Unlocking Soil Health: Creative Biolabs' Glycoproteinase Activity Analysis Service
Soil glycoproteinase activity analysis provides a powerful lens into the intricate biological processes governing soil health and fertility. Glycoproteinases, alongside other critical soil enzymes, play pivotal roles in the decomposition of complex organic matter, nutrient mineralization, and overall ecosystem functionality. These enzymes, often secreted by microbes and plant roots, are key drivers of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur cycling. Measuring soil enzyme activities provides robust indicators of soil quality, microbial community response, and the efficiency of nutrient transformations, offering valuable insights into sustainable land management. Creative Biolabs stands at the forefront of soil enzyme analysis, offering unparalleled precision, scientific rigor, and actionable insights. Our commitment to cutting-edge methodologies and profound biological expertise ensures that our clients receive the most reliable and impactful data. We leverage advanced Soil Analysis platforms, ensuring high sensitivity and throughput for even the most challenging soil matrices. Our long-standing experience, underscored by continuous research and method refinement, provides a distinct advantage in understanding the nuanced dynamics of soil biochemistry.
Detailed Analysis Process for Soil Enzyme Activities
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive suite of soil enzyme activity analyses, providing deep insights into soil biochemical processes. This comprehensive panel ensures a holistic assessment of your soil's metabolic health. We provide analysis for the following key soil enzyme activities:
The general analysis process for these soil enzyme activities at Creative Biolabs involves a standardized, multi-step approach designed for precision and reproducibility:
Soil samples are typically air-dried at room temperature or low heat to preserve enzyme activity, then sieved through a 2 mm mesh to remove coarse debris and homogenize the sample. For highly labile enzymes, fresh or frozen samples are processed directly.
-
Enzyme assay setup
-
Substrate selection: Specific synthetic or natural substrates are carefully chosen for each target enzyme. For many hydrolytic enzymes, chromogenic or fluorogenic substrates (e.g., p-nitrophenol (PNP) derivatives or methylumbelliferyl (MUB) derivatives) are commonly used because their enzymatic hydrolysis releases a detectable product. For enzymes like urease, urea is the natural substrate, and its hydrolysis product (ammonium) is measured. Dehydrogenase activity is often measured by the reduction of tetrazolium salts.
-
Buffer system: Each assay employs an optimized buffer system (e.g., acetate, phosphate, Tris-HCl) to maintain the optimal pH for the specific enzyme's activity and mimic in situ soil conditions.
-
Soil suspension: A known amount of prepared soil is weighed into a reaction vessel.
-
Adding substrate and buffer: The specific substrate solution and the appropriate buffer are added to the soil sample, forming a soil-substrate suspension.
The reaction vessels are incubated at a controlled temperature for a specific duration (e.g., 1-24 hours). This allows the enzyme to react with its substrate.
After incubation, the enzymatic reaction is stopped. This is usually achieved by adding a strong acid (e.g., H2SO4), a strong base, or a specific enzyme inhibitor. The reaction product is then extracted from the soil suspension using a suitable extraction solution. Centrifugation and filtration steps are often followed to obtain a clear supernatant.
The concentration of the liberated product in the supernatant is measured using a spectrophotometer or a fluorometer.
Enzyme activity is calculated according to the amount of product formed, the incubation time, and the dry weight of the soil sample.
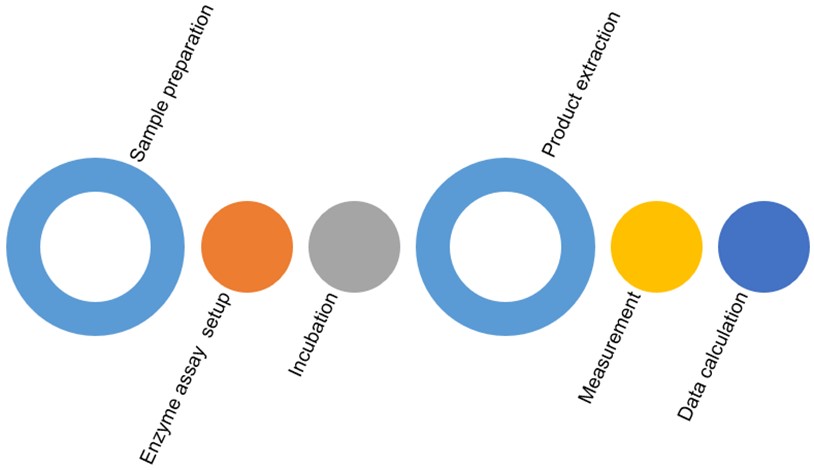 Fig.1 Enzyme activity analysis workflow.
Fig.1 Enzyme activity analysis workflow.
Related Services
To further enhance your understanding of soil ecosystems and optimize your agricultural or environmental projects, Creative Biolabs offers a suite of complementary services, which can be seamlessly integrated with our soil glycoproteinase activity analysis to provide a holistic view:
-
Soil Polysaccharide Content Analysis: This service is designed to accurately determine the polysaccharide content in the soil, which is essential for evaluating the quality of soil organic matter, aggregate stability, and carbon cycling capacity.
-
Soil Physical and Chemical Property Analysis: This service provides a comprehensive determination of key physical and chemical parameters of soil, including pH, conductivity, organic matter, total nitrogen, available phosphorus, potassium, etc. These data are the basis for evaluating soil health, crop growth potential, and formulating scientific fertilization plans, providing core support for precision agricultural management.
-
Soil Elements and Heavy Metal Content Analysis: This service accurately detects the macro and trace elements and potential heavy metal content in the soil. This is of decisive significance for evaluating soil nutrient abundance, identifying environmental pollution risks, ensuring the food safety of agricultural products, and ensuring the sustainability of the soil environment.
