Introduction of Glycoproteomics Quantitative Analysis
The glycosylation of proteins is a crucial post-translational modification that significantly impacts biological functions and disease progression. Understanding these complex changes is essential for biomarker discovery and therapeutic development. Our glycoproteomics quantitative analysis services provide a comprehensive solution to this challenge by integrating advanced purification, labeling, and mass spectrometry techniques. We offer unparalleled data depth and accuracy, enabling you to identify novel biomarkers and unravel the molecular mechanisms of disease with confidence. This service is supported by extensive published research, which highlights the importance of an integrated approach for characterizing diseases.
Glycoproteomics is an emerging and highly important area of Proteomics that focuses on the comprehensive analysis of glycoproteins. These services are critical for a wide range of applications, from biomarker discovery to understanding disease mechanisms. The fundamental principle is the use of high-resolution mass spectrometry (MS) to identify and quantify glycoproteins and their attached glycan structures. This is typically achieved by a multi-step process that involves:
-
Isolation and enrichment: Glycoproteins or glycopeptides are selectively isolated from complex biological samples using methods like lectin affinity chromatography or chemical tagging.
-
Labeling: Samples from different experimental groups are labeled with stable isotopes to allow for precise relative quantification in a single MS run.
-
MS analysis: The labeled samples are analyzed by a high-resolution mass spectrometer, which measures the mass of precursor ions and their fragments.
-
Data analysis: Specialized software is used to interpret the complex mass spectra, identify the peptides and glycan structures, and quantify their relative abundance across samples.
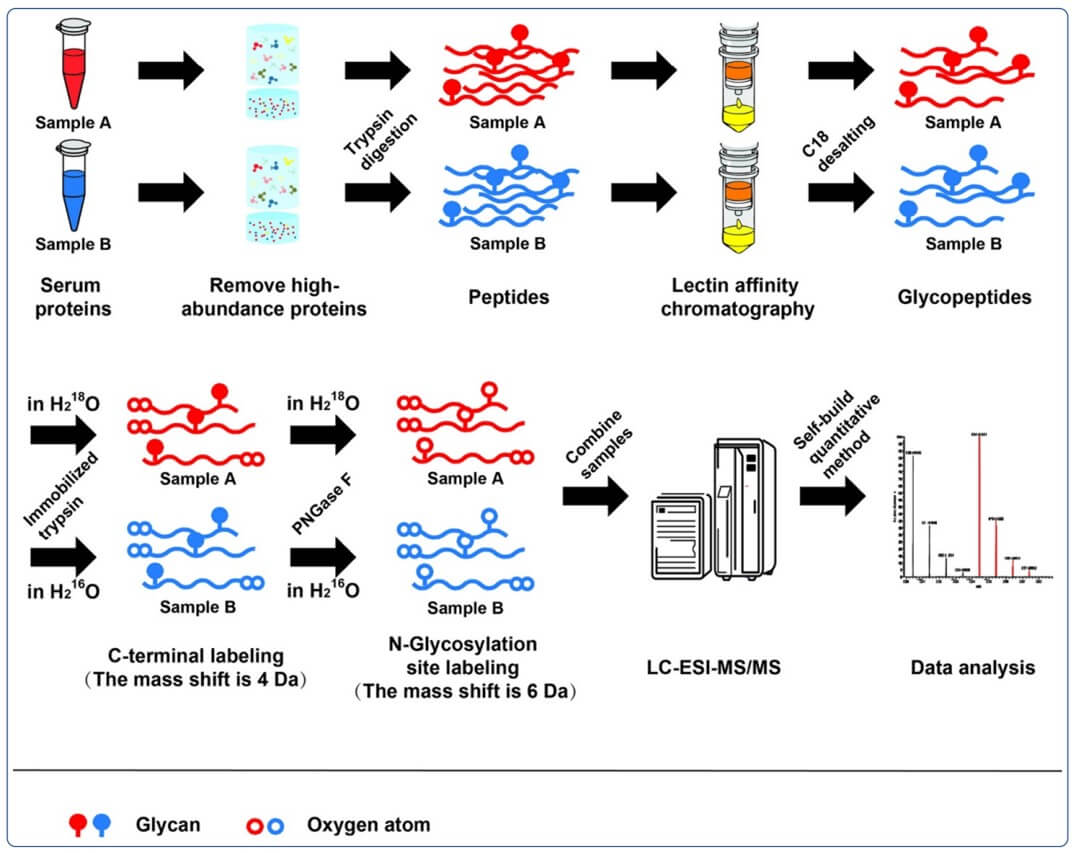 Fig.1 Strategies for glycoproteomics research.1
Fig.1 Strategies for glycoproteomics research.1
What Challenges Does the Glycoproteomics Quantitative Analysis Service Face?
