Introduction of Modification Proteomics
Proteins, the workhorses of the cell, undergo a vast array of post-translational modifications (PTMs) after their synthesis, dramatically expanding their functional diversity. These modifications are crucial for regulating nearly all biological processes. Common PTMs include:
The addition of a phosphate group, primarily to serine, threonine, or tyrosine residues. It is the most ubiquitous PTM, acting as a molecular switch to regulate enzyme activity, protein-protein interactions, and signal transduction pathways.
Acetylation
The addition of an acetyl group (CH3CO) to the ε-amino group of a lysine residue. Acetylation is a highly dynamic and reversible process, impacting diverse functions ranging from gene expression (where histone acetylation influences chromatin structure) to metabolism (regulating enzyme activity, as seen with aldolase), protein stability, protein-protein interactions, and even bacterial antibiotic resistance.
The covalent attachment of ubiquitin, a small regulatory protein, to a lysine residue. Ubiquitination can target proteins for proteasomal degradation, regulate protein localization, mediate protein-protein interactions, and play critical roles in the DNA damage response.
Methylation
The addition of a methyl group, commonly to lysine or arginine residues. It can regulate gene expression (histone methylation), protein-protein interactions, and signal transduction.
Glycosylation
The attachment of carbohydrate moieties to proteins. It plays vital roles in protein folding, cell-cell recognition, immune response, and cell surface receptor functions.
Unlocking Cellular Regulation: Precision Proteomics for Deeper Biological Insights
Are you currently facing challenges in understanding complex disease mechanisms, identifying novel drug targets, or deciphering cellular adaptive responses? Our acetylation modification proteomic quantitative analysis service helps you unravel the intricate regulatory roles of protein acetylation, providing unparalleled insights into protein functions, cellular pathways, and disease states. We achieve this through cutting-edge mass spectrometry, advanced bioinformatics, and a comprehensive multi-omics integration approach.
-
Sample Preparation: Proteins are extracted from biological samples (cells, tissues, biofluids) and then enzymatically digested into peptides. Deacetylase inhibitors are crucial at this stage to preserve the acetylation marks.
-
Affinity Enrichment: The core principle involves using highly specific antibodies (e.g., anti-acetyllysine antibodies) that selectively bind to and capture peptides containing acetylated lysine residues. This enrichment step significantly reduces the complexity of the sample, allowing for deeper detection of less abundant acetylated peptides.
-
Quantitative Labeling: For quantitative comparisons between different conditions (e.g., disease vs. healthy, treated vs. untreated), techniques like Tandem Mass Tag (TMT) labeling are employed. TMT reagents covalently attach to peptides, introducing unique isotopic tags that allow multiple samples to be pooled and analyzed simultaneously in a single mass spectrometry run. This minimizes technical variability and enables precise relative quantification. Alternatively, label-free quantitative proteomics can be used, which quantifies peptides based on their ion intensities without isotopic labels.
-
High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS): The enriched and labeled peptides are separated by liquid chromatography (LC) and then introduced into a high-resolution mass spectrometer. The mass spectrometer first measures the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of the intact peptides (MS1 scan). Then, it fragments these peptides (MS/MS or MS2 scan) and measures the m/z of the resulting fragments.
-
Data Analysis & Bioinformatics: The fragmentation patterns allow for the identification of peptide sequences and the precise localization of the acetylation sites. For quantitative data, the relative intensities of the TMT reporter ions (or label-free intensities) are used to determine the fold change of acetylation levels between samples. Advanced bioinformatics tools are then used for statistical analysis, functional annotation (GO, KEGG pathways), and protein-protein interaction network analysis.
Providing an acetylation modification proteomic quantitative analysis service requires a highly specialized workflow, integrating advanced mass spectrometry with sophisticated bioinformatics. Key elements include:
-
Rigorous sample quality control: Ensuring the integrity and stability of acetylation marks.
-
Optimized protein extraction and digestion: Maximizing protein yield and generating suitable peptides.
-
High-specificity acetyl-peptide enrichment: Using cutting-edge antibody-based methods, often combined with fractionation to enhance coverage.
-
Advanced quantitative MS: Employing TMT-labeling or label-free approaches on high-resolution instruments.
-
Comprehensive bioinformatics pipeline: For data processing, peptide/protein identification, PTM localization, quantification, statistical analysis, and functional annotation.
-
Biological interpretation and reporting: Translating raw data into meaningful biological insights and providing a detailed, actionable report.
Why Choose Us?

Unparalleled Expertise
With over years in the field, our biology specialists possess profound scientific knowledge in post-translational modifications, cellular signaling, and disease mechanisms, ensuring intelligent experimental design and insightful data interpretation.

