach, which typically involves the use of a combination of antiretroviral drugs from different classes to target various stages of the HIV life cycle.
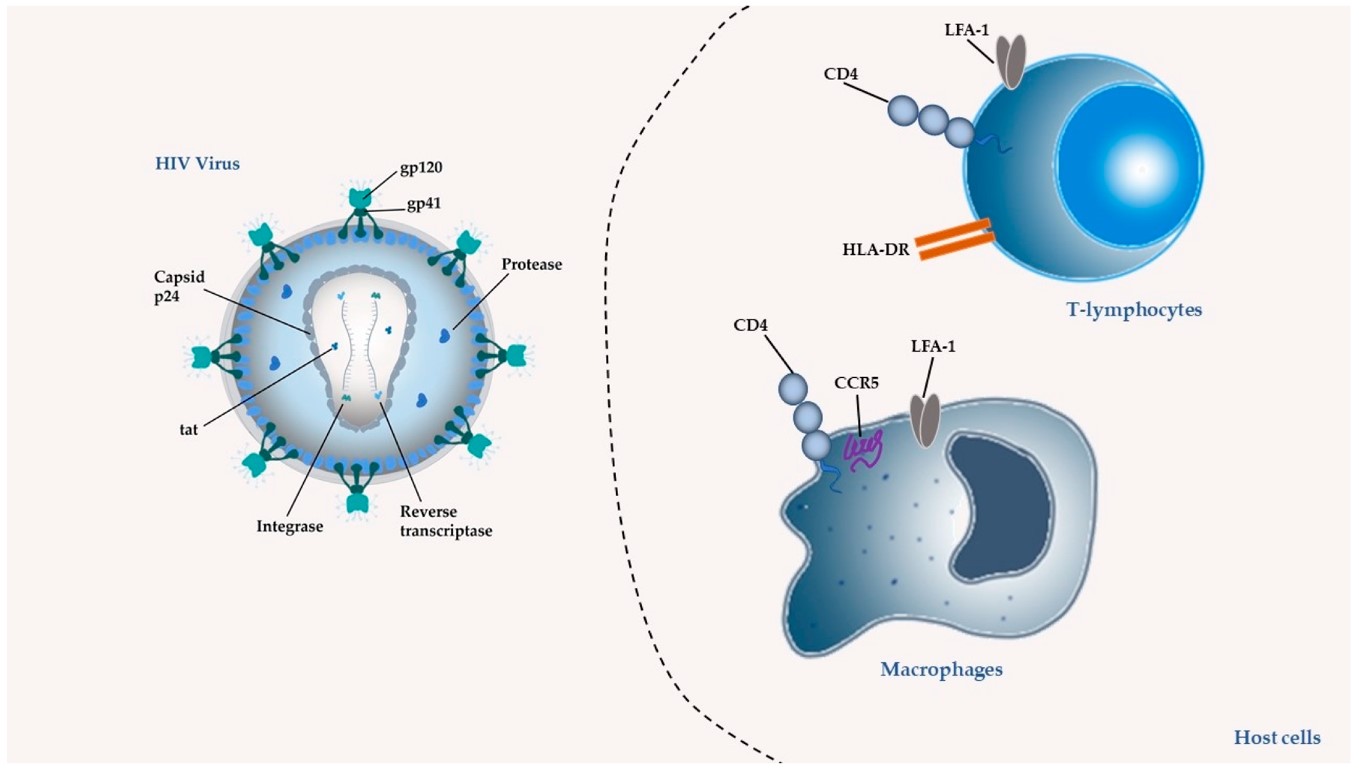 Fig. 2 Molecular components of HIV virus and targets of ARV drugs.1,3
Fig. 2 Molecular components of HIV virus and targets of ARV drugs.1,3
|
ARV Therapeutic Class
|
Mechanism of Action
|
|
Cell entry inhibitors
|
CCR5 antagonists
|
Interfere with CCR5 coreceptors on specific immune cells, stopping HIV cellular entry.
|
|
Attachment inhibitors
|
Attach to the viral surface gp120 protein, thwarting HIV's CD4 cell invasion.