Glycoproteomics is a complex field due to several inherent challenges:
-
Sample complexity: Biological fluids like serum or plasma contain a vast dynamic range of proteins, making it difficult to detect low-abundance glycoproteins.
-
Glycan heterogeneity: A single protein can have multiple glycosylation sites, and each site can be occupied by a diverse array of glycan structures, a phenomenon known as microheterogeneity.
-
Technical artifacts: Sample preparation and analysis can introduce errors, such as non-specific deamidation of peptides, which can lead to false-positive identification of glycosylation sites.
Glycosylation is not just a passive modification; it plays a critical role in cellular communication, immune response, and disease pathogenesis. Providing a dedicated analysis service is necessary because it allows researchers to:
-
Discover new biomarkers: Many clinically used biomarkers (e.g., AFP for liver cancer) are glycoproteins. Quantifying changes in their abundance and glycan structure can lead to the discovery of new, more specific markers.
-
Unravel disease mechanisms: Changes in glycosylation are often linked to disease progression, including cancer metastasis and neurodegeneration. This service helps researchers understand these underlying molecular mechanisms.
-
Accelerate drug development: By identifying disease-specific glycoproteins, researchers can find new therapeutic targets and monitor the efficacy of drug treatments.
Various Glycoproteomics Quantitative Analysis Services
Are you currently facing challenges in identifying new disease biomarkers, understanding protein functions, or dealing with complex biological samples? Our glycoproteomics quantitative analysis services help you unlock a deeper understanding of disease mechanisms and accelerate your research through integrated, high-throughput mass spectrometry platforms. Our glycoproteomics quantitative analysis services are designed to deliver precise, quantitative data on a large scale, moving your research from hypothesis to validated insight. We provide a streamlined, start-to-finish solution that delivers clear, actionable results tailored to your specific project goals.
Focuses on N-linked glycans, which are attached to the asparagine (Asn) residue in an N-X-S/T motif. This analysis often involves the enzymatic release of glycans and subsequent analysis.
Focuses on O-linked glycans, which are attached to serine (Ser) or threonine (Thr) residues. These glycans are more challenging to analyze due to the lack of a simple consensus motif and the presence of microheterogeneity.
In addition to glycoproteomics, we also provide a comprehensive view of the proteome, leading to a more complete understanding of biological systems, which includes:
DIA is a shotgun proteomics method that improves on traditional Data-Dependent Acquisition (DDA). Instead of selecting a few precursor ions for fragmentation, DIA fragments all ions within a broad mass range. It provides deep and unbiased proteome coverage, which can be correlated with glycoproteomics data to understand if changes in glycosylation are due to a change in protein abundance or an altered glycosylation state.
PRM is a targeted proteomics method that uses a high-resolution mass spectrometer to monitor specific peptide ions and their fragments. It is highly sensitive and accurate for quantifying a pre-defined set of proteins. It is ideal for validating a list of candidate biomarkers identified through a discovery-based glycoproteomics or proteomics workflow.
Focuses on the identification and quantification of phosphorylation, a critical post-translational modification involved in cell signaling. It is a complementary service that can be used to investigate how changes in glycosylation might affect upstream or downstream signaling pathways in a disease state.
Concentrates on the identification and quantification of acetylation, another key post-translational modification involved in gene expression and protein stability. It used to provide a more complete picture of protein regulation, especially in the context of epigenetics and metabolic diseases.
