Unlocking Next-Generation Therapeutics Insights from Glycoproteomic Analysis
Glycosylation, the enzymatic attachment of glycans to proteins, is a fundamental post-translational modification critical for protein functions, cellular interactions, and disease pathogenesis. O-glycosylation, specifically, involves the attachment of glycans to serine or threonine residues. Unlike N-glycosylation, O-glycans lack a consensus sequence, making their analysis inherently more challenging yet vital for comprehensive biological understanding. O-glycan analysis presents several formidable challenges that necessitate specialized expertise and advanced methodologies.
-
Firstly, the lack of a universal enzymatic release method, unlike N-glycans, means chemical methods are primarily employed. These traditional chemical methods, such as reductive beta-elimination or hydrazinolysis, often suffer from significant "peeling" (sequential degradation of glycan units), leading to incomplete release and inaccurate representation of the native glycan profile. Hydrazinolysis, while effective, also requires extremely hazardous anhydrous conditions and can deacylate amide groups, complicating the analysis of glycans containing sensitive modifications like NeuGc.
-
Secondly, O-glycans exhibit immense structural heterogeneity, with multiple core structures and diverse branching patterns, making their separation and identification highly complex. The presence of isomers, which share the same mass but differ in linkage or branching, further complicates characterization.
-
Lastly, O-glycans are often present in low abundance within complex biological matrices, requiring highly sensitive detection methods and robust sample clean-up procedures to minimize interference.
 Fig.1 Structures of common O-glycans, N-glycans, and HMOs.1
Fig.1 Structures of common O-glycans, N-glycans, and HMOs.1
Despite these challenges, providing an O-glycan-based glycoproteomic quantitative analysis service is essential due to the profound biological and clinical significance of O-glycosylation. O-glycans play critical roles in numerous physiological processes. Aberrant O-glycosylation is a hallmark of many diseases, including various cancers (e.g., Pancreatic, Breast, and Colon), and congenital disorders of glycosylation, serving as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. In the biopharmaceutical industry, understanding the O-glycosylation profile of therapeutic proteins is paramount for ensuring product safety, efficacy, and batch-to-batch consistency. Our O-glycan-based glycoproteomic quantitative analysis service leverages advanced mass spectrometry and innovative chemical release methods to provide detailed structural and quantitative insights into these complex glycans, supporting biomarker discovery, biopharmaceutical development, and fundamental research.
How to Provide O-Glycan-based Glycoproteomic Quantitative Analysis Service?
At Creative Biolabs, we provide unparalleled solutions for the intricate world of O-glycans, delivering precise, quantitative insights crucial for understanding protein functions, disease mechanisms, and biopharmaceutical quality. Our service offers specific deliverables designed to empower your research and development efforts. We provide detailed structural elucidation of O-glycans, enabling you to identify novel glycan biomarkers, characterize glycosylation patterns critical for drug efficacy and safety.
Our O-glycan-based glycoproteomic quantitative analysis service follows a meticulously designed, multi-stage workflow to ensure accuracy and comprehensive data delivery. Our methodologies are designed to overcome the inherent complexities of O-glycosylation, providing a clearer picture of your biological samples than ever before.
Key Steps Involved
O-Glycan Release
This initial phase involves the crucial step of liberating O-glycans from glycoprotein samples. We employ advanced chemical methods, including our optimized hydroxylamine approach or the "one-pot" beta-elimination with 1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone (PMP) labeling. These techniques are designed to minimize "peeling" (glycan degradation) and ensure high yields of intact, reducing glycans. The outcome is a purified mixture of released O-glycans ready for analysis.
Fluorescent or Affinity Labeling
For enhanced detection and chromatographic separation, the released O-glycans can be derivatized with fluorescent tags (e.g., anthranilic acid (2-AA)) or other labels like PMP. This step improves sensitivity for subsequent analysis and facilitates detailed characterization. The expected outcome is a labeled glycan mixture.
High-Resolution Chromatographic Separation
The labeled O-glycans are then subjected to liquid chromatography. We utilize a combination of techniques, including hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) for separation based on glycan size and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) for separation based on linkage type and three-dimensional structure. This multi-dimensional approach ensures maximum resolution of complex glycan mixtures. The outcome is highly resolved glycan peaks.
Mass Spectrometric Analysis and Identification
Eluted glycan fractions are directly introduced into high-resolution mass spectrometers (e.g., ESI-MS). We employ advanced fragmentation techniques such as collision-induced dissociation (CID) and electron transfer dissociation (ETD) to obtain detailed structural information, including monosaccharide composition, sequence, and linkage positions.
