Liposomes are a nanoscale drug delivery system with a lipid bilayer that encapsulates active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). This system offers several benefits, such as preserving the activity of APIs, enabling precise drug release, enhancing therapeutic efficacy, reducing the risk of adverse reactions, improving drug stability, and prolonging the half-life. With extensive experience in liposome technology, Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive professional characterizations, including encapsulation efficiency.
The aqueous core and the bilayer interstice of liposomes are suitable for encapsulating hydrophilic and lipophilic substances, respectively. Encapsulation efficiency (EE) is a key indicator for assessing the preparation process and quality of liposomes, representing the percentage of the API encapsulated within the liposomes relative to the total drug input. This metric reflects API encapsulation, providing a basis for process optimization. A high EE not only maximizes therapeutic efficacy but also minimizes the loss of valuable API, thereby enhancing the cost-effectiveness of the formulations.
The key to determining EE is to first separate the encapsulated API from the unencapsulated free API, then use quantitative methods to detect the concentration of the encapsulated API or free API, and subsequently calculate the EE based on the formula.
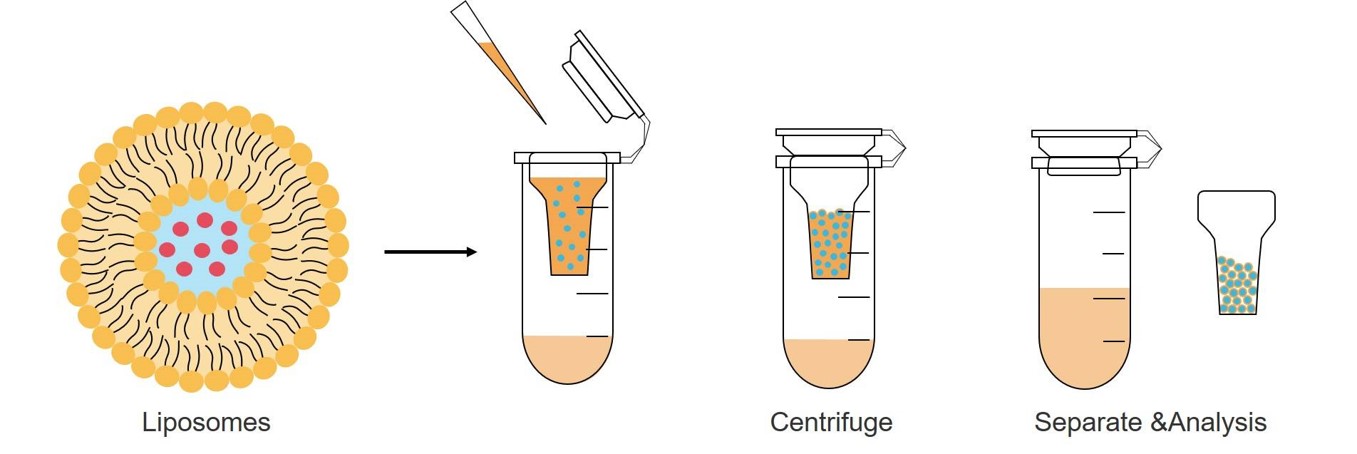 Fig.1 Drug separation for EE based on ultrafiltration centrifugation.
Fig.1 Drug separation for EE based on ultrafiltration centrifugation.
The encapsulated API can be assessed using direct or indirect methods. The direct approach measures API after liposome disruption, while the indirect approach, which is more commonly employed as it preserves liposome integrity, determines the encapsulated API by measuring the free API concentration and subtracting it from the total drug input.
The methods for measuring API concentration are largely determined by the characteristics of the API and can encompass UV-Vis and fluorescence spectroscopy, as well as enzyme or protein assays. For more precise quantification, advanced analytical techniques such as liquid chromatography (HPLC, etc), and mass spectrometry coupled with chromatography (LC-MS, GC-MS), and 1HNMR can be employed.
Once the quantity of encapsulated API has been established through direct or indirect methods, the EE can be computed with the formula:

This formula allows for the precise calculation of the percentage of API that has been successfully encapsulated, providing a clear metric for assessing the effectiveness of the encapsulation process.
At Creative Biolabs, we stand at the forefront of liposome research and development, armed with an in-depth understanding of EE and its pivotal role in the success of liposome-based drug delivery systems. Our commitment to excellence extends to offering comprehensive support services that encompass both pure EE testing and formula optimization based on EE. We invite you to contact us to discuss your specific needs regarding EE testing and explore how we can assist you in enhancing the performance of your liposomal formulations.
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry