Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Rabies Treatment
Background Treatment Strategies Creative Biolabs’ Solutions Workflow Published Data Products Related Services Resources
Rabies presents a significant challenge in the medical research community due to its complex pathophysiology and the limitations of current treatment options. Creative Biolabs is committed to breaking through these barriers and providing innovative solutions for rabies treatment. Our advanced lipid-based drug delivery systems help you enhance therapeutic efficacy and vaccine delivery for rabies through innovative nanoparticle engineering and optimized payload encapsulation.
Background of Rabies
Rabies is a serious and often deadly viral disease that affects animals and can spread to humans, making it a big public health issue around the world. It's caused by the rabies virus (RABV), which is a type of neurotropic RNA virus in the Lyssavirus genus. It primarily transmits through direct contact with infected animals. Every year, it causes countless deaths, mostly in Asia and Africa, and sadly, children are often more affected. Right now, the main treatment is something called post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), which works really well but only if you get it quickly after being exposed. But in remote areas, it's hard to get, expensive, and there are a lot of logistical issues. Once the actual symptoms of rabies start to show, the disease gets worse very fast, and almost always leads to death because of the progressive encephalitis. Other serious issues that can come up include severe neurological problems, paralysis, and respiratory failure.
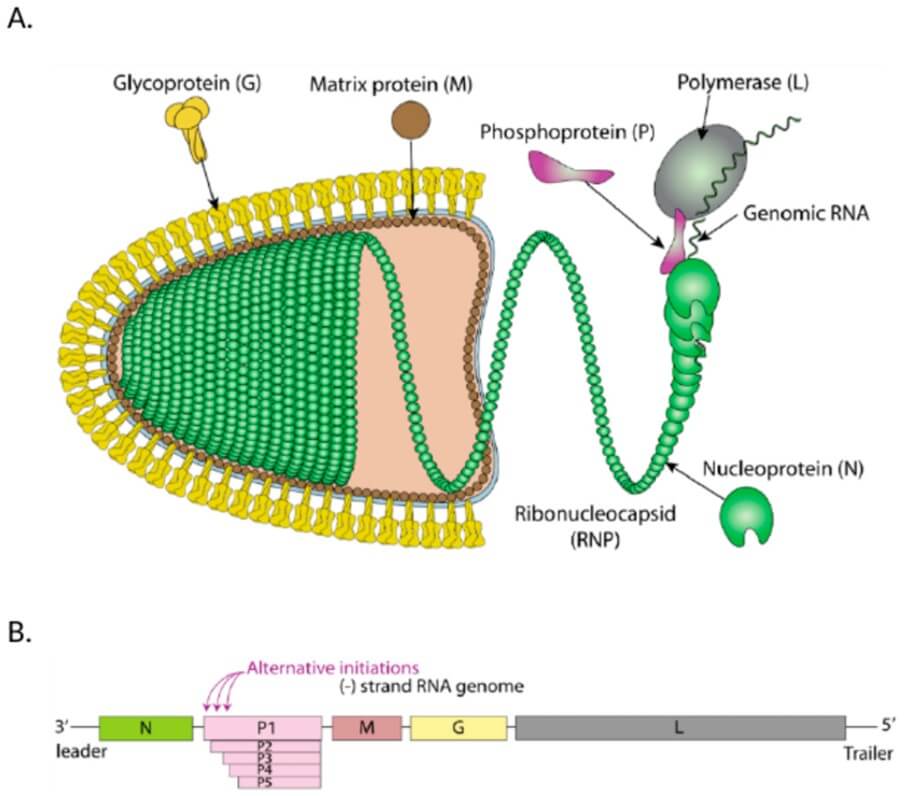 Fig. 1 RABV virion structure and genome.1,4
Fig. 1 RABV virion structure and genome.1,4
RABV
-
Bullet Shape: RABV has a characteristic bullet-like morphology, approximately 180 nm long and 75 nm wide.
-
Genome: It possesses a single-stranded, negative-sense RNA genome, which encodes five proteins: glycoprotein (G), matrix protein (M),nucleoprotein (N), phosphoprotein (P), and RNA polymerase (L).
-
Neurotropism: RABV is highly neurotropic, meaning it has a strong affinity for nerve tissue.
-
G protein: The G protein is vital for viral attachment and inducing neutralizing antibodies, making it a primary vaccine target.