Quantitative Analysis
Utilizing label-free or labeled quantitative approaches, we determine the relative or absolute abundance of each identified O-glycan. Our expert bioinformaticians then process and interpret the vast datasets, providing meaningful biological insights and comparative analyses.
Diverse Biological Sample Types
Our service is versatile and suitable for a wide range of biological sample types, enabling diverse research and clinical applications.
|
Sample Types
|
Purified glycoproteins: Recombinant proteins, antibodies, enzymes, and other therapeutic proteins.
|
|
Biological fluids: Serum, plasma, urine, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), saliva, milk (human and bovine), and other bodily fluids.
|
|
Cellular samples: Cell lysates, membrane fractions, and conditioned media from various cell lines (mammalian, insect, yeast).
|
|
Tissue samples: Homogenates from various tissues.
|
|
Natural bioresources: Extracts from plants, microorganisms, and other natural sources rich in glycoproteins (e.g., whey protein concentrates).
|
Related Services
-
N-Glycan Glycoproteomic Quantitative Analysis Service: For comprehensive characterization of N-linked glycosylation patterns.
-
Glycoprotein Characterization and Engineering: Services for the expression, purification, and modification of glycoproteins, including site-specific glycosylation.
-
Biomarker Discovery and Validation: Integrated platforms for identifying and validating novel biomarkers, including glycan-based markers.
-
Custom Glycan Synthesis: Tailored synthesis of specific glycan structures for use as standards or research tools.
Creative Biolabs invites you to connect with our expert team to discuss your specific O-glycan analysis requirements. Whether you're characterizing a novel therapeutic protein, searching for disease biomarkers, or exploring natural bioactive compounds, Creative Biolabs is your trusted partner for comprehensive glycoproteomic solutions. Please contact us for more information!
Published Data
This study investigated the diverse landscape of N- and O-glycans, alongside human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs), in 200 samples of Japanese maternal milk collected one to two months postpartum. Utilizing a label-free liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) approach, researchers aimed to understand the variations in these complex sugar structures and their relationship to maternal secretor status. A key aspect of the research, visually represented in Figure 2, involved comparing the relative concentrations of these glycans between secretor and non-secretor mothers. Out of the 200 milk samples, 161 (80.5%) were classified as secretor milk, while 39 (19.5%) were non-secretor. The figure illustrated distinct patterns: glycans with fucose linked to galactose, including specific O-glycans (O1, O20, O28) and certain HMOs (2'-FL, LDFT, LNFP-I, LNDFH-II), were found in significantly higher concentrations in milk from secretor mothers. Conversely, several O-glycans (O8, O9, O24, O26, O27) and other fucosylated HMOs (3-FL, LNFP-II, LNDFH-II) were more abundant in non-secretor milk. While some N-glycans also showed concentration differences between the two groups, their presence or absence was not consistently linked to secretor status based on fucose content. This comprehensive analysis revealed that maternal secretor status plays a significant role in shaping the composition and abundance of both HMOs and O-glycans in human milk, but its influence on N-glycans appears less pronounced.
