We utilize advanced chemical and enzymatic synthesis pathways to ensure that the precise location of the sulfate group and glycosidic linkages are defined. Each lot is rigorously analyzed to confirm purity and its exact linkage and sulfation position, eliminating the ambiguity inherent in naturally extracted samples.
-
Services
- Custom Synthesis
- Therapeutic Glycoprotein Development
- Glycan & Glycoprotein Structure & Profiling
- Glycoprotein Detection
- Glycoprotein Structure Analysis
- Glycoprotein Quantification
- High-Throughput Glycan Screening
- Glycosylation Analysis for Virus Glyoprotein
- Antibody Glycoprofiling
- Serum Glycoprofiling
- Plasma Glycoprofiling
- Tumor Tissue Glycoprofiling
- Tumor Cell Line Glycoprofiling
- Urine Glycoprofiling
- Quantitative Sialic Acid Analysis
- Quantitative Monosaccharaide Analysis
- Sugar Nucleotide Analysis
- Glycosaminoglycan Analysis
- Glycosylation Analysis in Diseases
- Glycoengineering
- Carbohydrate Analysis
- Glycan Modification & Labeling
- Glycoconjugation
- Glycoprotein Conjugation
- GFP Binding Protein Glycoconjugation
- Antibody Glycoconjugation
- Growth Factor Glycoconjugation
- GlcNAc-type Glycoprotein Conjugation
- LacNAc-type Glycoprotein Conjugation
- LacNAc-Sia-type Glycoprotein Conjugation
- Aldehyde Reaction based Glycoprotein Conjugation
- Azide Reaction based Glycoprotein Conjugation
- Glycoprotein Conjugation
- Bioactive Carbohydrates Screening
- Tumor Glyco-diag
- Anti-Carbohydrate Antigen Antibody Development
- Anti-Tumor-associated Glycan Antibody Development
- Anti-Tumor-associated Glycoprotein Antibody Development
- Anti-Tumor-associated Glycolipid Antibody Development
- Anti-Sialic Acid Antibody Development
- Anti-Poly-Sialic Acid Antibody Development
- Anti-Lewis Antigen Antibody Development
- Anti-Blood Group Antibody Development
- Anti-Viral Glycan Antibody Development
- Anti-Bacterial Glycan Antibody Development
- Anti-Fungal Glycan Antibody Development
- Anti-Plant & Algal Glycan Antibody Development
- Anti-Proteoglycan Antibody Development
- Anti-Glycan related Enzyme Antibody Development
- Anti-Glycosaminoglycan Antibody Development
- Glyco-based Vaccine Development
- Glycoproteomics-based Liquid-biopsy LDT Development
- Glyan-related Enzyme Activity Analysis
- Biomass Enzyme Degradation Efficiency Analysis
- Enzymatic Decomposition Reaction-based Residue Content Analysis
- Enzymatic Decomposition Reaction-based Fermentation Inhibitors Analysis
- Enzyme-Mediated Saccharification Efficiency Analysis
- Cellulase Activity Assessment
- Cellulolytic Enzyme Activity Assessment
- Amylolytic Enzyme Activity Assessment
- Sucrase Activity Assessment
- Biomass Components Quantitative Profiling
- Lignocellulose Quantitative Profiling
- In-process Chemical Composition Analysis
- Plant Chemistry Profiling
- Seaweed Multi-component Quantitative Profiling
- Seaweed Simple Sugar Quantitative Profiling