-
Host Range: RABV can infect all mammals, including humans, dogs, bats, foxes, and raccoons.
Treatment Strategies for Rabies
-
Rabies Immunoglobulin (RIG): Administered directly into and around the wound to provide immediate passive immunity by neutralizing the virus before the body can produce its own antibodies. This passive transfer of antibodies is critical in bridging the gap until the body mounts an active immune response from vaccination.
-
Rabies Vaccines: A series of vaccine doses are given over several weeks to stimulate active immunity, prompting the body to produce antibodies against the virus.
-
Antiviral Drugs: While no highly effective antiviral exists for symptomatic rabies, some candidates showing promise in preclinical studies include ribavirin, amantadine, and coumarin.
-
siRNA Therapy: Experimental approaches involving small interfering RNA (siRNA) aim to silence viral gene expression, thereby inhibiting virus replication.
Despite these measures, the rapid progression of rabies once it invades the central nervous system presents formidable difficulties. A major challenge for both existing and emerging therapies, including vaccines, antibodies, antiviral drugs, and siRNA, is the blood-brain barrier (BBB). This highly selective physiological barrier severely restricts the passage of most large molecules and many small molecules from the bloodstream into the brain, thereby limiting the therapeutic efficacy of systemic treatments for neurotropic viruses like rabies. Creative Biolabs specifically addresses these critical challenges by developing advanced lipid-based drug delivery systems, particularly those based on lipid nanoparticles (LNPs).
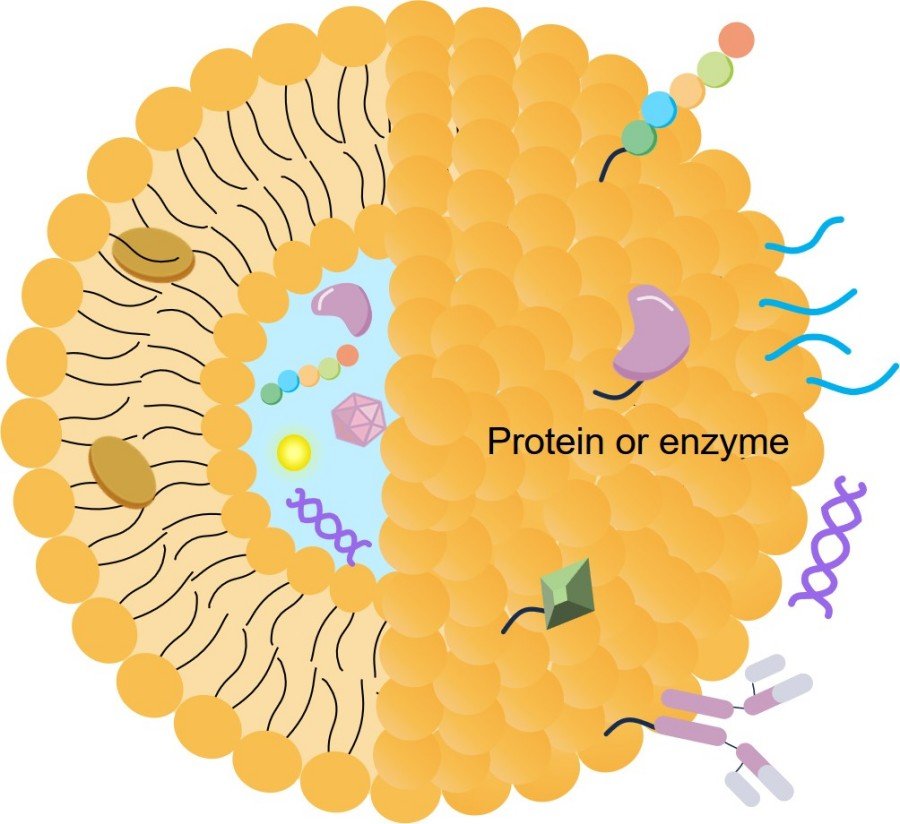
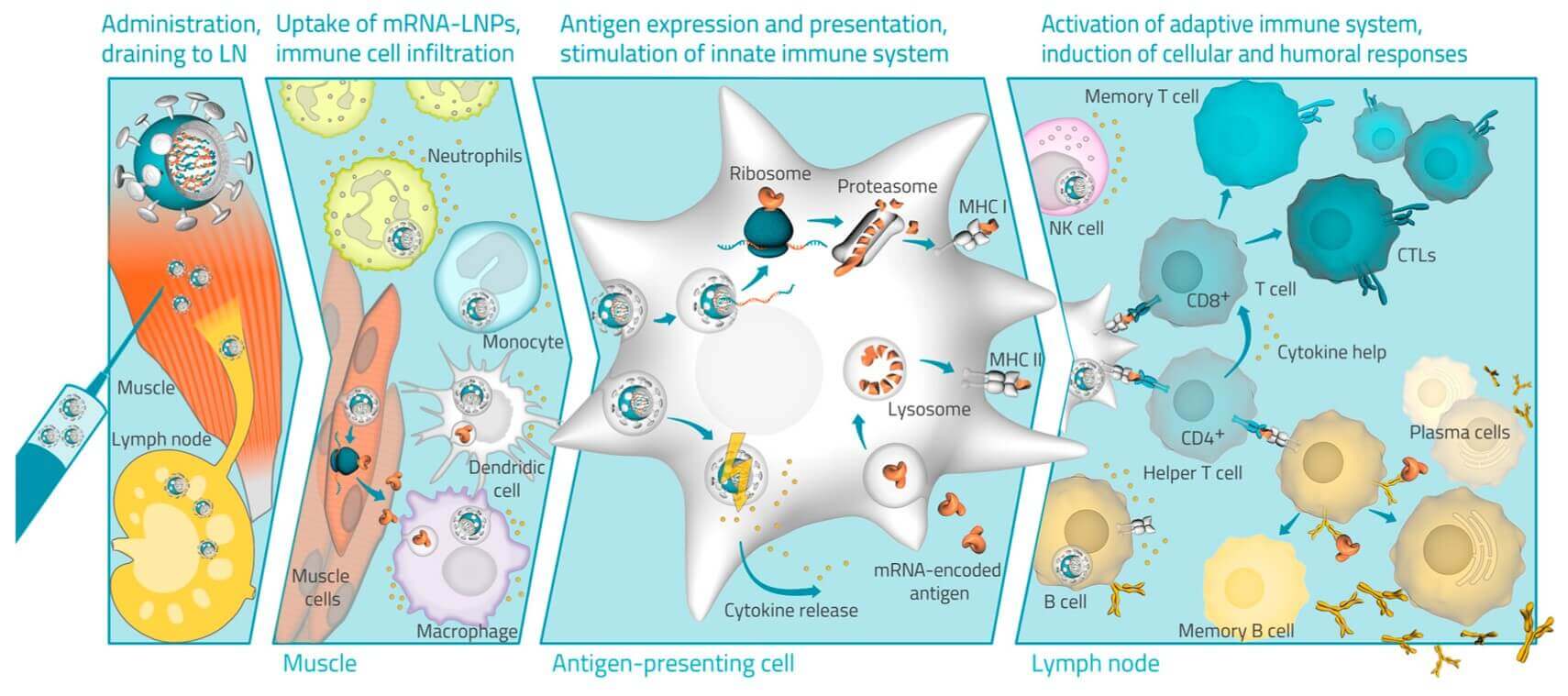 Fig. 2 Schematic illustration of the mode of action of LNP mRNA formulations.2,4
Fig. 2 Schematic illustration of the mode of action of LNP mRNA formulations.2,4
How Creative Biolabs' Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems Can Assist Your Project
Overcoming the inherent challenges in rabies treatment and prevention is made possible through a transformative approach offered by Creative Biolabs' lipid-based drug delivery systems. Our systems are precisely engineered to enhance the bioavailability, stability, and targeted delivery of sensitive therapeutic molecules, including small molecule antivirals, mRNA vaccines, and therapeutic antibodies. We specialize in custom formulation development, optimizing lipid composition, particle size, and surface modifications to achieve superior encapsulation efficiency and controlled release kinetics. This ensures that the therapeutic payload reaches its intended cellular target with maximal efficacy, minimizing off-target effects.