Advanced Glycoproteomics Platforms
We leverage the latest generation of high-resolution mass spectrometers and quantitative proteomic techniques to achieve industry-leading depth and accuracy in acetylome profiling, identifying thousands of acetylation sites.

Proprietary Enrichment Strategies
Our optimized acetyl-peptide enrichment protocols, including advanced fractionation methods, maximize the detection of even low-abundance acetylated proteins.

Multi-Omics Integration Capability
We don't just provide acetylation data; we offer the capability to integrate it with your transcriptomics, genomics, and other proteomic data for a truly holistic understanding of complex biological processes and disease states.

Functional Insights into PTMs
Our expertise extends to understanding the functional consequences of acetylation, including influencing chromatin dynamics or mediating non-enzymatic regulation.

Comprehensive Data Interpretation
Beyond raw data, we provide in-depth bioinformatics analysis, pathway enrichment, and protein-protein interaction networks, translating complex proteomic data into actionable biological insights.
Applications of Acetylation Modification Proteomic Analysis
-
Disease research: Studying cancer, metabolic disorders, neurological diseases, inflammatory conditions (e.g., COPD), and infectious diseases to identify key acetylated proteins involved in pathogenesis.
-
Drug discovery and development: Identifying novel drug targets, understanding drug mechanisms of action, assessing off-target effects, and developing strategies to overcome drug resistance.
-
Basic biological research: Elucidating the roles of acetylation in fundamental processes like gene expression, metabolism, cell signaling, and development across various organisms.
-
Agricultural biotechnology: Investigating acetylation's role in plant stress responses, crop improvement, and pathogen resistance.
-
Biomarker development: Discovering and validating acetylation-based biomarkers for early diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring treatment efficacy.
Creative Biolabs' acetylation modification proteomic quantitative analysis service offers an unparalleled opportunity to delve into the intricate world of protein regulation. By providing a comprehensive, quantitative atlas of acetylation changes, we empower your research to uncover novel biomarkers, decipher disease mechanisms, and identify new therapeutic targets. Our expertise, cutting-edge technology, and commitment to integrated solutions ensure that your projects yield not just data but also transformative biological insights. Please contact us to unlock the full potential of protein acetylation in your research.
Published Data
This research paper presents a comprehensive quantitative proteomic analysis of lysine acetylation in gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), aiming to identify novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets for this often aggressive cancer. Recognizing the critical role of post-translational modifications, the study utilized TMT labeling combined with high-sensitivity MS to map the acetylome in GIST samples. The study's key findings, visually articulated in Figure 1, underscore the centrality of acetylation. Figure 1A illustrates, via Western blotting, that acetylation is a highly prevalent and significantly altered post-translational modification in GIST tissues when compared to other modifications investigated. A broad quantitative overview is provided in Figure 1B, detailing the identification of 2904 acetylation sites across 1319 proteins, with precise quantitative data available for 2548 sites on 1169 proteins. Figure 1C summarizes that acetylated sites on proteins exhibited upregulation and downregulation. This intricate pattern of changes is further visualized in the volcano plot of Figure 1D, where the red data points signify increased acetylation and blue points represent decreased levels, clearly highlighting the most significant alterations. Among these, Ki67 K1063Ac showed the most pronounced upregulation, and FCHSD2 K24Ac the greatest downregulation. These pioneering insights into the GIST acetylome pave the way for potential acetylation-targeted diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