Studies the ubiquitination of proteins, a process that regulates protein degradation and localization. This service can be used to understand how changes in protein turnover, possibly influenced by glycosylation, contribute to disease pathology.
-
Glycomics Quantitative Analysis in Complex Matrix
We provide specialized glycomics quantitative analysis services for complex matrices, enabling clients to understand the glycomic profiles within complex samples.
We provide a mature glycomics quantitative analysis service in milk, utilizing a high-resolution mass spectrometry technology platform to provide a one-stop solution for human and animal milk research. This service can accurately identify and quantify complex free oligosaccharides and protein-linked N/O-glycans in milk, providing in-depth analysis of their structural isomers and modification patterns.
Leveraging cutting-edge analytical platforms and a professional bioinformatics analysis system, we provide efficient and accurate quantitative glycomics analysis services for food products to clients worldwide. Through highly sensitive detection and in-depth characterization of complex glycans in food, we support food nutrition research.
Sample Types of Glycoproteomics Quantitative Analysis Services
Our service is suitable for a wide range of biological samples, including but not limited to:
Ready to accelerate your research with high-quality, quantitative glycoproteomics data? Contact our team of experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our services can provide the insights you need to succeed. We are committed to helping you achieve your research goals.
Published Data
This research paper addresses the critical need for more effective biomarkers for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA), which is currently difficult to diagnose early. The authors explored changes in N-linked glycosylation, a common modification of proteins, by analyzing tissue and serum samples from patients with iCCA and other liver diseases. The goal was to identify specific glycan structures that could serve as a noninvasive diagnostic tool. The study employed matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) imaging mass spectrometry (IMS) to examine two tissue cohorts and one independent serum cohort. The tissue analysis revealed that bisected fucosylated N-glycan structures were specifically expressed in iCCA tumor regions. To test the translational potential of this discovery, the researchers then analyzed the serum cohort, with its detailed workflow in the Figure below. The results showed that the overall finding was that the N-glycan profile in serum closely resembled the trends observed in the tissue samples, reinforcing the idea that these molecular changes could be reliably detected in blood. This suggests the potential for developing a powerful new biomarker for the noninvasive detection of iCCA.
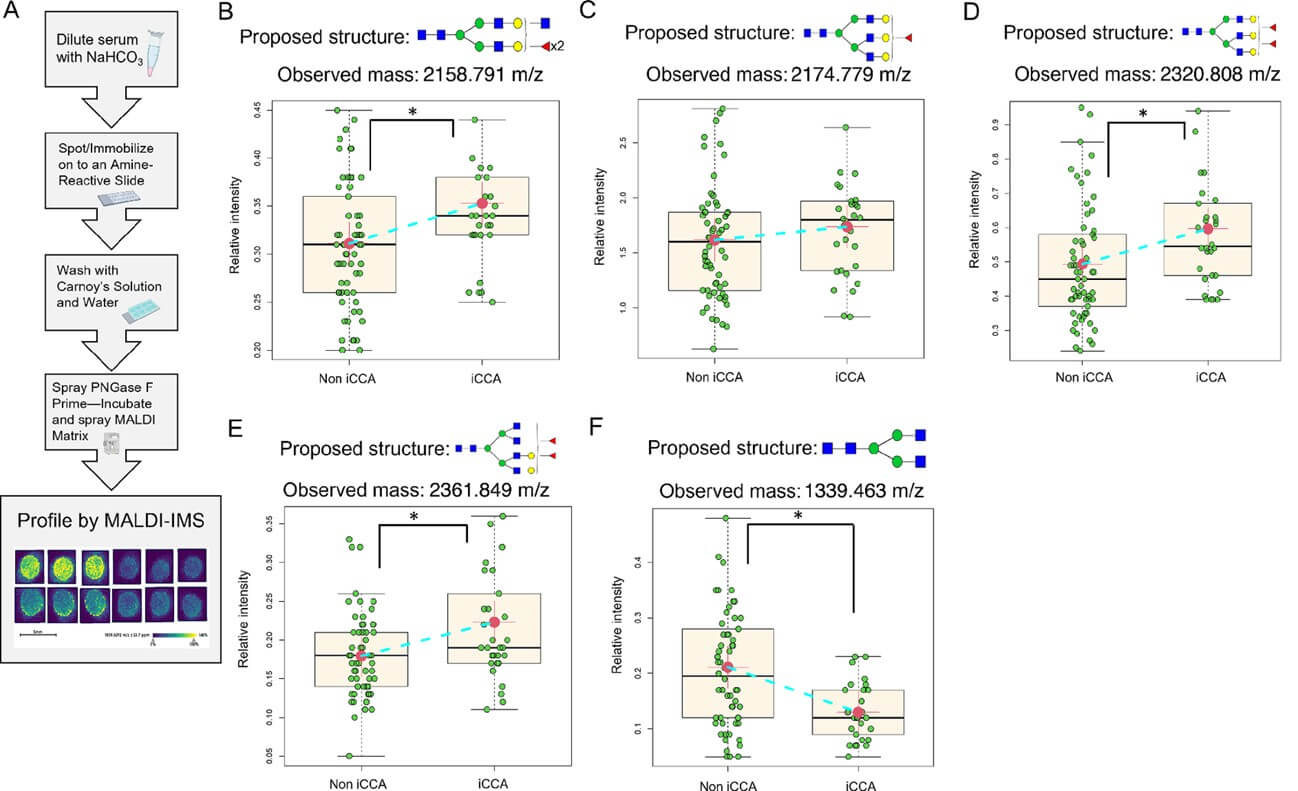 Fig.2 N-glycosylation analysis process and results in serum.2
