Liposomes carry charges—negative, positive, or neutral—depending on their lipid head groups, lipid composition, and ligands. The surface charge influences liposome stability, circulation times, clearance, tissue distribution, interactions with cells, and biocompatibility. Creative Biolabs has been committed to developing and testing high-quality liposomes, and is fully capable of addressing your questions about liposome surface charges and providing personalized testing services for you.
The charge density on liposome surfaces and the affinity of various ions for lipid vesicles can be assessed through the measurement of Zeta potential. Zeta potential is defined as the average electrostatic potential at the shear plane of the hydrodynamic flow, typically located 0.2 nm from the surface, and is significantly influenced by factors such as pH, temperature, conductivity (ionic strength), and solvent. The zeta potential reflects the magnitude of repulsive or attractive forces between particles, and for stability, the repulsive forces must be greater than the attractive forces.
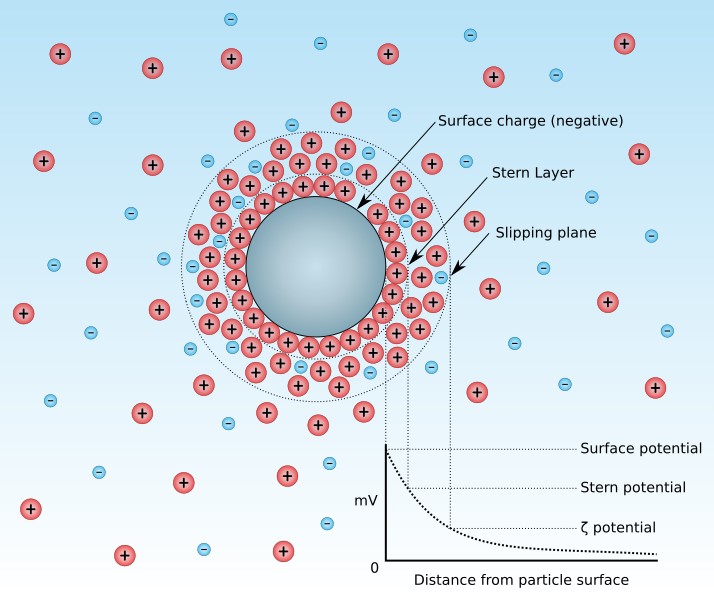 Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Zeta potential measurements serve as a pivotal tool in assessing the stability of liposome. Liposomes exhibiting low zeta potentials or neutral charge profiles are predisposed to aggregation over extended periods, primarily because of the lack of repulsive forces. Conversely, liposomes characterized by substantial negative or positive zeta potentials engender robust repulsive forces within the surrounding medium. These forces actively counterbalance the attractive forces, thereby mitigating the propensity for aggregation and enhancing the colloidal stability of liposome. This understanding is fundamental in the design and optimization of liposomal drug delivery systems, where maintaining the integrity and uniformity of the liposomal population is paramount for therapeutic efficacy and safety.
| Zeta Potential (mV) | Stability |
|---|---|
| 0 to |±5| | Rapid coagulation and aggregation |
| |±10| to |±30| | Poor stability |
| |±30| to |±40| | Moderate stability |
| |±40| to |±60| | Good stability |
| >|±60| | Excellent stability |
The Zeta potential of liposomes significantly influences their distribution and clearance rate within the body. Liposomes with a negative charge are more readily cleared by Kupffer cells in the liver, while those with a positive charge may accumulate in other tissues. Additionally, liposomes are susceptible to adsorption by negatively charged nonspecific proteins in the bloodstream, which can lead to recognition and clearance by macrophages. Reducing the surface charge of liposomes can prolong their circulation time, thereby extending their half-life.
To enhance drug delivery efficiency, the Zeta potential of liposomes can be precisely regulated, thereby enhancing the interaction between liposomes and nucleic acids as well as target cells. During the gene delivery, cationic liposomes carrying a positive charge are capable of binding with nucleic acids that possess a negative charge via electrostatic forces. This interaction enables the effective transportation and subsequent transfection of the nucleic acids. Regarding cellular uptake, charged liposomes (both positively and negatively charged) typically aggregate and adhere to the cell membrane more rapidly than neutral liposomes, subsequently binding tightly with cells and being internalized. This is because positively charged liposomes can effectively bind to the negatively charged cell membrane through electrostatic adsorption, while negatively charged liposomes can interact with non-specific receptors such as type B scavenger receptors, making them more susceptible to cellular phagocytosis.
The Zeta potential is a crucial parameter for evaluating the quality of liposomal formulations. During the research and development phase, measuring the Zeta potential can provide valuable guidance for formula optimization. When alterations occur in the Zeta potential, modifications to the liposome's constituents and surface characteristics can be implemented, thereby enhancing their overall efficacy. Moreover, by detecting the Zeta potential, one can effectively determine whether the preparation process of liposomes is scientifically sound and whether the stability of the final product meets the established standards.
The zeta potential is a function of the adsorbed layer at the interface, the surface charge of liposomes, and the composition and properties of the liposome medium. Measurement isn't feasible directly, but it can be derived from theoretical models and experimentally assessed electrophoretic mobility. Electrophoretic light scattering (ELS), electroacoustic methods, and phase analysis light scattering (PALS) are the main techniques currently widely used for Zeta potential determination. ELS helps to avoid multiple scattering effects, with high resolution and reliable results, making it the most commonly used method at present. Electroacoustic methods induce acoustic waves in liposome suspensions and analyze the generated signals to determine the potential, which is advantageous for measuring the potential in opaque or high-concentration samples. PALS, an improved technique of ELS, has higher sensitivity and is particularly useful for studying the potential of liposomes in complex biological environments.
Zeta potential measurement serves not only as a crucial reference for liposome research, development, and production, but also ensures enhanced product quality and extended shelf life. It serves as a key pillar for our company's ongoing innovation and enhancement in the liposome field. At Creative Biolabs, we offer a comprehensive Zeta potential characterization service that supports liposomal product development from the initial stages to the final product. Contact us today to discuss your project needs and discover how our services can help you achieve superior product quality and extended shelf life.
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry