Importance of Glycosylation Analysis for Disease Research
Protein glycosylation is a fundamental post-translational modification that involves the attachment of diverse carbohydrate structures to proteins. These intricate glycoforms are not merely structural components; they actively participate in critical biological processes such as molecular recognition, cell signaling, and immune responses. As a dynamic and highly sensitive modification, glycosylation acts as a real-time indicator of physiological status, reflecting genetic, epigenetic, and environmental influences. Aberrant glycosylation is a recognized hallmark across a wide spectrum of diseases, underscoring its immense potential as a source of novel and highly specific biomarkers for diagnostics, prognostics, and therapeutic targets.
Glycosylation analysis provides a unique molecular perspective on disease. It helps unravel the complex interplay between genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and cellular responses, leading to a deeper understanding of disease mechanisms and the identification of highly specific biomarkers. This is critical for advancing precision medicine. Creative Biolabs' glycosylation analysis services for disease research help clients accelerate disease research, obtain high-quality glycan profiles, and unlock novel therapeutic targets through advanced mass spectrometry-based glycomics, comprehensive data analysis, and sophisticated statistical tools. We provide comprehensive solutions tailored to your specific research needs.
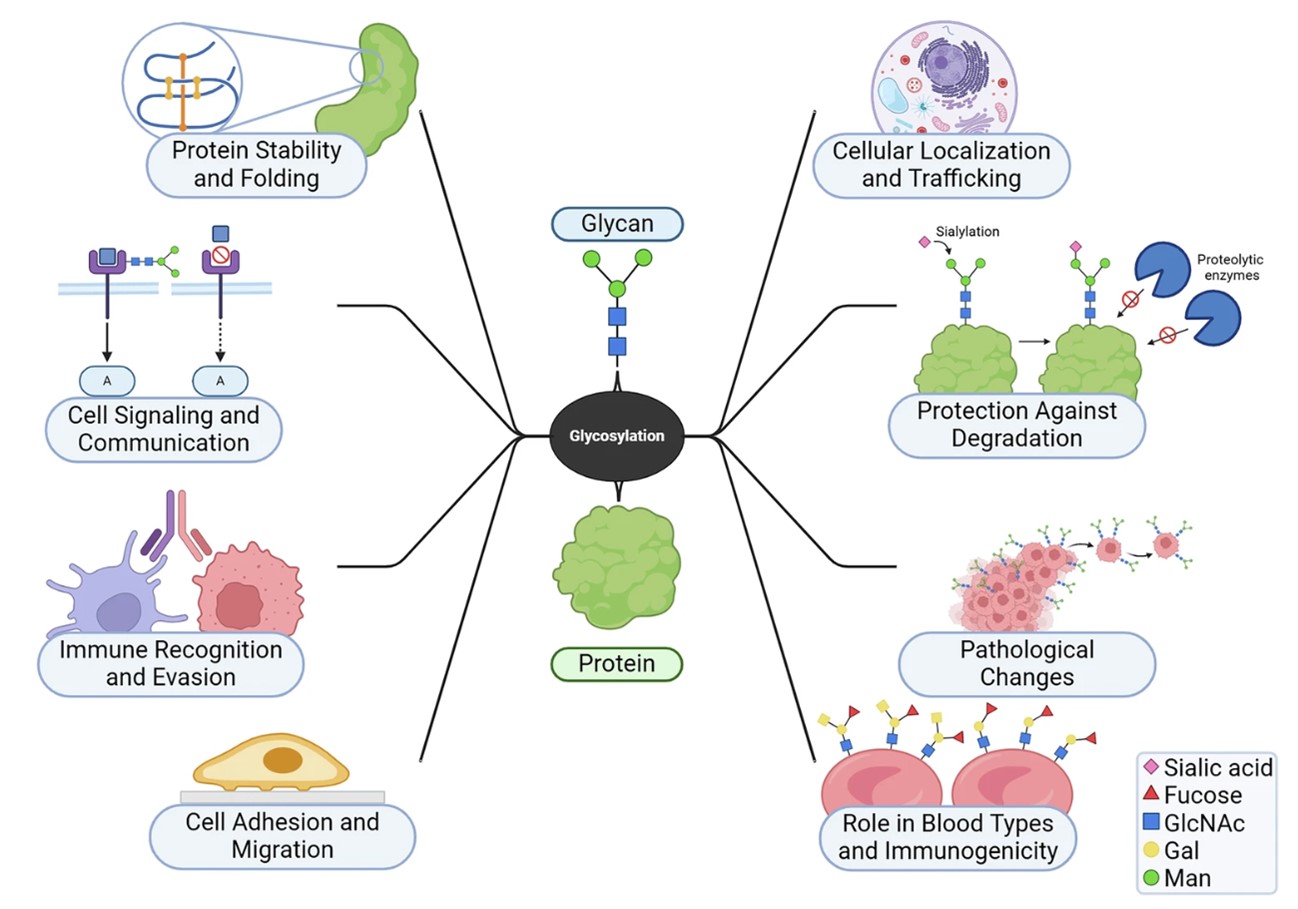 Fig.1 Glycosylation in cells and its relationship to health.1,3
Fig.1 Glycosylation in cells and its relationship to health.1,3
Unlocking Glycosylation Insights from Sample to Solution
Our streamlined, robust workflow is designed for clarity, efficiency, and deep biological insight, ensuring you receive actionable data from your complex samples.
Upon receipt, samples undergo rigorous quality assessment to ensure integrity and suitability for downstream analysis.
-
Glycoprotein/Glycan Isolation & Preparation
This involves tailored enrichment and release strategies based on the type of glycosylation (N-linked, O-linked) and specific project requirements. Enzymatic digestion (e.g., using PNGase F for N-glycans) or chemical release is performed to detach glycans from proteins. Crucially, labile sialic acid residues may undergo specific chemical derivatization (e.g., amidation, esterification, stable-isotope-based approaches) to ensure their stability and enable linkage-specific analysis, which is vital for distinguishing between α−2,6− and α-2,3-linked sialic acids relevant in disease pathogenesis. Subsequent purification via methods like lectin affinity chromatography or hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) ensures optimal recovery and removal of interfering compounds.
-
Mass Spectrometry (MS) Analysis
Our state-of-the-art MS platforms perform high-resolution qualitative and quantitative glycan profiling, including LC-MS, MALDI-MS, GC-MS, and imaging mass spectrometry.
-
Data Processing & Interpretation
Raw MS data are processed using specialized bioinformatics software for accurate glycan identification, annotation, and precise quantification. This step transforms complex spectral data into structured glycan profiles. Advanced statistical tools are applied to the processed glycan data.
-
Biological Insights & Reporting
The statistical findings are interpreted within a broader biological context. This involves correlating glycan alterations with disease phenotypes, proposing mechanistic insights, and identifying compelling biomarker candidates for further validation. Our final reports provide a clear, comprehensive summary of results and interpretations.
Types of our Glycosylation Analysis Services for Disease Research
At Creative Biolabs, we offer a comprehensive suite of glycosylation analysis services tailored for disease research, focusing on critical conditions where glycosylation plays a significant role. These services are designed to address the unique challenges of specific disease contexts and provide actionable insights.
02BC related Glycosylation Analysis Service
Main Changes: Increased high-mannose and core-fucosylated glycans, decreased bisected and sialylated glycans in tissues; specific IgG N-glycan structures altered even in early stages.
03CRC related Glycosylation Analysis Service
Main Changes: As individuals age, the fucosylation and branching patterns of their transferrin glycans undergo noticeable shifts. Concurrently, there's a significant increase in the levels of both sialylation and fucosylation within these glycans.
06Lung Disease related Glycosylation Analysis Service
Main Changes: In inflammatory lung diseases, there's often a decrease in sulfation and fucosylation, with a concomitant increase in sialylation of mucins, and shortening of overall glycan chain length.
10IBD related Glycosylation Analysis Service
Main Changes: There's a greater prevalence of larger glycans, accompanied by a reduction in high-mannose structures. Additionally, both fucosylation and galactosylation levels are diminished.
Key Advantages

Unparalleled Scientific Expertise
With over two decades of specialized experience, our team of expert biologists and analytical chemists possesses deep knowledge of glycosylation biology and advanced analytical methodologies.