|
Our Delivery Systems
|
Key Advantages
|
Applicable Rabies Therapeutics
|
Inquiry
|
|
|
-
Highly efficient encapsulation of nucleic acids (mRNA, siRNA) and small molecules
-
Excellent stability
-
Tunable size and surface properties for targeted delivery
-
Biocompatible and biodegradable
-
BBB penetration
-
Controlled release
|
-
mRNA vaccines (for sustained antigen expression)
-
siRNA therapeutics (for viral gene silencing)
-
Small molecule antivirals
-
Passive antibodies (RIG)
-
Recombinant protein antigens
|
Inquiry
|
Workflow for Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems Development for Rabies
Published Data
Recent research highlights the effectiveness of using muscle-targeting LNPs to deliver mRNA that encodes the rabies virus G-protein, a crucial antigen for eliciting an immune response. A study evaluating this approach in mice demonstrated compelling results. The mRNA vaccine, encapsulated within LNPs, successfully induced high titers of virus-neutralizing antibodies and specific Virus-IgG binding antibodies. More importantly, this robust immune response translated into effective protective efficacy when the vaccinated mice were subsequently challenged with the rabies virus. The precise formulation of these LNPs, involving specific lipid components dissolved in ethanol and combined with mRNA in a citrate buffer using microfluidic technology, underscores the sophisticated engineering behind these powerful vaccine platforms. This work signifies a major step forward in developing highly effective and innovative strategies for rabies prevention.
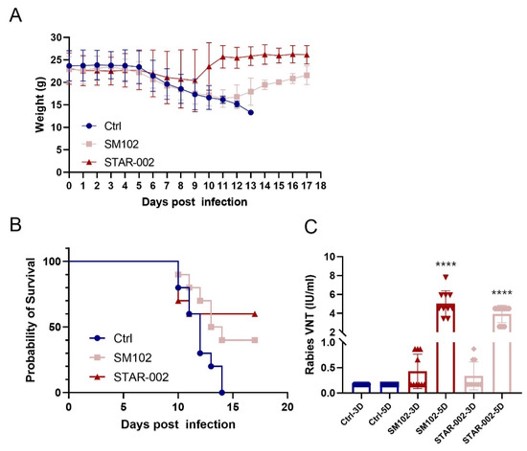 Fig. 3 Post-exposure protection of RV-G mRNA vaccine in mice.3,4
Fig. 3 Post-exposure protection of RV-G mRNA vaccine in mice.3,4
Ready-to-Use Products
We offer a range of high-quality, pre-formulated lipid-based drug delivery systems suitable for various experimental setups. Below is a selection of products relevant to your rabies research needs.
Browse our full product catalog
Creative Biolabs is dedicated to advancing therapeutic solutions for complex diseases like rabies through our cutting-edge lipid-based drug delivery systems. Our expertise in designing, developing, and optimizing these advanced delivery platforms positions us as your ideal partner for accelerating drug discovery, enhancing vaccine efficacy, and bringing innovative treatments to fruition. Our team is eager to collaborate with you and provide the tailored solutions that can make a difference in your quest to conquer rabies. If you are ready to push the boundaries of rabies treatment and explore new possibilities with our innovative lipid-based delivery systems, reach contact us now.
Related Services
Resources
References
-
Kiflu, Abraha Bahlbi. "The Immune Escape Strategy of Rabies Virus and Its Pathogenicity Mechanisms." Viruses 16.11 (2024): 1774. doi:10.3390/v16111774.
-
Armbruster, Nicole, Edith Jasny, and Benjamin Petsch. "Advances in RNA vaccines for preventive indications: a case study of a vaccine against rabies." Vaccines 7.4 (2019): 132. doi:10.3390/vaccines7040132.
-
Li, Qin, et al. "Immunogenicity of Rabies Virus G-Protein mRNA Formulated with Muscle-Targeting Lipid Nanoparticles in Mice." Vaccines 13.3 (2025): 217. doi:10.3390/vaccines13030217IF: 5
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.

For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
 Fig. 3 Post-exposure protection of RV-G mRNA vaccine in mice.3,4
Fig. 3 Post-exposure protection of RV-G mRNA vaccine in mice.3,4

 Fig. 1 RABV virion structure and genome.1,4
Fig. 1 RABV virion structure and genome.1,4
 Fig. 2 Schematic illustration of the mode of action of LNP mRNA formulations.2,4
Fig. 2 Schematic illustration of the mode of action of LNP mRNA formulations.2,4



 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use