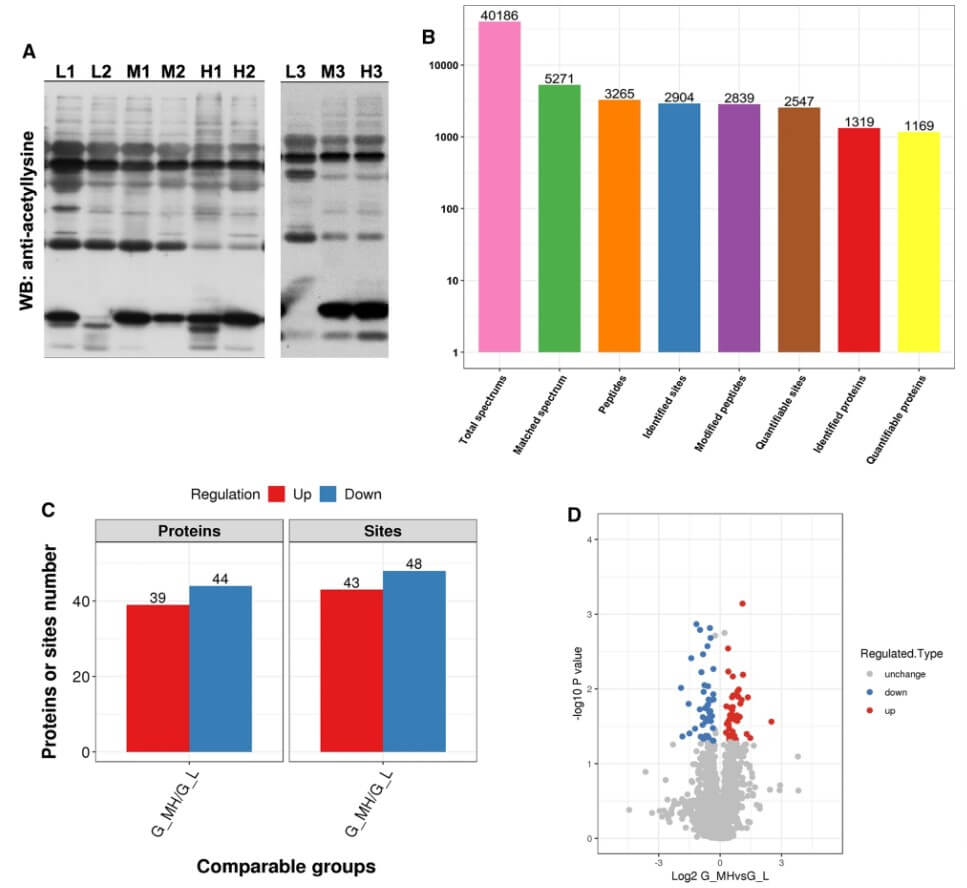 Fig.1 Proteomic analysis of aberrantly expressed lysine acetylation in GIST.1
Fig.1 Proteomic analysis of aberrantly expressed lysine acetylation in GIST.1
FAQs
Q1: How can Creative Biolabs' acetylation modification proteomic quantitative analysis service help me identify novel drug targets?
A1: By comprehensively mapping changes in protein acetylation, our service can pinpoint specific acetylated proteins or pathways that are aberrantly regulated in disease states. For instance, in cancer or metabolic disorders, identifying hyper- or hypo-acetylated enzymes or signaling proteins can reveal novel therapeutic intervention points. We provide the quantitative data and bioinformatics insights to guide your target validation efforts.
Q2: What kind of sample input is best for achieving the most comprehensive acetylation profile?
A2: For optimal results, we recommend using fresh-frozen tissue or cell pellets that have been rapidly quenched to preserve PTMs. Including appropriate deacetylase inhibitors during lysis is also critical. While we can work with various sample types, higher quality and quantity of starting material generally lead to deeper and more comprehensive acetylome coverage.
Q3: I'm concerned about the biological relevance of identified acetylation sites. How does Creative Biolabs ensure this?
A3: We employ rigorous statistical analysis and functional enrichment (GO, KEGG, PPI networks) to prioritize biologically significant changes. Furthermore, our expertise allows us to interpret findings in the context of known pathways and literature. For key findings, we can recommend and assist with downstream functional validation experiments, such as enzymatic assays or targeted Western blots, to confirm the biological impact of specific acetylation events.
Customer Review
Game-Changer for Metabolic Research
"Creative Biolabs' acetylation modification proteomic quantitative analysis service provided critical insights into the metabolic adaptations of our engineered cell lines. We were particularly impressed by their ability to identify acetylation events that directly modulated enzyme activity, a finding that completely reshaped our understanding of cellular energy flux. Their expertise in interpreting these complex PTM changes was a distinct advantage over other providers." - Mr. Y. Her***z.
Unprecedented Depth
"Using Creative Biolabs' acetylation modification proteomic quantitative analysis service in our research has significantly improved our understanding of how acetylation impacts DNA repair. The sheer number of sites identified, far exceeding our internal capabilities, enabled us to uncover novel regulatory nodes that we had previously been unable to see. The data quality was exceptional, and the bioinformatics support was invaluable." - Prof. K. Ki***g.
Reference
-
Wang, Bo, et al. "Quantitative proteomic analysis of aberrant expressed lysine acetylation in gastrointestinal stromal tumors." Clinical Proteomics 18.1 (2021): 16. DOI: 10.1186/s12014-021-09322-0. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Services
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on







 Fig.1 Proteomic analysis of aberrantly expressed lysine acetylation in GIST.1
Fig.1 Proteomic analysis of aberrantly expressed lysine acetylation in GIST.1