|
|
Post-attachment inhibitors
|
Obstruct CD4 receptors on specific immune cells, stopping HIV entry.
|
|
Fusion inhibitors (FI)
|
Shield the virus-host cell membrane from the gp41 glycoprotein, disrupting HIV binding, fusion, and cell entry.
|
|
Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTI)
|
Inhibit viral reverse transcriptase to block HIV replication.
|
|
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTI)
|
Modify viral reverse transcriptase upon binding, restricting HIV replication.
|
|
Integrase inhibitors (II)
|
Inhibit viral integrase to prevent HIV DNA integration into the host genome.
|
|
Protease inhibitors (PI)
|
Restrict viral protease to block viral protein cleavage and virion maturation, producing non-infectious viral particles.
|
However, current ART faces several challenges, such as drug toxicity, resistance development, poor drug delivery to certain tissues and reservoirs, and the need for lifelong treatment. To address these issues, researchers are exploring novel drug delivery systems, among which lipid-based drug delivery systems show great potential.
Leveraging Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems for AIDS Treatment
Lipid-based drug delivery systems offer a multifaceted approach to addressing the challenges of AIDS treatment.
-
Targeted Delivery: Our systems can be engineered to specifically target HIV-infected cells, such as CD4+ T cells and macrophages, ensuring that the therapeutic agent reaches the intended site of action.
-
Enhanced Drug Stability: Encapsulating antiretroviral drugs within lipid-based delivery systems protects them from degradation, extending their half-life and improving their overall efficacy.
-
Reduced Dosage Frequency: By enabling controlled and sustained drug release, our systems can reduce the frequency of dosing.
-
Overcoming Drug Resistance: Lipid-based systems can help overcome drug resistance by ensuring higher drug concentrations at the site of infection, potentially restoring the effectiveness of existing antiretroviral therapies.
-
Potent Adjuvant Activity: Acts as a powerful adjuvant for vaccines, triggering robust and durable immune responses essential for HIV prevention.
These features make Creative Biolabs' lipid-based drug delivery systems a powerful tool for advancing AIDS treatment research and developing more effective therapeutic strategies.
How Creative Biolabs' Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems Can Assist Your Project
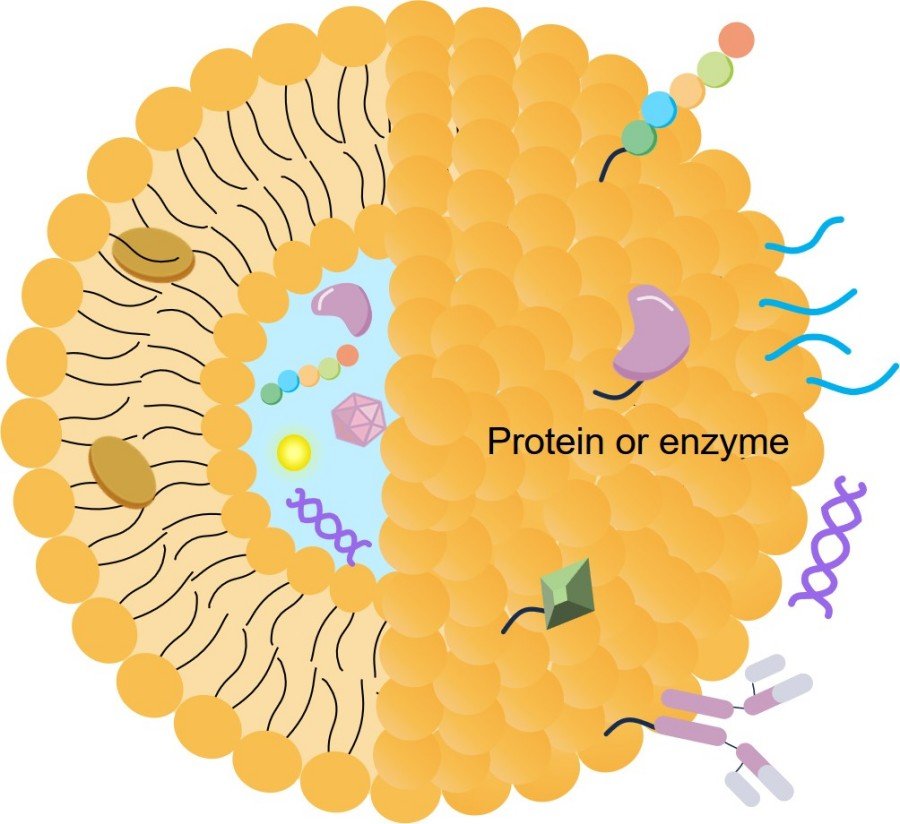
Creative Biolabs' lipid-based drug delivery systems offer a transformative approach to developing more effective and safer therapies for AIDS. Our proprietary delivery systems technology provides a robust platform for encapsulating a diverse range of therapeutic molecules, including small molecules, protein/peptide, nucleic acids, and vaccines, within a protective lipid bilayer. This innovation directly addresses the critical limitations of conventional AIDS treatments, ensuring your projects achieve superior outcomes.