Fig.2 N-glycosylation analysis process and results in serum.2
FAQs
Q1: How does your glycoproteomics service handle the complexity of serum samples?
A1: We use advanced enrichment techniques, such as lectin affinity chromatography and reverse glycoblotting, to specifically isolate the glycopeptides of interest. This approach effectively reduces sample complexity, allowing our high-resolution mass spectrometers to detect and quantify even low-abundance biomarkers that might otherwise be masked.
Q2: What is the main advantage of using a combined glycomics and proteomics approach?
A2: Our integrated strategy provides a more holistic view of your biological system. You can determine if observed changes in glycan structures are due to a change in protein abundance or an alteration in the glycosylation state itself. This dual-analysis approach provides a deeper and more accurate understanding of disease mechanisms.
Q3: How long does a typical project take, and what is your required starting material?
A3: The typical timeframe is 8-12 weeks, depending on the scope of the project. To begin, we need high-quality biological samples such as serum or tissue lysates. We recommend contacting us early in your planning to ensure optimal sample preparation and project design.
Customer Review
High-Quality Results
"Using Creative Biolabs's glycoproteomics quantitative analysis services in our research has significantly improved the confidence in our data. The in-depth analysis of glycosylation sites and the quantitative accuracy allowed us to confirm our findings in a diabetic mouse model, which was crucial for a recent publication." - Dr. R. Tay***r.
Streamlined Workflow
"We previously spent months manually processing glycoproteomics data. Creative Biolabs' integrated platform, which handles both glycomics and proteomics from a single sample, reduced our processing time by over 40%. The consistency between runs was exceptional, providing a clear advantage over our previous methods." - Ms. L. Tho***s.
References
-
Wang, Ji, et al. "An integrative strategy for quantitative analysis of the N-glycoproteome in complex biological samples." Proteome science 12.1 (2014): 4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-5956-12-4. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 2.0, without modification.
-
Ochoa-Rios, Shaaron, et al. "Analysis of N-linked glycan alterations in tissue and serum reveals promising biomarkers for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma." Cancer research communications 3.3 (2023): 383-394. https://doi.org/10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-22-0422. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY, without modification.
Related Services
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Strategies for glycoproteomics research.1
Fig.1 Strategies for glycoproteomics research.1

 Fig.2 N-glycosylation analysis process and results in serum.2
Fig.2 N-glycosylation analysis process and results in serum.2

