Discover the cutting-edge in targeted drug delivery with Creative Biolabs' glucose-responsive liposome. As pioneers in the field of stimuli-responsive liposome, our revolutionary technology promises intelligent drug delivery tailored to glucose levels. Engineered with precision, these advanced systems offer a dynamic response to fluctuating glucose concentrations, ensuring optimal therapeutic outcomes with minimal side effects.
Diabetes is characterized by elevated blood glucose levels, which typically necessitates precise insulin delivery to maintain glucose levels within the normal range. The pursuit of precision medicine has spurred the development of glucose-responsive insulin delivery systems, such as liposomes, microspheres, hydrogels and micelles. These systems, which incorporate glucose-responsive elements, can detect changes in glucose concentration as well as indirect signals like pH, H+ concentration, and O2 levels, among others. These systems then adjust their physical or chemical properties to release insulin through mechanisms including expansion/contraction, dissolution, changes in pore size, charge reversal, and polymer degradation.
Liposomes excel as drug carriers due to their biocompatibility, high encapsulation efficiency, adjustable release kinetics, and diverse administration routes. By integrating glucose-responsive elements into liposomes, we can develop glucose-responsive liposome that leverage both the glucose reactivity and the inherent benefits of liposomes. These advanced systems can alter their chemical or physical structure in response to glucose concentration shifts, undergo disassembly or degradation, all of which facilitate precise drug release.
Depending on the type of glucose-responsive element, glucose-responsive liposome can be developed for intelligent drug delivery.
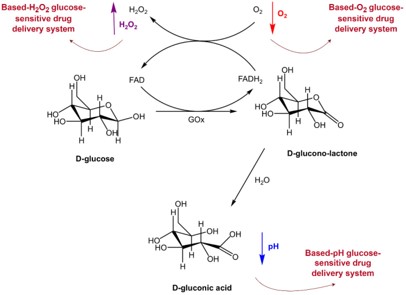 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of GOx catalyzed glucose oxidation.1
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of GOx catalyzed glucose oxidation.1
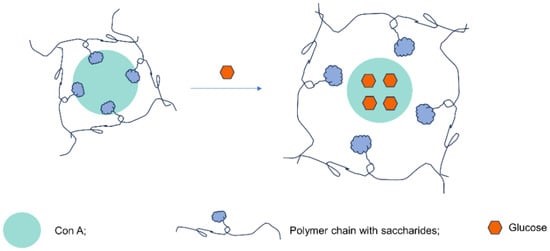 Fig.2 Schematic diagram of Con A's response to glucose.1
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of Con A's response to glucose.1
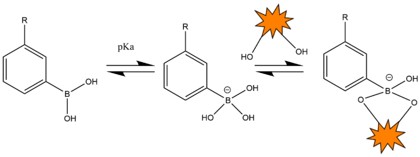 Fig.3 Schematic diagram of PBA combined with adjacent diols.1
Fig.3 Schematic diagram of PBA combined with adjacent diols.1
Compared to protein-based liposomes, PBA does not elicit an immune response and offers excellent stability and long-term storability.
| Classification of glucose-responsive compounds | |||
| Property | GOx | Con A | PBA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural proteins | Natural proteins | Chemical synthesis |
| Molecular weight | 130-186 kDa | 25.5 kDa | 100-1000 Da |
| Mechanism | Enzymatic oxidation of glucose by GOx | Competitive binding of ConA to glucose | Reversible covalent bond formation between PBA and glucose |
| Interferents | / | D-mannose and D-fructose | D-fructose, D-galactose and other 1,2-cis−/1,3-diols |
Glucose-responsive liposome have been extensively utilized in various biomedical applications, such as controlled drug delivery and glucose concentration diagnostics, to detect changes in glucose levels in the surrounding environment and achieve controlled and sustained drug release.
Cancer Treatment: Glucose uptake fuels aerobic glycolysis, providing nutrients and energy necessary for the abnormal proliferation of cancer cells. Glucose-responsive liposome enhance drug delivery and release by targeting the acidic tumor microenvironment and leveraging the high glucose levels in cancerous regions, thereby improving the efficacy of cancer therapy.
Artificial Pancreas: Glucose-responsive liposome mimic the function of pancreatic β cells by self-regulating insulin release in response to changes in glucose concentration, effectively controlling blood glucose levels and reducing the risk of hypoglycemia.
In the pursuit of excellence in glucose-responsive liposome applications, Creative Biolabs' commitment to innovation and quality is unparalleled. Our cutting-edge capabilities and expertise ensure the delivery of top-tier solutions in our advanced glucose-responsive liposome technology. For further information on how our services can empower your projects or to discuss potential collaborations, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Reference
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseServices
Online Inquiry