Phase transition behavior is crucial when considering liposomes for drug delivery. As the bilayer's fluidity increases, its permeability to encapsulated hydrophilic substances also rises, which is a critical factor in evaluating liposomal stability (such as fusion, aggregation, etc.) and the drug release rate in vivo. With extensive development experience in the field of lipid-based drug delivery system, Creative Biolabs is well-equipped to address your queries regarding liposomal phase transition behavior.
Lipid bilayer phase transition temperature (Tc) is crucial for liposome formation, storage stability, and drug release in vivo. It dictates the bilayer's fluidity and permeability (i.e., its ability to allow substances to pass through), which are influenced by the type of polar head groups, the length and saturation of fatty acid chains, the ionic strength of the medium, and associated charges. Phospholipids with longer, fully saturated hydrocarbon chains form more rigid bilayers with lower permeability due to increased inter-chain interactions, leading to a higher Tc.
When dispersed in water or aqueous solutions, lipid bilayers primarily adopt three lamellar phases: the crystal phase (LC), the gel phase (Lβ), and the liquid-crystal phase (Lα). In the LC phase, the hydrocarbon chains are fully extended in an all-trans conformation, with the polar head groups relatively immobile. The Lβ phase features acyl chains predominantly in an all-trans conformation, but with slightly more mobility than the LC phase. The Lα phase is the most disordered, with rapid movement of individual molecules. Below Tc, bilayers shift to the ordered Lβ phase, and further cooling leads to the LC (subgel) phase. Conversely, when the temperature rises to the melting transition temperature (Tm), the bilayer shifts from the ordered Lβ to the disordered Lα. This increased fluidity and permeability reduce the barrier for drug molecules crossing the bilayer, enhancing drug release.
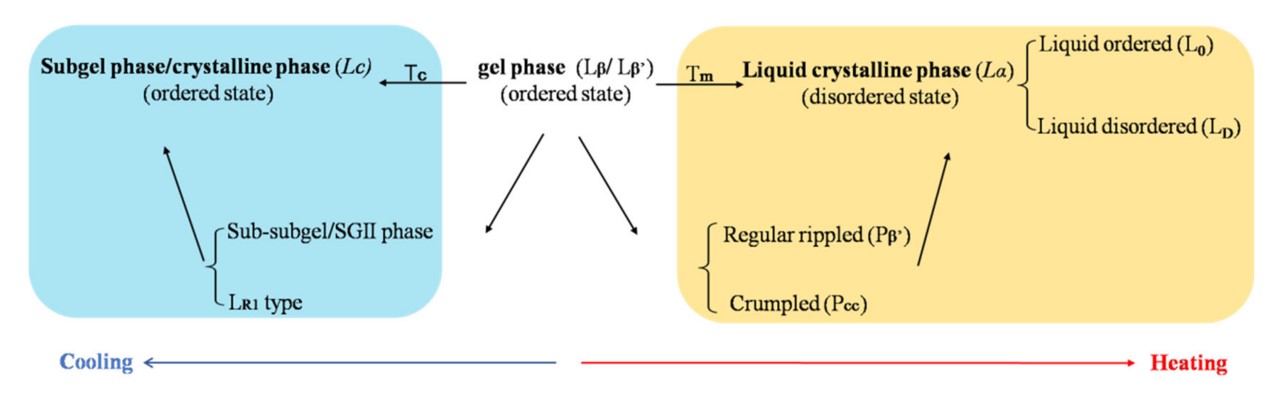 Fig.1 The phase transition of liposomal bilayer.1
Fig.1 The phase transition of liposomal bilayer.1
Understanding liposomal phase behavior allows tailoring of lipid compositions to modify stability and drug release characteristics. Creative Biolabs can employ saturated phospholipids with higher Tm, such as distearoylphosphatidylcholine (DSPC) and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), to create liposomes with increased rigidity and stability, thereby minimizing drug leakage. Additionally, we can utilize unsaturated phospholipids like soybean or egg phosphatidylcholine to develop liposomes with enhanced permeability and flexibility, catering to your diverse delivery requirements.
| Cat | Product Name | Lipid | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDLY-0123-LY11 | DMPC Liposomes | Saturated | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0123-LY87 | Hydro Egg PC Liposomes | Saturated | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0123-LY88 | Hydrogenated Soy PC Liposomes | Saturated | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0123-LY89 | Hydro Egg PC:Chol Liposomes | Saturated | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0123-LY90 | Hydrogenated Soy PC:Chol Liposomes | Saturated | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0123-LY104 | 12:0 PC (DLPC) Liposomes | Saturated | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0123-LY107 | 16:0 PC (DPPC) Liposomes | Saturated | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0123-LY112 | 22:0 PC (DBPC) Liposomes | Saturated | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0123-LY131 | 14:1 (Δ9-Cis) PC Liposomes | Unsaturated | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0123-LY132 | 14:1 (Δ9-Trans) PC Liposomes | Unsaturated | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0123-LY133 | 16:1 (Δ9-Cis) PC Liposomes | Unsaturated | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0123-LY134 | 16:1 (Δ9-Trans) PC Liposomes | Unsaturated | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0123-LY135 | 18:1 (Δ6-Cis) PC Liposomes | Unsaturated | Inquiry |
| LDLY-0123-LY136 | 18:1 (Δ9-Trans) PC Liposomes | Unsaturated | Inquiry |
| In addition to our standard products, we offer customized liposome development services and are available for one-on-one technical support upon request. | |||
DSC is the most commonly used method for studying phase transitions in phospholipids. By measuring the heat absorbed or released by a sample during heating, a temperature-heat flow curve is plotted, with the phase transition temperature corresponding to the endothermic peak on the curve. However, this method analyzes phase transitions based solely on thermal properties, disregarding conformational and elastic changes.
XRD involves exposing a sample to a collimated X-ray beam and detecting the intensity and type of scattering caused by the stacking of parallel sample atomic planes at specific angles, thereby identifying the type of crystalline phase, and orientation, and crystallinity degree.
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC), and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) are also methods used to detect the phase behavior of liposomes. FTIR complements DSC analysis of liposomal membranes, ITC can study the thermodynamics of drug-lipid interactions and related binding processes, and NMR provides important information about changes in the structure and dynamics of lipid molecules and bilayers.
Liposome phase behavior is influenced by numerous factors, and understanding it is essential for creating effective drug delivery systems. At Creative Biolabs, we specialize in unraveling these complexities and optimizing liposome performance. We invite you to contact us to leverage our expertise and support in enhancing your liposomal formulations for superior drug delivery outcomes.
Reference
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry