Necessity of Bile Acid Analysis
Bile acids (BAs), synthesized in the liver from cholesterol, play a pivotal role in lipid digestion and absorption. However, their influence extends far beyond these primary functions, impacting glucose metabolism, signaling pathways, and even gut microbiota composition. Consequently, the precise quantification of BA profiles provides a powerful window into diverse physiological and pathological states. Creative Biolabs' BAs quantitative analysis service provides clients with a comprehensive and reliable platform to explore these complex interactions, which allows for the identification of specific bile acid species that may serve as biomarkers for disease diagnosis, prognosis, or therapeutic monitoring.
Comprehensive BAs Analysis Service at Creative Biolabs
Our service extends beyond the measurement of total BA levels. We provide detailed profiling, identifying, and quantifying individual BA species. This comprehensive approach allows for a nuanced understanding of BA's composition, crucial for studies exploring specific bile acid roles in physiological and pathological processes. We provide targeted quantification of over 50 primary, secondary, and conjugated BAs, with a specialized focus on their interplay with carbohydrate regulatory pathways. We utilize state-of-the-art analysis platforms, primarily liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), for BAs quantification. This technology provides exceptional sensitivity and specificity, enabling the accurate measurement of even trace amounts of BAs. The use of LC-MS/MS ensures robust data quality, minimizing interference from matrix effects and providing reliable results.
-
Lithocholic acid (LCA)
-
Norcholic acid (NorCA)
-
Deoxycholic acid (DCA)
-
Isolithocholic acid (IsoLCA)
-
Dehydrocholic acid (DHCA)
-
Allolithocholic acid (AlloLCA)
-
Hyodeoxycholic acid (HDCA)
-
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA)
-
Chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA)
-
23-Nordeoxycholic acid (NorDCA)
-
6-Ketolithocholic acid (6-KetoLCA)
-
7-Ketolithocholic acid (7-KetoLCA)
-
3β-Ursodeoxycholic acid (β-UDCA)
-
12-Ketolithocholic acid (12-KetoLCA)
-
Cholic acid (CA)
-
Allocholic acid (ACA)
-
3β-Cholic acid (β-CA)
-
Ursocholic acid (UCA)
-
6,7-Diketolithocholic acid
-
7,12-Diketolithocholic acid
-
α-Muricholic acid (α-MCA)
-
β-Muricholic acid (β-MCA)
-
Glycolithocholic acid (GLCA)
-
Glycodeoxycholic acid (GDCA)
-
Lithocholic acid 3-sulfate (LCA-3S)
-
Glycohyodeoxycholic acid (GHDCA)
-
Glycoursodeoxycholic acid (GUDCA)
-
Glycochenodeoxycholic acid (GCDCA)
-
Hyocholate (HCA)
-
Glycohyoholic acid (GHCA)
-
Taurolithocholic acid (TLCA)
-
Taurodeoxycholic acid (TDCA)
-
Taurocholate 3-sulfate (TCA-3S)
-
Glycocholenate sulfate (GCA-3S)
-
Taurodehydrocholic acid (TDHCA)
-
Glycine-β-muricholic acid (Gly-MCA)
-
Tauro-α-muricholic acid (T-α-MCA)
-
Tauro-β-muricholic acid (T-β-MCA)
-
Tauro-ω-muricholic acid (T-ω-MCA)
-
Taurolithocholate 3-sulfate (TLCA-3S)
-
Sodium gycocholate hydrate
-
7-α-Hydroxy-3-oxo-4-cholestenoate
-
Taurocholic acid (TCA)
-
Taurohyocholic acid (THCA)
-
Taurohyodeoxycholic acid (THDCA)
-
Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA)
-
Isochenodeoxycholic acid (IsoCDCA)
-
Taurochenodeoxycholic acid (TCDCA)
-
Glycolithocholic acid-3-sulfate (GLCA-3S)
-
Chenodeoxycholic acid-3-sulfate (CDCA-3S)
-
3-Sulfo-taurochenodeoxycholic acid (TCDCA-3S)
-
Glycochenodeoxycholic acid 3-sulfate (GCDCA-3S)
-
Chenodeoxycholic acid-3-β-D-glucuronide (CDCA-3G)
-
Chenodeoxycholic acid 24-acyl-β-D-glucuronide (CDCA-24G)
-
(3a,5b,7a)-3,7-Dihydroxycholan-24-oic acid
Multiple Sample Types
The versatility of BA analysis allows for the examination of a broad spectrum of sample types, reflecting the systemic nature of BA circulation. We support BA analysis for a variety of sample types.
Workflow Overview
The BA quantitative analysis service consists of several key steps. First, we communicate with the client to clarify the type of samples and analysis requirements. Next, the client provides the necessary biological samples and completes the relevant submission forms. Upon receipt of the samples, our laboratory conducts a preprocessing stage to ensure their suitability for subsequent analysis. Then, we employ advanced analysis techniques (such as LC-MS/MS) for the separation and quantification of BAs. Finally, we compile the analysis results and generate a detailed report for the client's reference.

Extensive Range of Services
Our BA quantitative analysis service supports a wide range of research applications, including:
-
Metabolic disease studies: Investigating the role of BAs in conditions such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), diabetes, and obesity.
-
Gastrointestinal studies: Exploring BA involvement in intestinal health, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and BA malabsorption.
-
Drug development: Assessing the impact of drugs on BA metabolism and identifying potential therapeutic targets.
-
Nutritional studies: Examining the influence of dietary interventions on BA profiles.
The BA analysis service from Creative Biolabs operates based on core principles of quality assurance, precise accuracy measurement, and ensuring client satisfaction. The experts on our scientific team deliver full support throughout every stage, including sample preparation and data interpretation. Our customizable and reliable platform enables clients to explore BA metabolism complexities while improving their knowledge of human health and diseases. In addition, we also provide analysis services for Organic Acid, Arachidonic Acid, Catechin, Biogenic Amine, Neurotransmitter, and other compounds related to Metabolism Research. Please contact us for more information if you are very interested in these analysis services.
Published Data
This research introduces a refined and highly effective method for precisely measuring BAs in human biological samples using LC-MS/MS. This advanced technique offers significant improvements over previous methods, such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), by simplifying the process and providing rapid, sensitive, and specific detection without requiring extensive sample preparation like hydrolysis or derivatization. The study validates the LC-MS/MS method's accuracy and reproducibility, demonstrating its capability to identify and quantify various conjugated bile acids, including their glycine and taurine forms, in a mere five minutes. Figure 1 showcases the unique MS signatures obtained from samples of bile, serum, urine, and feces. In both bile and serum, the analysis consistently reveals the presence of only conjugated BAs. Conversely, the urine samples present a more diverse composition, while containing some conjugated BAs similar to bile and serum, they notably exhibit additional, more complex forms. This suggests different metabolic pathways or excretion mechanisms in the kidneys. The fecal samples predominantly display only free BAs, indicating the significant role of intestinal bacteria in deconjugating these compounds. These varying profiles underscore the LC-MS/MS method's power in discerning the metabolic state and distribution of BAs throughout the body.
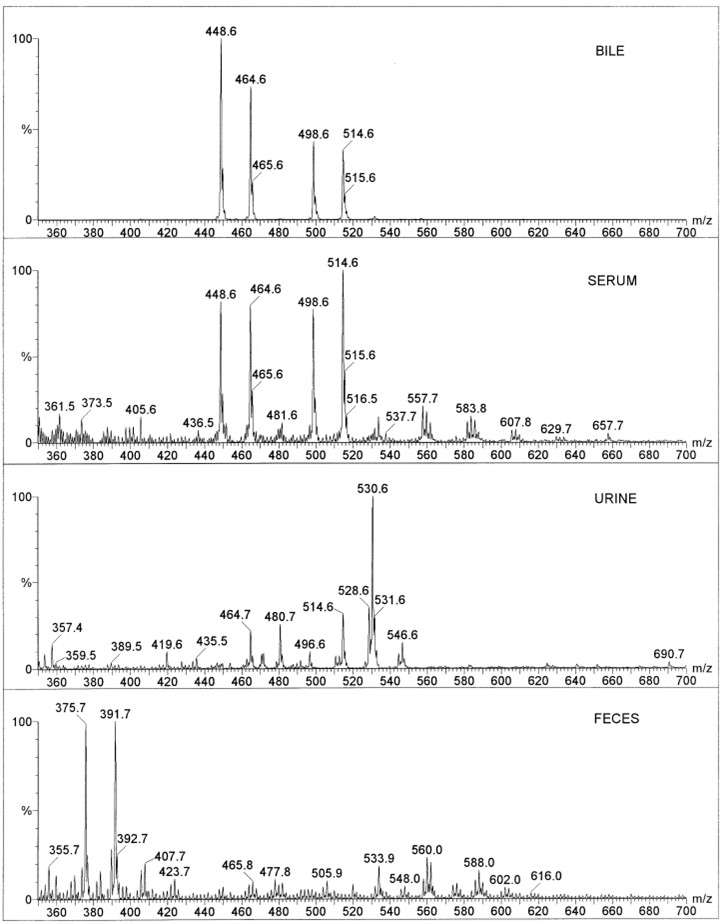 Fig.1 LC-MS/MS spectra of BAs in different samples.1
Fig.1 LC-MS/MS spectra of BAs in different samples.1
FAQs
Q1: What analytical platforms and methodologies do you employ for BA quantification?
A1: We primarily utilize LC-MS/MS for BA quantification. This platform offers unparalleled sensitivity, allowing for the detection of bile acids at picomolar to nanomolar concentrations, which is critical for low-abundance species or small sample volumes. Its high specificity, achieved through multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) and chromatographic separation, ensures accurate quantification even in complex biological matrices by minimizing interference from co-eluting compounds. For certain applications, we can also leverage gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) or enzymatic assays, depending on the specific project requirements and target analytes.
Q2: What is your typical turnaround time (TAT) for a standard batch of samples?
A2: Our standard TAT for BA quantitative analysis typically ranges from 3 to 4 weeks, depending on the number of samples, the complexity of the requested panel, and the current laboratory workload. This timeframe includes sample preparation, LC-MS/MS analysis, data processing, and quality control. Please discuss your specific timeline requirements with our project managers, and we will do our best to accommodate your needs.
Q3: How do you ensure the stability of BAs during sample processing, storage, and analysis?
A3: To ensure the stability of BAs during sample processing, storage, and analysis, it is crucial to maintain controlled environmental conditions, such as low temperatures (typically -80 °C for long-term storage) to prevent degradation. Samples should be processed promptly after collection to minimize enzymatic activity and chemical transformations. Utilizing appropriate preservatives or stabilizers can also help maintain BA integrity. Moreover, employing rapid and efficient extraction methods, followed by analysis using stable techniques like LC-MS, ensures accurate quantification.
Customer Review
Comprehensive BA Analysis Results
"The BA quantitative analysis provided by Creative Biolabs was incredibly thorough. Each BA was measured with precision, and the report included detailed graphs that helped visualize the data effectively." - Mr. E. Dav***s
Reliable and Reproducible Results
"The results I received were reliable and reproducible, which is crucial for my ongoing research. I performed replicate assays, and the consistency was remarkable." - Dr. F. Gar***a
Reference
-
Perwaiz, Shahid, et al. "Determination of bile acids in biological fluids by liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry." Journal of lipid research 42.1 (2001): 114-119. DOI: 10.1016/S0022-2275(20)32342-7. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Services
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on



 Fig.1 LC-MS/MS spectra of BAs in different samples.1
Fig.1 LC-MS/MS spectra of BAs in different samples.1