Available Products
-
Liposomal Antiretroviral Formulations
Our liposomal formulations are designed to encapsulate a variety of antiretroviral drugs, enhancing their delivery to HIV-infected cells.
-
LNP Products
We provide ready-to-use LNPs engineered for nucleic acid protection and cellular uptake.
-
Kits Products
With our kits, researchers can easily encapsulate their drugs, mRNA, siRNA, and other nucleic acids into liposomes or LNPs.
Creative Biolabs can assist your project by providing a range of lipid-based drug delivery system development services, including the design, synthesis, characterization, and optimization of lipid nanocarriers. We also offer in vitro and in vivo evaluation of drug delivery systems to ensure their safety and efficacy.
Workflow for Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems Development for AIDS
Published Data
A recent study in Nature Communications provides compelling evidence for the use of liposomes in HIV treatment strategies. Researchers developed cobalt porphyrin-phospholipid (CoPoP) liposomes displaying stabilized HIV-1 Env proteins. Crucially, this approach generated significant antibody responses in rabbits, achieving neutralization against 18 out of 20 challenging, diverse HIV strains. The sequential immunization strategy using these engineered liposomes effectively boosted the immune reaction, demonstrating their capacity to elicit broad-spectrum protection. This data strongly supports the viability of liposome technology for delivering HIV antigens and potentially therapeutic agents.
 Fig. 3 In vivo immunogenicity of CoPoP HIV-1 Env particles in NZW rabbits.2,3
Fig. 3 In vivo immunogenicity of CoPoP HIV-1 Env particles in NZW rabbits.2,3
Creative Biolabs is dedicated to advancing global health through innovative lipid-based drug delivery systems for AIDS treatment. Our comprehensive services encompass everything from customized nanoparticle formulation (such as liposome, LNP) and optimization to rigorous characterization and preclinical support. Whether you require enhanced drug targeting, improved bioavailability, reduced toxicity, or superior vaccine delivery, Creative Biolabs is equipped to provide the solutions you need. Contact us for more information on our lipid-based drug delivery systems and to discuss how we can assist in accelerating your breakthrough in AIDS treatment.
Related Services
Resources
References
-
Faria, Maria J., et al. "Lipid nanocarriers for anti-HIV therapeutics: A focus on physicochemical properties and biotechnological advances." Pharmaceutics 13.8 (2021): 1294. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13081294.
-
Koornneef, Annemart, et al. "CoPoP liposomes displaying stabilized clade C HIV-1 Env elicit tier 2 multiclade neutralization in rabbits." Nature Communications 15.1 (2024): 3128. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-47492-1.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.

For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
 Fig. 3 In vivo immunogenicity of CoPoP HIV-1 Env particles in NZW rabbits.2,3
Fig. 3 In vivo immunogenicity of CoPoP HIV-1 Env particles in NZW rabbits.2,3

 Fig. 1 Stages in HIV lifecycle.1,3
Fig. 1 Stages in HIV lifecycle.1,3
 Fig. 2 Molecular components of HIV virus and targets of ARV drugs.1,3
Fig. 2 Molecular components of HIV virus and targets of ARV drugs.1,3



 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use