- Amino Acid Composition Profiling
- Aflatoxin Profiling
- Seaweed Elemental Quantitative Analysis
- Seaweed Multi-element Simultaneous Profiling
- Fatty Acid Composition Analysis
- Pigment Quantitative Analysis
- Seaweed Plant Hormones Determination
- Seaweed Vitamers Quantitative Analysis
- Total Phenolics Analysis
- Phenolic Composition Analysis
- Seaweed Tannin Qualitative & Quantitative Profiling
- Alginate Molecular Size Analysis
- Seaweed Total Phlorotannins Content Analysis
- Seaweed Bromoform Content Analysis
- Algae Multi-Component Quantitative Profiling
- Biogas Fermentation Process-based Quantitative Profiling
- BMP Assessment
- Biological & Chemical Analysis
- Chemical Oxygen Demand Detection
- Biological Oxygen Demand Detection
- VFA Profiling
- Digestate Solid Impurities Determination
- Ammoniacal Nitrogen Profiling
- Nitrates Profiling
- Viable Weed Seed Analysis
- Organic Matter Profiling
- SHA Determination
- SAdA Determination
- SMA Determination
- Microbiological Activity Assessment
- FOS/TAC Ratio Analysis
- Sludge Granule Size Analysis
- Sludge Activity Analysis
- Toxicity Assessment in Microbial Digestion Processes
- Persistent Digestion Process Profiling
- Bio-Oil Components Profiling
- Biochar Manufacturing & Characterization
- Biomass Combustion Property Profiling
- Biomass Physical Property Characterization
- Polyamine Quantitative Profiling
- Polyphenol Quantitative Profiling
- Terpene Quantitative Profiling
- Energy Metabolite Analysis
- Nutrition & Metabolism Research based Compound Analysis
- Organic Acid Quantitative Analysis
- Bile Acid Quantitative Analysis
- Arachidonic Acid Quantitative Analysis
- Carotenoid Quantitative Analysis
- Catechin Quantitative Analysis
- Anthocyanin Quantitative Analysis
- Biogenic Amine Quantitative Analysis
- Alkaloid Quantitative Analysis
- Flavonoid Quantitative Analysis
- Neurotransmitter Quantitative Analysis
- TMAO Quantitative Analysis
- Soil Analysis
- Glycoproteomics Quantitative Analysis
- One-Stop Glycan Crystal & Glycoprotein Crystal Analysis
-
Products
- Glycopeptides
- Glycoproteins
- Monosaccharides
- Oligosaccharides
- Polysaccharides
- Carbohydrate-based Surfactants
- Blood Group Antigens
- Glycoprotein Assay Kits
- Glycoprotein Reagents
- Glycoengineered Cells
- Glycoengineering Viral Particles
- Nucleotide Sugars
- Glycolipids
- Glycan Libraries
- N-Glycan Libraries
- O-Glycan Libraries
- HMO-Glycan Libraries
- Mannose Glycan Libraries
- Lacto Glycan Libraries
- Tandem Repeat Epitope Glycan Libraries
- Blood Group Antigen Libraries
- Glycosaminoglycan Libraries
- Methylated Glycan Libraries
- Sulfated Glycan Libraries
- Tag based Glycan Libraries
- Monoclonal Antibody Glycan Libraries
- Technologies
- Resources
- Company

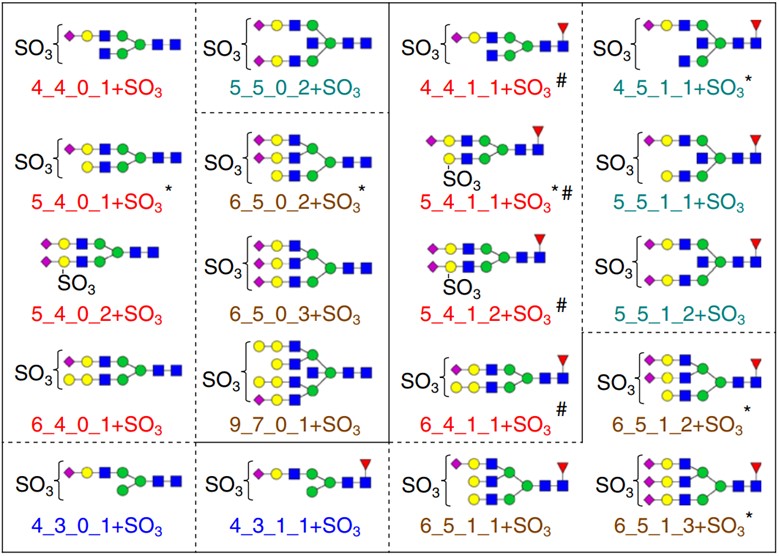 Fig.1 The structure of sulfated N-glycans identified in human serum IgG.1
Fig.1 The structure of sulfated N-glycans identified in human serum IgG.1