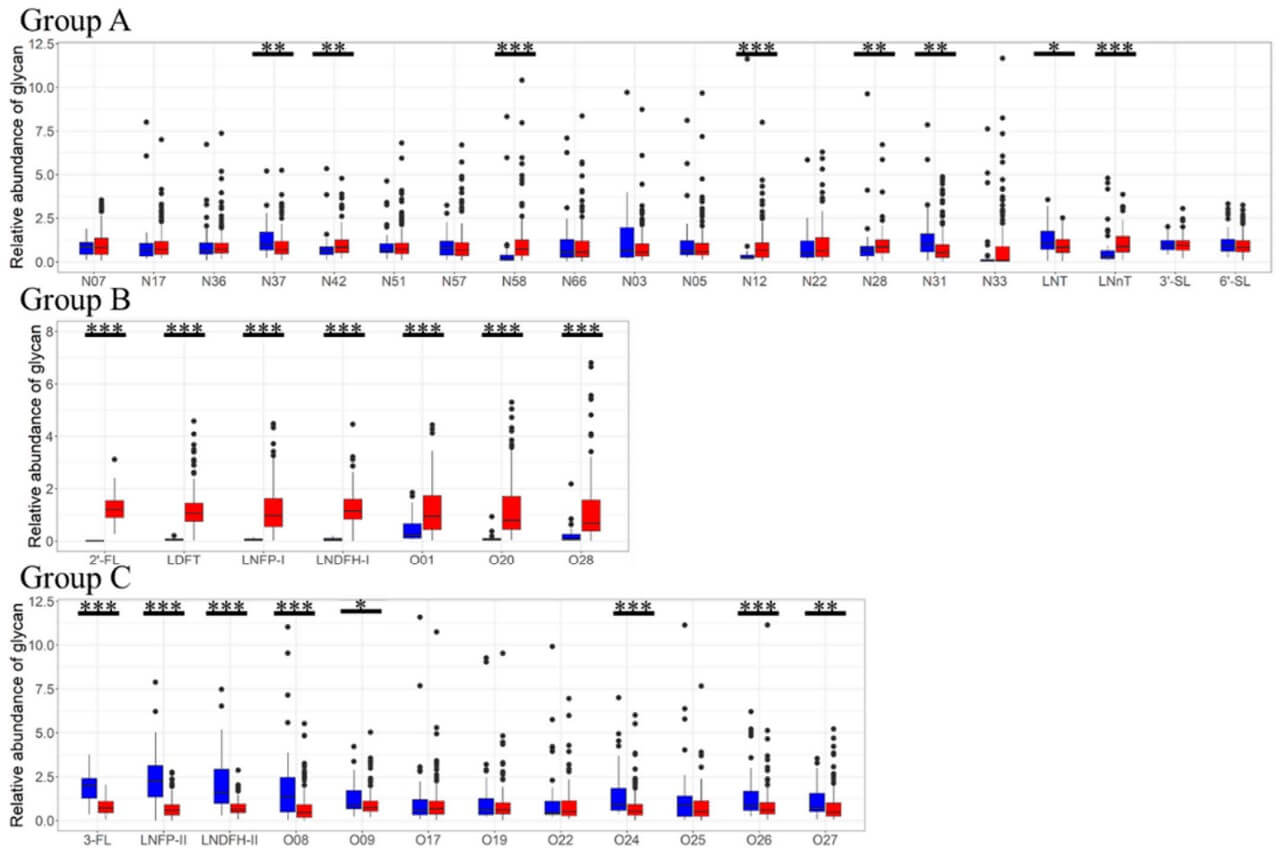 Fig.2 Comparison of relative concentrations of N/O-glycans and HMOs in milk.1
Fig.2 Comparison of relative concentrations of N/O-glycans and HMOs in milk.1
FAQs
Q1: How does Creative Biolabs's O-glycan analysis method minimize glycan degradation?
A1: We utilize advanced chemical release methods, including an optimized hydroxylamine approach and a "one-pot" beta-elimination with PMP labeling. These techniques are specifically designed to reduce the "peeling" side reaction common in traditional methods, ensuring that the released O-glycans maintain their native structures for accurate analysis. This significantly improves the integrity of your glycan profiles.
Q2: Can your service analyze O-glycans from complex biological samples like serum or tissue homogenates?
A2: Absolutely. Our O-glycan-based glycoproteomic quantitative analysis service is robustly designed to handle a wide array of complex biological samples, including serum, plasma, urine, cell lysates, and tissue homogenates. Our sophisticated sample preparation and clean-up protocols effectively remove interfering substances, allowing for precise glycan analysis even from challenging matrices.
Q3: What are the typical applications for Creative Biolabs's O-glycan-based glycoproteomic quantitative analysis service?
A3: Our service has broad applications across various fields. It is invaluable for biomarker discovery in disease research, critical for quality control and process optimization in biopharmaceutical development, essential for understanding the bioactive properties of glycans in functional foods, and fundamental for advancing basic glycobiology research. Whatever your specific needs, our service provides the detailed glycan insights you require.
Customer Review
Detailed Data Interpretation
"We needed precise quantitative data on human milk O-glycans for our infant nutrition research. Creative Biolabs's service delivered exactly that, even for low-abundance glycans. Their expertise in handling complex biological samples and their detailed data interpretation saved us immense time and resources compared to our in-house capabilities." - Dr. J. Har***s.
Advancing Biomarker Discovery
"The clarity of O-glycan profiles we obtained using Creative Biolabs's service was exceptional. They are giving us the most accurate representation of our mucin samples to date, which was crucial for our biomarker discovery efforts." - Ms. P. Mar***n.
References
-
Yamaguchi, Toshiyuki, et al. "Label-Free Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Quantitation of Relative N-and O-Glycan Concentrations in Human Milk in Japan." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.3 (2024): 1772. DOI: 10.3390/ijms25031772. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Services
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Structures of common O-glycans, N-glycans, and HMOs.1
Fig.1 Structures of common O-glycans, N-glycans, and HMOs.1
 Fig.2 Comparison of relative concentrations of N/O-glycans and HMOs in milk.1
Fig.2 Comparison of relative concentrations of N/O-glycans and HMOs in milk.1