State-of-the-Art Technology
We operate a comprehensive suite of cutting-edge glycomics platforms designed for sensitivity, throughput, and accuracy.

Sophisticated Statistical Analysis
Our advanced statistical tools are specifically adapted to interpret large and complex glycomics datasets, providing deeper biological understanding.

Robust and Reproducible Results
Our stringent protocols, validated methods, and rigorous quality control ensure high-quality, reliable, and reproducible data.

Discovery of Novel Biomarkers
Our targeted and comprehensive approach helps identify novel diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive glycan biomarkers across a wide range of age-related and other complex diseases.

Actionable Insights for Lead Generation
We excel at translating complex glycan data into clear, concise, and actionable insights that empower our clients to make informed decisions for drug development, diagnostic assay design, and therapeutic intervention strategies.
Related Services
Creative Biolabs offers a suite of complementary services designed to provide a holistic understanding of biological systems and accelerate your research and development initiatives.
-
Proteomics Services: Comprehensive protein identification, quantification, and post-translational modification analysis, providing a broader context for glycosylation changes.
-
Metabolomics Services: Small molecule profiling and metabolic pathway analysis to understand the metabolic underpinnings of altered glycosylation.
-
Antibody Engineering and Characterization Services: Complementary to our glycosylation analysis, this service supports the design, development, and comprehensive characterization of therapeutic antibodies.
-
Biomarker Discovery: Integrated solutions for identifying, validating, and developing novel biomarkers for various disease indications.
At Creative Biolabs, we are committed to being your trusted partner in advancing glycoscience for disease research. Our unparalleled expertise, state-of-the-art technology, and dedication to delivering actionable insights make us the ideal choice for your next project. We are confident that our comprehensive glycosylation analysis services will provide the critical data and understanding you need to accelerate your discoveries and pave the way for innovative diagnostic and therapeutic solutions. Please contact us to inquire about more content.
Published Data
This study investigated whether analyzing serum N-glycan profiles could provide distinct indicators for diagnosing pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). The methodology involved a systematic approach, mirroring the workflow illustrated in the study's procedural diagram. Initially, serum samples were carefully collected from individuals with PDAC and age- and sex-matched healthy controls. These samples were then meticulously organized into plates, ensuring proper distribution for quality control. A sophisticated, automated process was followed, where N-glycans were released from proteins, chemically modified to differentiate between specific sialic acid linkages, and subsequently purified. These prepared glycans then underwent ultra-high-resolution mass spectrometry to acquire their detailed profiles. The vast amount of resulting data was rigorously processed, annotated, and quality-controlled. Crucially, the analysis moved beyond individual glycan structures to calculate "derived traits," which represented broader glycosylation features like branching, fucosylation, and sialylation. Statistical analyses, including logistic regression and meta-analysis across discovery and independent validation cohorts, were performed to identify consistent differences in these traits between patients and controls. Finally, the diagnostic utility of these identified glycosylation patterns was evaluated using Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis, assessing their ability to accurately distinguish PDAC cases from healthy individuals. The study successfully identified significant glycosylation alterations, such as increased branching and a shift in sialylation types, which allowed for the classification of PDAC patients, laying the groundwork for a potential new diagnostic tool.
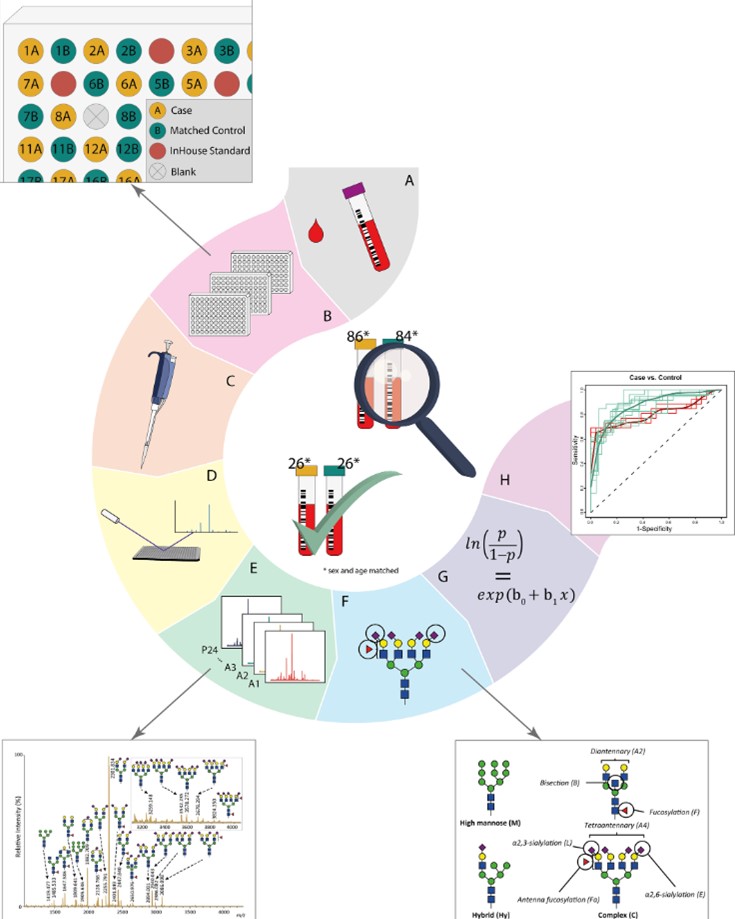 Fig.2 Workflow for N-glycosylation profiling in pancreatic cancer samples.2,3
Fig.2 Workflow for N-glycosylation profiling in pancreatic cancer samples.2,3
FAQs
Q1: What types of samples do you accept for glycosylation analysis?
A1: We accept a wide range of biological samples, including serum, plasma, urine, tissue biopsies (fresh or FFPE), and cell cultures. Our team provides expert guidance on optimal sample collection and preparation protocols to ensure the highest quality results for your research.
Q2: How does Creative Biolabs' glycosylation analysis service differentiate from other glycomics providers?
A2: Our distinct advantage lies in our comprehensive, integrated approach. We combine cutting-edge mass spectrometry platforms (including advanced LC-MS, MALDI-MS, and IM-MS), sophisticated statistical analysis tools, and deep biological expertise. This allows us to provide not just raw data but actionable biological insights and validated biomarker candidates, focusing critically on site-specific and quantitative analysis, which is essential for understanding true disease mechanisms.
Q3: Can your services help identify biomarkers for early disease detection?
A3: Absolutely. Aberrant glycosylation often occurs in the very early stages of disease progression, sometimes even before clinical symptoms appear. Our sensitive and specific analysis methods are meticulously designed to detect these subtle, early changes, offering significant potential for the discovery of novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for a wide array of diseases.
Customer Review
Robust MS Workflow and Detailed Reports
"The clarity and depth of the site-specific glycan data from Creative Biolabs's services significantly improved our understanding of protein functions in our autoimmune disease model. Their robust MS workflow and detailed reports expedited our research by months, something we couldn't achieve with our in-house capabilities." - Mr. J. Wil***ms.
Professional Insights and Analysis
"Creative Biolabs's expertise in analyzing complex O-glycan profiles from tissue samples for our lung inflammation study was a game-changer. The insights into sulfation and sialylation changes were crucial, and their statistical validation truly made the data actionable for identifying novel inflammatory markers. Their team was incredibly collaborative." - Dr. A. Sm***h.
References
-
Pienkowski, Tomasz, et al. "Leveraging glycosylation for early detection and therapeutic target discovery in pancreatic cancer." Cell Death & Disease 16.1 (2025): 227. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-025-07517-z.
-
Vreeker, Gerda CM, et al. "Serum N-glycome analysis reveals pancreatic cancer disease signatures." Cancer Medicine 9.22 (2020): 8519-8529. DOI: 10.1002/cam4.3439.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Services
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Glycosylation in cells and its relationship to health.1,3
Fig.1 Glycosylation in cells and its relationship to health.1,3
 Fig.2 Workflow for N-glycosylation profiling in pancreatic cancer samples.2,3
Fig.2 Workflow for N-glycosylation profiling in pancreatic cancer samples.2,3

