Escherichia coli Glycoengineering Service for Human Protein Production
Escherichia coli for Human Protein Production
Escherichia coli (E. coli) holds a preeminent position in the biotechnology industry as the preferred microorganism for large-scale production of heterologous proteins owing to its well-characterized genome, ease of genetic manipulations, cost-effectiveness, high yield of protein products, and easy scale-up process. As E. coli inherently lacks native protein glycosylation pathways, bottom-up glycoengineering of synthetic pathways emerges as a pivotal method for generating customized glycan structures that can be site-specifically attached to target proteins. The successful transfer of an N-glycosylation pathway from Campylobacter jejuni (C. jejuni) to E. coli represents a crucial milestone in this engineering endeavor. As the glycoengineering toolbox has expanded, the field of bacterial glycoengineering has transitioned from its initial focus on transferring glycosylation processes to E. coli towards the development of human-like recombinant glycoproteins.
E. coli Glycoengineering Services at Creative Biolabs
Drawing on insights from various studies and a deep understanding of bacterial glycosylation processes, Creative Biolabs has made significant efforts to utilize natural biological pathways and engineered synthetic pathways in E. coli for the production of complex glycans and their conjugation to proteins. We have already successfully established versatile platforms for N-linked Glycoengineering in Bacteria and O-linked Glycoengineering in Bacteria, which have been effectively harnessed in E. coli, as an expression host for the production of humanized glycoproteins. In addition, we have explored several strategies to further enhance the glycosylation efficiency and achieve industrially relevant production levels of glycoproteins from E. coli.
-
Optimizing the periplasmic glycosylation system from C. jejuni and removing proteins from competing pathways.
-
Guiding correctly folded proteins to the periplasmic space by modifying the signal peptides.
-
Increasing the production of precursor molecules and minimizing the metabolic burden on the E. coli host.
Applications of Glycoengineered E. coli System
-
Production of therapeutic glycoproteins like antibody fragments (scFvs)
-
Production of glycoconjugate vaccines
-
Research in biopharmaceutics
-
Research in the glycosylation process
Highlights of Our Services
-
Optional strategies for E. coli glycoengineering
-
Cutting-edge technologies for genetic modulation
-
Higher glycosylation efficiency of glycoprotein products
-
High-yield and low-cost production of glycoprotein products
-
Customized solutions for specific needs
Published data
There are many significant advantages to producing N-linked glycoproteins in genetically engineered Escherichia coli, but there are still challenges in building stable and cost-effective microbial cell factories. This study developed an E. coli-based glycoengineering platform. By replacing multiple genes in the E. coli strain and optimizing the promoter to regulate transcription levels, humanized N-glycosylated proteins were successfully obtained. This study laid the foundation for the production of humanized N-glycoproteins and promoted industrial-scale applications. In addition, this technology platform could help the development of a variety of glycoprotein drugs.
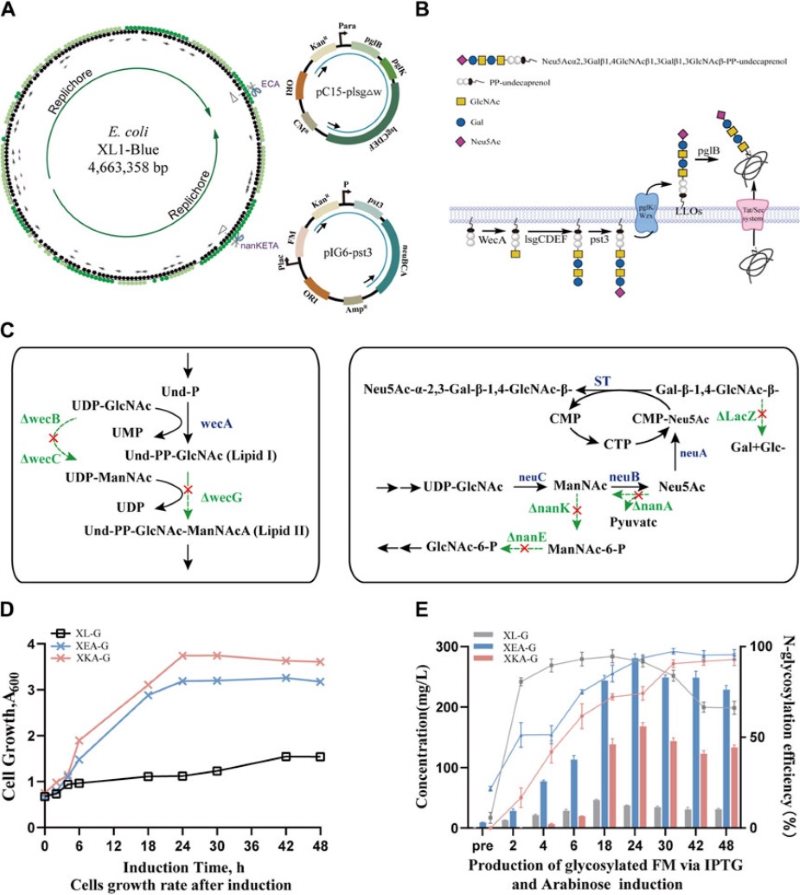 Fig.1 E. coli-based construction and production of human-like glycosylated proteins.1
Fig.1 E. coli-based construction and production of human-like glycosylated proteins.1
As pioneers in the field of glycoengineering, the scientists at Creative Biolabs have amassed a wealth of experience in E. coli glycoengineering for the production of humanized proteins with high yields, high quality, and custom-tailored to suit a wide range of applications. If you have any glycoengineering requirements, please don't hesitate to contact us for more information.
Reference
-
Bao, Zixin, et al. "Construction of an Escherichia coli chassis for efficient biosynthesis of human-like N-linked glycoproteins." Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 12 (2024): 1370685. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.

 Fig.1 E. coli-based construction and production of human-like glycosylated proteins.1
Fig.1 E. coli-based construction and production of human-like glycosylated proteins.1