Creative Biolabs' soil glycoproteinase activity analysis service provides an indispensable tool for researchers, agricultural professionals, and environmental managers seeking to understand and optimize soil health. By offering precise, comprehensive, and actionable insights into soil enzyme dynamics, we empower you to make data-driven decisions that foster sustainable practices, improve nutrient cycling, and enhance overall soil vitality. Please contact us to obtain more service content.
Published Data
This research examined the impact of different manure application rates and types, alongside various tillage practices, on key soil enzyme activities. These enzymes are vital indicators of the intricate biogeochemical cycling processes occurring within the soil, which are fundamental to its health and productivity. Specifically at the Colorado site, where beef manure was applied to a fine sandy loam. As illustrated, after just the first year of manure application, the highest rate of beef manure prompted a distinct clustering and separation of all measured enzyme activities from both the untreated control and the low application rate at the shallow 0-5 cm soil depth. This pronounced visual distinction indicated a rapid and strong positive response in the soil's biological activity due to the significant organic input. While the high rate consistently demonstrated a potent effect, a subtle yet emerging trend in the visual data after the second year suggested a gradual separation between the control and the low manure application rate, hinting that even moderate organic inputs could begin to differentiate from unamended soils over time, though perhaps not as dramatically as with the highest rates. This early responsiveness underscores the potential of organic amendments to quickly enhance essential soil functions, particularly those related to carbon and phosphorus cycling.
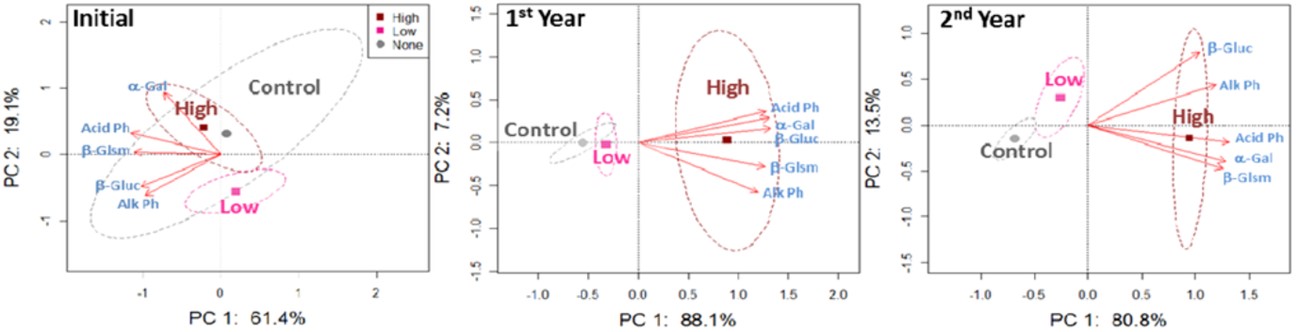 Fig.2 Effect of cow dung application on soil enzyme activity.1
Fig.2 Effect of cow dung application on soil enzyme activity.1
FAQs
Q1: How can Creative Biolabs' soil glycoproteinase activity analysis service help my specific agricultural challenge?
A1: Our service provides precise insights into the metabolic health of your soil, helping you understand how different practices (like tillage, fertilization, or organic amendments) impact nutrient cycling and microbial vitality. For instance, knowing the activity levels of enzymes like urease or phosphatases can guide you in optimizing fertilizer application, reducing waste, and improving nutrient availability for your crops. It's a proactive approach to soil management.
Q2: What kind of soil samples are suitable for analysis, and what precautions should I take during collection?
A2: We provide a wide range of soil-type analysis services. For optimal results, please ensure your samples are representative of the area of interest. Collect samples from consistent depths and locations. Air-drying or freezing immediately after collection is crucial to preserve enzyme activity, avoiding direct sunlight or excessive heat. Please refer to our detailed sample submission guidelines or contact us for specific advice tailored to your project.
Q3: Is this service applicable for long-term ecological studies or only for immediate agricultural optimization?
A3: Our service is incredibly versatile! The data on soil enzyme activity is highly valuable for both short-term agricultural optimization (e.g., assessing immediate impacts of manure application) and long-term ecological studies. By monitoring enzyme activity over time, researchers can track trends in soil health, evaluate the sustainability of different land management practices, and assess ecosystem resilience, as evidenced by various published studies on long-term fertilization and tillage impacts.
Customer Review
Significantly Improved Our Understanding of Nutrient Cycling
"Using Creative Biolabs's soil glycoproteinase activity analysis service in our soil remediation research has significantly improved the accurate assessment of microbial activity and the efficacy of our bioremediation agents. The detailed reports provided invaluable insights into enzyme kinetics and stability, helping us refine our treatment protocols." - Prof. K. Pat***l
Invaluable for Optimizing Organic Amendments
"We utilized Creative Biolabs's soil glycoproteinase activity analysis service to monitor enzyme responses to various animal manure applications precisely. The insights gained into specific enzyme activities, such as urease and phosphatase, helped us determine optimal application rates and timing, thereby preventing nutrient losses and maximizing nutrient availability for crops. The detailed comparative analysis was exceptional." - Dr. L. Coo***r
Reference
-
Acosta-Martinez, Veronica, et al. "Multi-location study of soil enzyme activities as affected by types and rates of manure application and tillage practices." Agriculture 1.1 (2011): 4-21. DOI: 10.3390/agriculture1010004. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 3.0, without modification.
Related Services
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Enzyme activity analysis workflow.
Fig.1 Enzyme activity analysis workflow.
 Fig.2 Effect of cow dung application on soil enzyme activity.1
Fig.2 Effect of cow dung application on soil enzyme activity.1

